行人识别yolov5和v7对比
yolo车距
yolo车距1
代码:yolov5车辆检测代码 已有1503人下载
代码无需更改,直接可以预测!!!
流程:
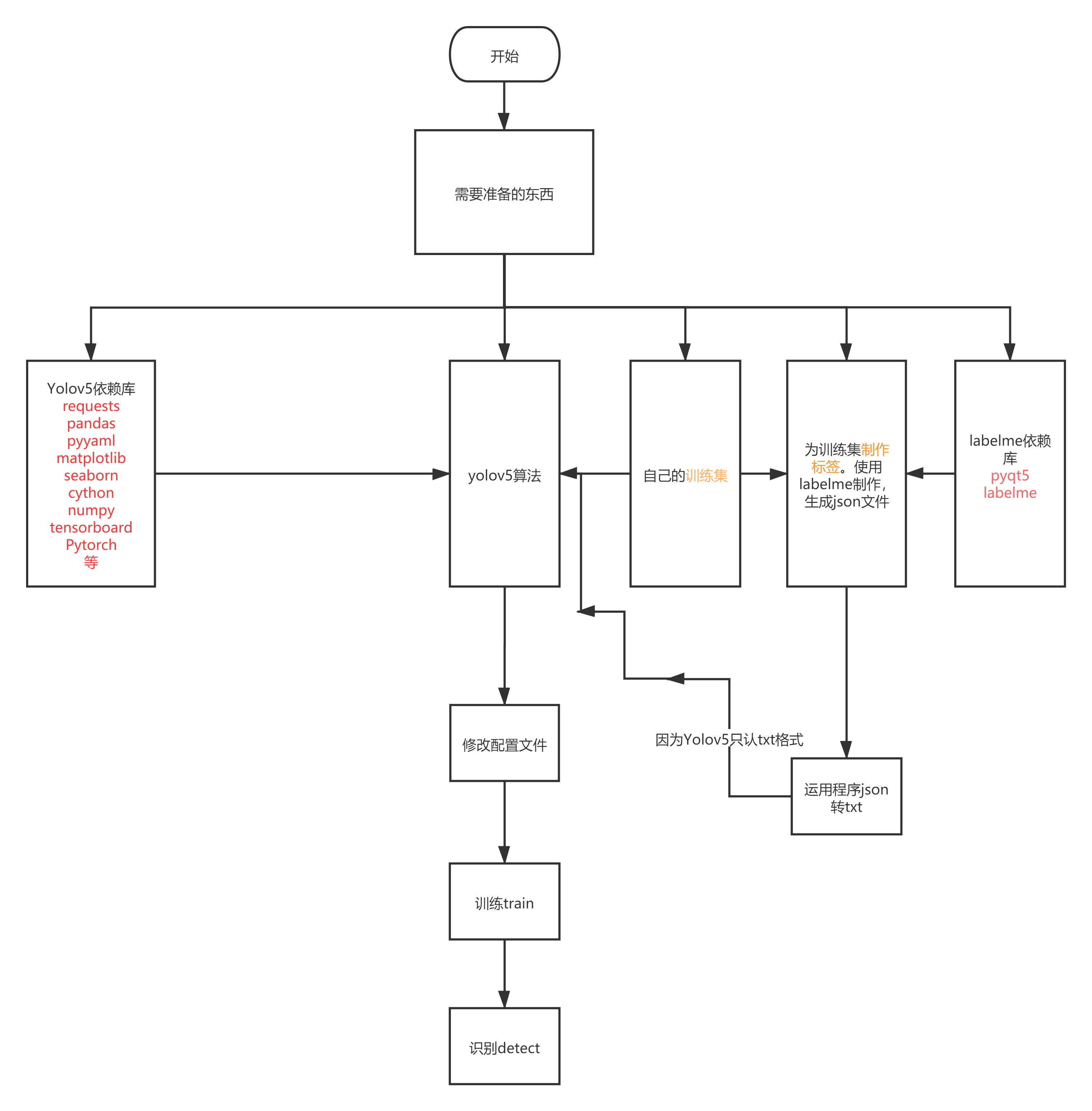
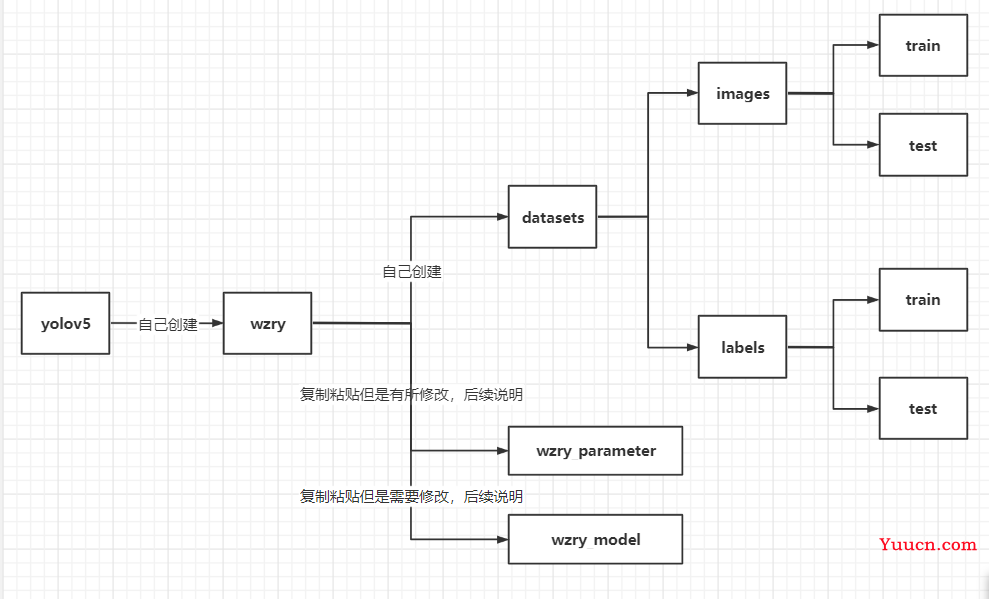
版本与配置声明
# YOLOv5 requirements
# Usage: pip install -r requirements.txt# Base ----------------------------------------
matplotlib>=3.2.2
numpy>=1.18.5
opencv-python>=4.1.1
Pillow>=7.1.2
PyYAML>=5.3.1
requests>=2.23.0
scipy>=1.4.1 # Google Colab version
torch>=1.7.0
torchvision>=0.8.1
tqdm>=4.41.0
protobuf<4.21.3 # https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/issues/8012# Logging -------------------------------------
tensorboard>=2.4.1
# wandb# Plotting ------------------------------------
pandas>=1.1.4
seaborn>=0.11.0# Export --------------------------------------
# coremltools>=4.1 # CoreML export
# onnx>=1.9.0 # ONNX export
# onnx-simplifier>=0.3.6 # ONNX simplifier
# scikit-learn==0.19.2 # CoreML quantization
# tensorflow>=2.4.1 # TFLite export
# tensorflowjs>=3.9.0 # TF.js export
# openvino-dev # OpenVINO export# Extras --------------------------------------
ipython # interactive notebook
psutil # system utilization
thop # FLOPs computation
# albumentations>=1.0.3
# pycocotools>=2.0 # COCO mAP
# roboflow
import json
import os
name2id = {'hero':0,'sodier':1,'tower':2}#标签名称
def convert(img_size, box):
dw = 1. / (img_size[0])
dh = 1. / (img_size[1])
x = (box[0] + box[2]) / 2.0 - 1
y = (box[1] + box[3]) / 2.0 - 1
w = box[2] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[1]
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return (x, y, w, h)
def decode_json(json_floder_path, json_name):
txt_name = 'C:\\Users\\86189\\Desktop\\' + json_name[0:-5] + '.txt'
#存放txt的绝对路径
txt_file = open(txt_name, 'w')
json_path = os.path.join(json_floder_path, json_name)
data = json.load(open(json_path, 'r', encoding='gb2312',errors='ignore'))
img_w = data['imageWidth']
img_h = data['imageHeight']
for i in data['shapes']:
label_name = i['label']
if (i['shape_type'] == 'rectangle'):
x1 = int(i['points'][0][0])
y1 = int(i['points'][0][1])
x2 = int(i['points'][1][0])
y2 = int(i['points'][1][1])
bb = (x1, y1, x2, y2)
bbox = convert((img_w, img_h), bb)
txt_file.write(str(name2id[label_name]) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bbox]) + '\n')
if __name__ == "__main__":
json_floder_path = 'C:\\Users\\86189\\Desktop\\哈哈哈\\'
#存放json的文件夹的绝对路径
json_names = os.listdir(json_floder_path)
for json_name in json_names:
decode_json(json_floder_path, json_name)

函数拆解
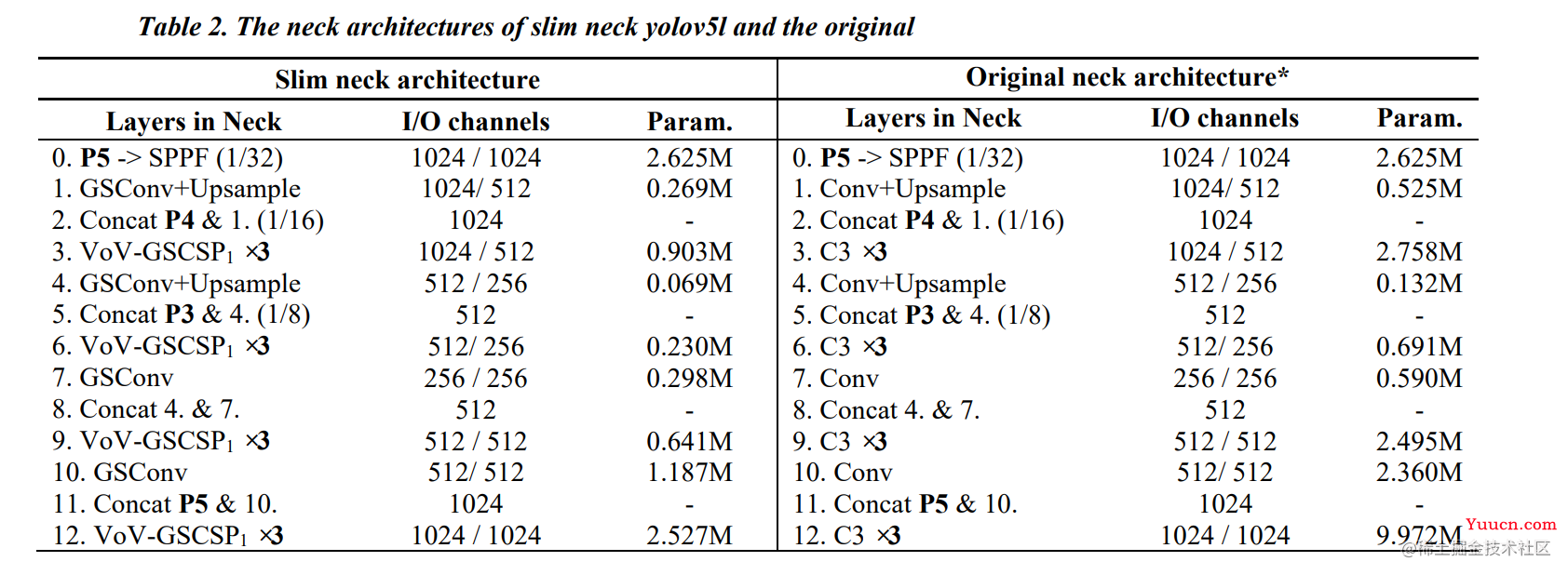
下图中的左侧表格中为论文中提出的方法,右侧为官方原版的yoloV5中的YoloBody部分,分析左右两表中的差异,我们可以根据论文中的连接,将GSConv和VoV-GSCSP提取出来进行实验分析使用方法以及作用(SPPF&Concat&Upsample函数作用相同):
GSConv函数
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
def autopad(k, p=None): # kernel, padding
# Pad to 'same'
if p is None:
p = k // 2 if isinstance(k, int) else [x // 2 for x in k] # auto-pad
return p
class Mish(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self,x):
x = x * (torch.tanh(F.softplus(x)))
return x
class Conv(nn.Module):
# Standard convolution
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, act=True): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups
super().__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(c1, c2, k, s, autopad(k, p), groups=g, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(c2)
self.act = Mish() if act else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
return self.act(self.bn(self.conv(x)))
def forward_fuse(self, x):
return self.act(self.conv(x))
class GSConv(nn.Module):
# GSConv https://github.com/AlanLi1997/slim-neck-by-gsconv
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, g=1, act=True):
super().__init__()
c_ = c2 // 2
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, k, s, None, g, act)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_, c_, 5, 1, None, c_, act)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.cv1(x)
x2 = torch.cat((x1, self.cv2(x1)), 1)
# shuffle
# y = x2.reshape(x2.shape[0], 2, x2.shape[1] // 2, x2.shape[2], x2.shape[3])
# y = y.permute(0, 2, 1, 3, 4)
# return y.reshape(y.shape[0], -1, y.shape[3], y.shape[4])
b, n, h, w = x2.data.size()
b_n = b * n // 2
y = x2.reshape(b_n, 2, h * w)
y = y.permute(1, 0, 2)
y = y.reshape(2, -1, n // 2, h, w)
return torch.cat((y[0], y[1]), 1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
base_channels = 64
P3Shape = (1, 256, 80, 80)
P3 = torch.ones(P3Shape)
gsc = GSConv(base_channels * 4, base_channels * 4, 3, 2)
P = gsc(P3)
print(P.shape)
通过上述的代码我们可以得到在GSConv的输入参数这边输入的维度为256,当k=3,s=2时,H和S将会降一半;当H和S为默认的1时则不变。
VoV-GSCSP函数
VoV-GSCSP函数是建立在GSConv函数上演变而来的,我们结合论文中的流程参数表可知,在VoV-GSCSP函数中我们仅需要确保输出与输出即可。
class GSBottleneck(nn.Module):
# GS Bottleneck https://github.com/AlanLi1997/slim-neck-by-gsconv
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=3, s=1, e=0.5):
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2*e)
# for lighting
self.conv_lighting = nn.Sequential(
GSConv(c1, c_, 1, 1),
GSConv(c_, c2, 3, 1, act=False))
self.shortcut = Conv(c1, c2, 1, 1, act=False)
def forward(self, x):
return self.conv_lighting(x) + self.shortcut(x)
class VoVGSCSP(nn.Module):
# VoVGSCSP module with GSBottleneck
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5):
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
# self.gc1 = GSConv(c_, c_, 1, 1)
# self.gc2 = GSConv(c_, c_, 1, 1)
# self.gsb = GSBottleneck(c_, c_, 1, 1)
self.gsb = nn.Sequential(*(GSBottleneck(c_, c_, e=1.0) for _ in range(n)))
self.res = Conv(c_, c_, 3, 1, act=False)
self.cv3 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1) #
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.gsb(self.cv1(x))
y = self.cv2(x)
return self.cv3(torch.cat((y, x1), dim=1))
if __name__ == "__main__":
base_channels = 64
P3Shape = (1, 256, 80, 80)
P3 = torch.ones(P3Shape)
VOV = VoVGSCSP(base_channels * 4, base_channels * 4)
P = VOV(P3)
复制代码YoloBady构造
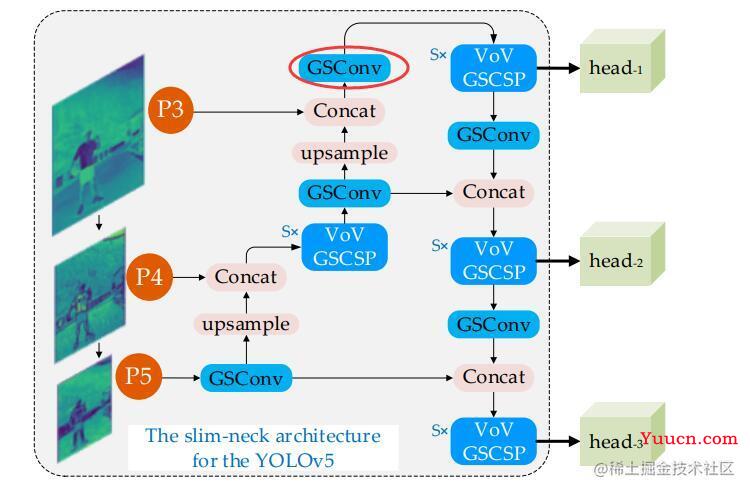
由上述的网络基础函数部分的构建结合yoloV5经过 backbone 层后得到的feat1、feat1和 feat1(也即:P5、P4和P3)到最后网络的输出部分,可以得到从输入部分的H和W是保持同P层相同,那么可以结合论文中的流程参数图以及输入输出的关系得到如下的流程参数图。
根据上文中流程表格参数图,我在重构的过程中省略了S=3的设定(本人的显存不够),另外根据论文中的流程示意图,我暂时无法没有找到下图中的红圈部分的参数,若大家需要可以自行添加,输入输出保持不变即可。
YoloBody部分
from torch import nn
from nets.CSPdarknet import CSPDarknet, SPPF, Concat, GSConv, VoVGSCSP
class YoloBody(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, anchors_mask, num_classes, phi, pretrained=False, input_shape=[640, 640]):
super(YoloBody, self).__init__()
depth_dict = {'n': 0.33, 's': 0.33, 'm': 0.67, 'l': 1.00, 'x': 1.33, }
width_dict = {'n': 0.25, 's': 0.50, 'm': 0.75, 'l': 1.00, 'x': 1.25, }
dep_mul, wid_mul = depth_dict[phi], width_dict[phi]
base_channels = int(wid_mul * 64) # 64
base_depth = max(round(dep_mul * 3), 1) # 3
# -----------------------------------------------#
# 输入图片是640, 640, 3
# 初始的基本通道是64
# -----------------------------------------------#
self.backbone = CSPDarknet(base_channels, base_depth, phi, pretrained)
self.upsample = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode="nearest")
self.concat = Concat(dimension=1)
self.SPPF = SPPF(base_channels * 16, base_channels * 16) # 1024 ---> 1024
self.P5GSConv = GSConv(base_channels * 16, base_channels * 8) # 1,1024,20,20 ---> 1,512,20,20
self.P4VoV = VoVGSCSP(base_channels * 16, base_channels * 8) # 1,512,40,40 ---> 1,1024,40,40
"""
self.P4VoV = nn.Sequential(VoVGSCSP(base_channels * 16, base_channels * 8),
VoVGSCSP(base_channels * 8, base_channels * 8),
VoVGSCSP(base_channels * 8, base_channels * 8))
"""
self.P4GSConv = GSConv(base_channels * 8, base_channels * 4) # 1,512,40,40 ---> 1,256,40,40
self.Head1VoV = VoVGSCSP(base_channels * 8, base_channels * 4) # 1,512,80,80 ---> 1,256,80,80
"""
self.Head1VoV = nn.Sequential(VoVGSCSP(base_channels * 8, base_channels * 4),
VoVGSCSP(base_channels * 4, base_channels * 4),
VoVGSCSP(base_channels * 4, base_channels * 4))
"""
self.P3GSConv = GSConv(base_channels * 4, base_channels * 4, 3, 2) # 1,256,80,80 ---> 1,256,40,40
self.Head2VoV = VoVGSCSP(base_channels * 8, base_channels * 8) # 1,512,40,40 ---> 1,512,40,40
"""
self.Head2VoV = nn.Sequential(VoVGSCSP(base_channels * 8, base_channels * 8),
VoVGSCSP(base_channels * 8, base_channels * 8),
VoVGSCSP(base_channels * 8, base_channels * 8))
"""
self.Head2GSConv = GSConv(base_channels * 8, base_channels * 8, 3, 2) # 1,512,40,40 ---> 1,512,20,20
self.Head3VoV = VoVGSCSP(base_channels * 16, base_channels * 16) # 1,1024,20,20 ---> 1,1024,20,20
"""
self.Head3VoV = nn.Sequential(VoVGSCSP(base_channels * 16, base_channels * 16),
VoVGSCSP(base_channels * 16, base_channels * 16),
VoVGSCSP(base_channels * 16, base_channels * 16))
"""
self.yolo_head_P3 = nn.Conv2d(base_channels * 4, len(anchors_mask[2]) * (5 + num_classes), 1)
self.yolo_head_P4 = nn.Conv2d(base_channels * 8, len(anchors_mask[1]) * (5 + num_classes), 1)
self.yolo_head_P5 = nn.Conv2d(base_channels * 16, len(anchors_mask[0]) * (5 + num_classes), 1)
def forward(self, x):
P3, P4, P5 = self.backbone(x)
P5 = self.SPPF(P5)
P5 = self.P5GSConv(P5)
P5_Up = self.upsample(P5)
P4 = self.concat([P4, P5_Up])
P4 = self.P4VoV(P4)
P4 = self.P4GSConv(P4)
P4_Up = self.upsample(P4)
P3 = self.concat([P3, P4_Up])
head1 = self.Head1VoV(P3)
P3 = self.P3GSConv(head1)
P34_Cat = self.concat([P3, P4])
head2 = self.Head2VoV(P34_Cat)
PHG = self.Head2GSConv(head2)
PHG_Cat = self.concat([PHG, P5])
head3 = self.Head3VoV(PHG_Cat)
Out1 = self.yolo_head_P3(head1) # 1,255,80,80
Out2 = self.yolo_head_P4(head2) # 1,255,40,40
Out3 = self.yolo_head_P5(head3) # 1,255,20,20
return Out3, Out2, Out1
# if __name__ == "__main__":
# anchors_mask = [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]]
# num_classes = 80
# phi = 's'
# model = YoloBody(anchors_mask, num_classes, phi, pretrained=False)
# x = torch.ones((1, 3, 640, 640))
# Out3, Out2, Out1 = model(x)
# print()