在CSS中定位有以下4种:
静态定位 - static
相对定位 - relative
绝对定位 - absolute
固定定位 - fixed
静态定位 - static
静态定位是css中的默认定位方式,也就是没有定位。在此定位方式中设置:top,bottom,left,right,z-index 这些属性都是无效的。
相对定位 - relative
<style>
div{
position: relative;
background-color: red;
border-top:1px solid #000
}
</style>
相对位置前的位置:
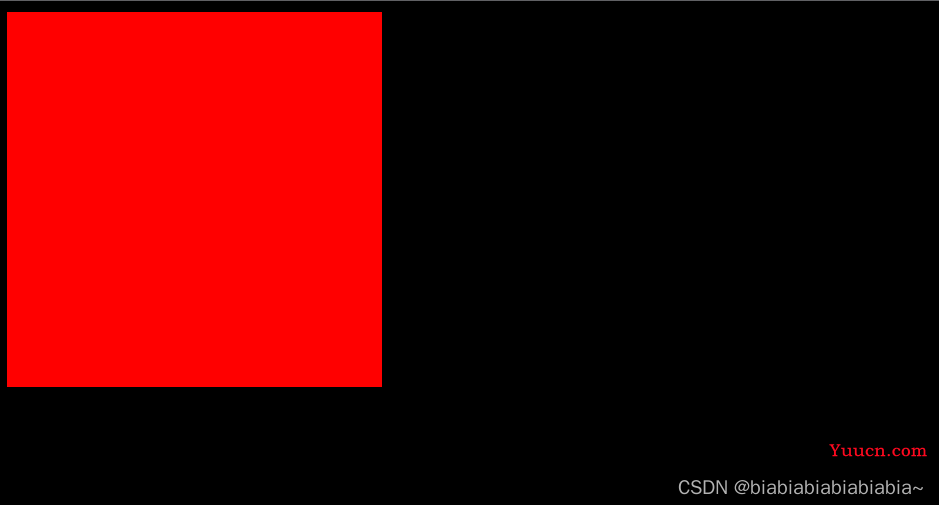
<style>
div{
position: relative;
background-color: red;
border-top:1px solid #000;
top: 30px;
left: 30px;
}
</style>
相对位置后的位置:

可以看到该元素向右下各偏移了30px.
相对定位的特点就是元素本身在文档流中的占位不变,无形的东西就是B元素在文档流中的占位,这也是为什么C元素不会浮动过去的原因。可以想象成B元素的本体依然处于普通文档流中,它的替身在参照本体进行移动。
绝对定位 - absolute
绝对定位是参考父元素的相对定位来实现的:
#A{
position: relative;
background-color: red;
border-top:1px solid #000;
height: 300px;
width: 300px;
/* left: 30px;
top: 30px; */
}
#B{
position: absolute;
background-color: rgb(17, 255, 0);
border-top:1px solid #000;
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
left: 30px;
top: 30px;
}
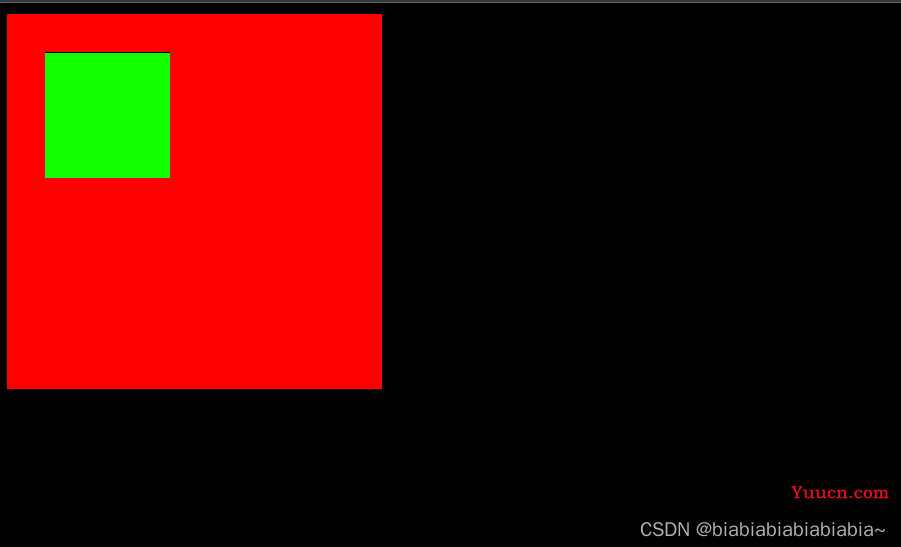
可以看出绿色div是以红色为定位位移30px,为了验证他是以父级进行定位,我们改变父级的位置:
#A{
position: relative;
background-color: red;
border-top:1px solid #000;
height: 300px;
width: 300px;
left: 30px;
top: 30px;
}
#B{
position: absolute;
background-color: rgb(17, 255, 0);
border-top:1px solid #000;
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
left: 30px;
top: 30px;
}
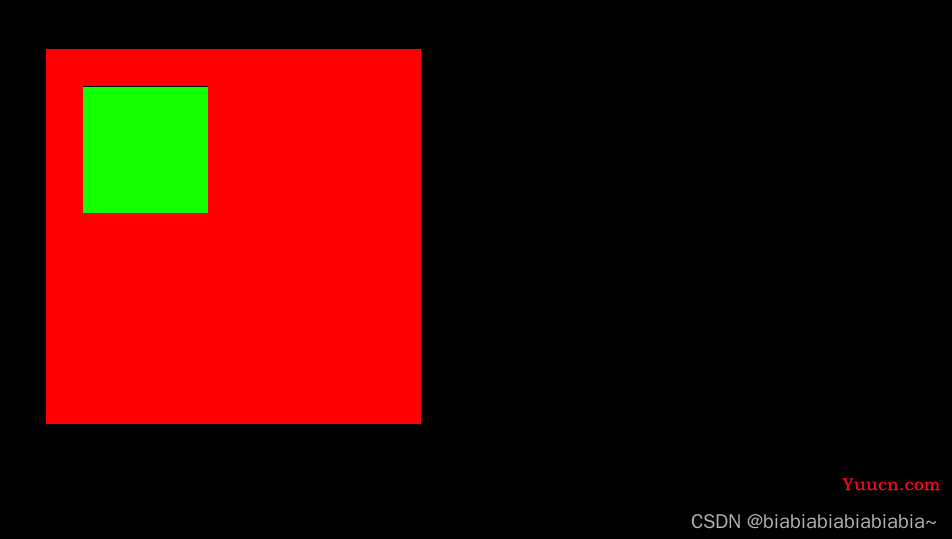
可以看出,B是以父级为参照进行定位,如果所有父级都没有设置相对定位,那么它将根据根元素html进行偏移。
固定定位 - fixed
固定定位比较简单,固定定位是参照浏览器窗口的左上角进行偏移。
固定定位的特点就是:无论如何滑动页面,固定定位的元素位置都不会被改变,完全脱离文档流。
另外,如果设置了固定定位的元素也设置了width或height的百分比值,那么此百分比的值是参照窗口宽高来计算的。
z-index属性:
z-index属性是设置元素的层级,数值低的会被数值高的遮住。