✅作者简介:在读博士,伪程序媛,人工智能领域学习者,深耕机器学习,交叉学科实践者,周更前沿文章解读,提供科研小工具,分享科研经验,欢迎交流!
📌个人主页:
https://blog.csdn.net/allein_STR?spm=1011.2559.3001.5343
💯特色专栏:深度学习和WRF,提供人工智能方方面面小姿势,从基础到进阶,教程全面。
📞联系博主:博文留言+主页底部联系方式+WeChat code: Allein_STR
📙本文内容:介绍
ProPlot9大亮点+python代码
ProPlot是Matplotlib面向对象绘图方法(object-oriented interface)的高级封装,整合了cartopy/basemap地图库、xarray和pandas,可弥补Matplotlib的部分缺陷,ProPlot让Matplotlib爱好者拥有更加smoother plotting experience。
-
代码更简洁,图形更好看
将Matplotlib一行代码设置一个参数的繁琐行为直接通过format方法一次搞定,比如下图,
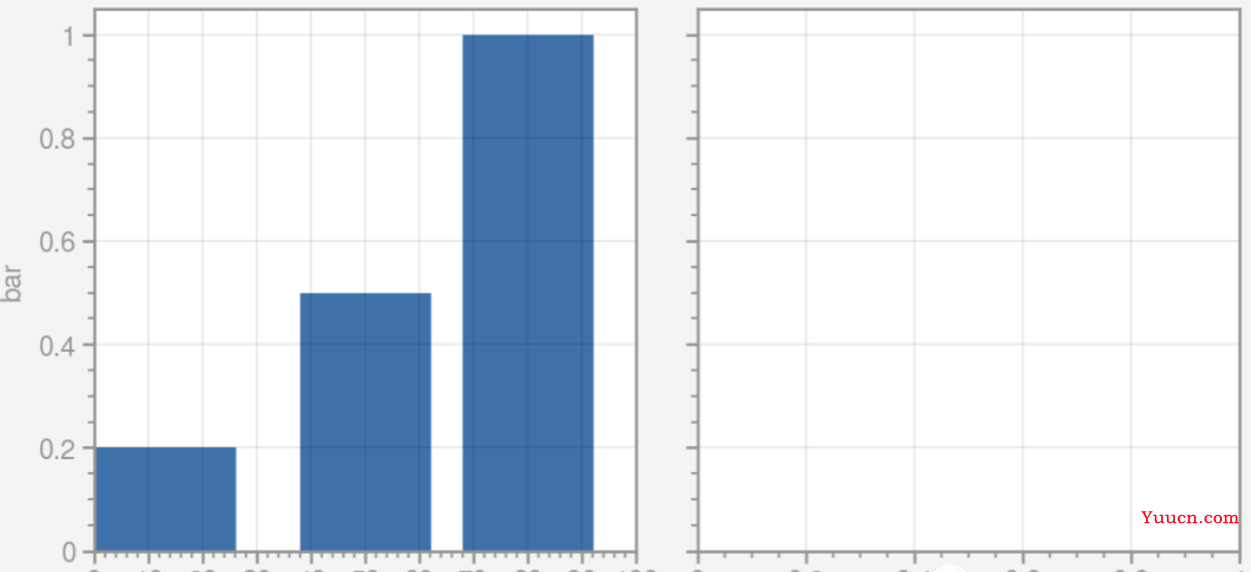
Proplot代码
import proplot as pplt
fig, axs = pplt.subplots(ncols=2)
axs.format(color='gray', linewidth=1) #format设置所有子图属性
axs[0].bar([10, 50, 80], [0.2, 0.5, 1])
axs[0].format(xlim=(0, 100), #format设置子图1属性
xticks=10,
xtickminor=True,
xlabel='foo',
ylabel='bar')一个完整的使用案例:
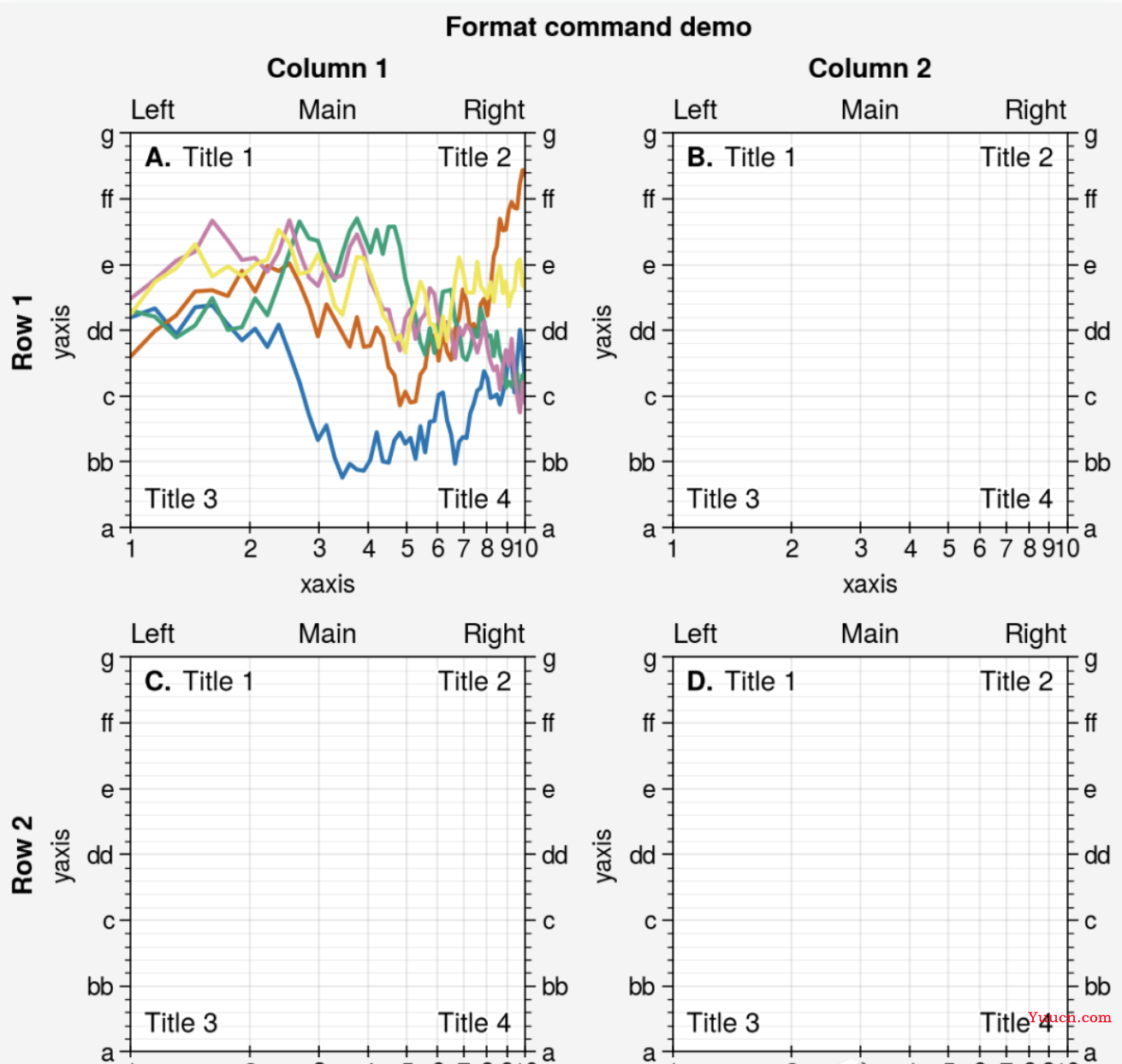
import proplot as pplt
import numpy as np
fig, axs = pplt.subplots(ncols=2, nrows=2, refwidth=2, share=False)
state = np.random.RandomState(51423)
N = 60
x = np.linspace(1, 10, N)
y = (state.rand(N, 5) - 0.5).cumsum(axis=0)
axs[0].plot(x, y, linewidth=1.5)
# 图表诸多属性可在format中设置
axs.format(
suptitle='Format command demo',
abc='A.',
abcloc='ul',
title='Main',
ltitle='Left',
rtitle='Right', # different titles
ultitle='Title 1',
urtitle='Title 2',
lltitle='Title 3',
lrtitle='Title 4',
toplabels=('Column 1', 'Column 2'),
leftlabels=('Row 1', 'Row 2'),
xlabel='xaxis',
ylabel='yaxis',
xscale='log',
xlim=(1, 10),
xticks=1,
ylim=(-3, 3),
yticks=pplt.arange(-3, 3),
yticklabels=('a', 'bb', 'c', 'dd', 'e', 'ff', 'g'),
ytickloc='both',
yticklabelloc='both',
xtickdir='inout',
xtickminor=False,
ygridminor=True,
)
-
更友好的类构造函数
将Matplotlib中类名书写不友好的类进行封装,可通过简洁的关键字参数调用。例如,mpl_toolkits.basemap.Basemap()、matplotlib.ticker.LogFormatterExponent()、ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(MultipleLocator(1.000))等等,封装后,
-
图形大小、子图间距自适应
proplot通过refwidth、refheight、refaspect、refheight、proplot.gridspec.GridSpec等控制图形大小和子图间距,替代Matplotlib自带的tightlayout,避免图形重叠、标签不完全等问题
案例:
proplot控制图形大小:
import proplot as pplt
import numpy as np
state = np.random.RandomState(51423)
colors = np.tile(state.rand(8, 12, 1), (1, 1, 3))
fig, axs = pplt.subplots(ncols=3, nrows=2, refwidth=1.7) #refwidth的使用
fig.format(suptitle='Auto figure dimensions for grid of images')
for ax in axs:
ax.imshow(colors)
# 结合上文第2部分看,使用proj='robin'关键字参数调用cartopy projections'
fig, axs = pplt.subplots(ncols=2, nrows=3, proj='robin')
axs.format(land=True, landcolor='k')
fig.format(suptitle='Auto figure dimensions for grid of cartopy projections')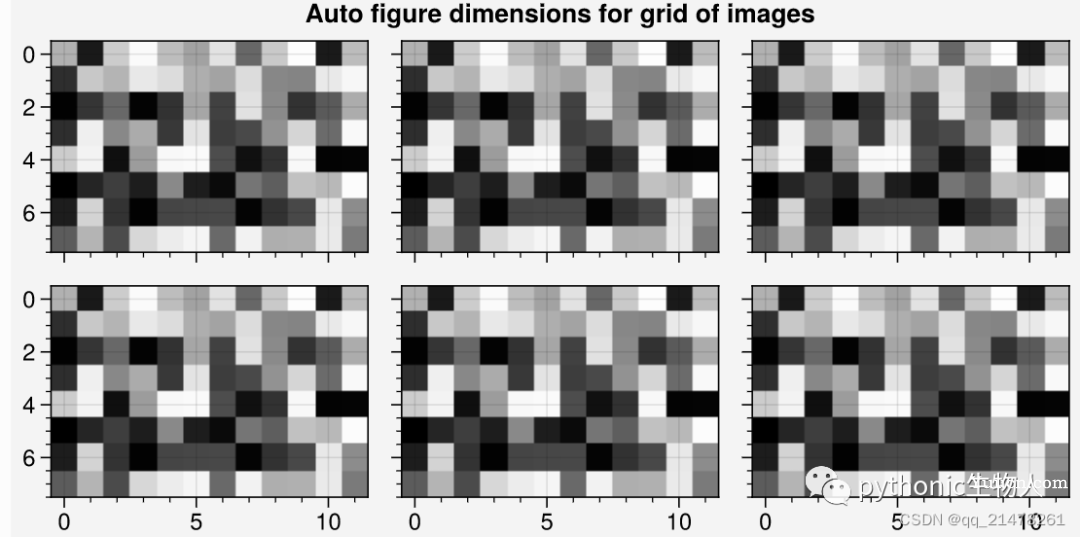
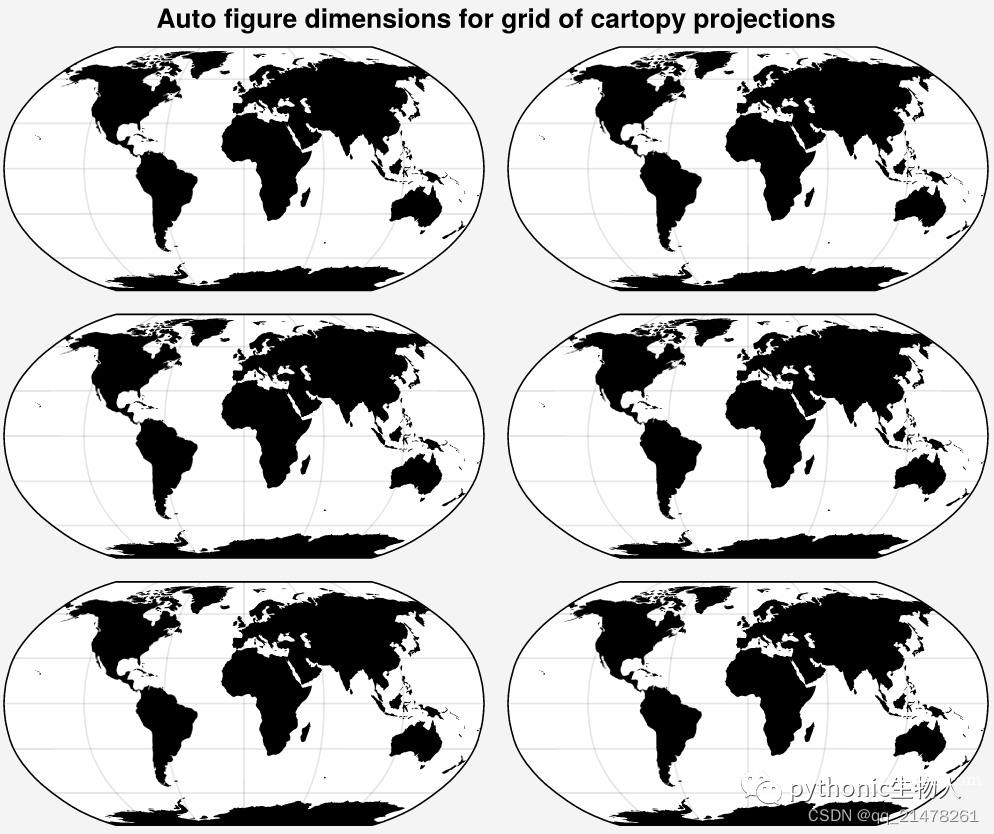
proplot如何控制子图间距?
import proplot as pplt
fig, axs = pplt.subplots(
ncols=4, nrows=3, refwidth=1.1, span=False,
bottom='5em', right='5em',
wspace=(0, 0, None), hspace=(0, None),
) # proplot新的子图间距控制算法
axs.format(
grid=False,
xlocator=1, ylocator=1, tickdir='inout',
xlim=(-1.5, 1.5), ylim=(-1.5, 1.5),
suptitle='Tight layout with user overrides',
toplabels=('Column 1', 'Column 2', 'Column 3', 'Column 4'),
leftlabels=('Row 1', 'Row 2', 'Row 3'),
)
axs[0, :].format(xtickloc='top')
axs[2, :].format(xtickloc='both')
axs[:, 1].format(ytickloc='neither')
axs[:, 2].format(ytickloc='right')
axs[:, 3].format(ytickloc='both')
axs[-1, :].format(xlabel='xlabel', title='Title\nTitle\nTitle')
axs[:, 0].format(ylabel='ylabel')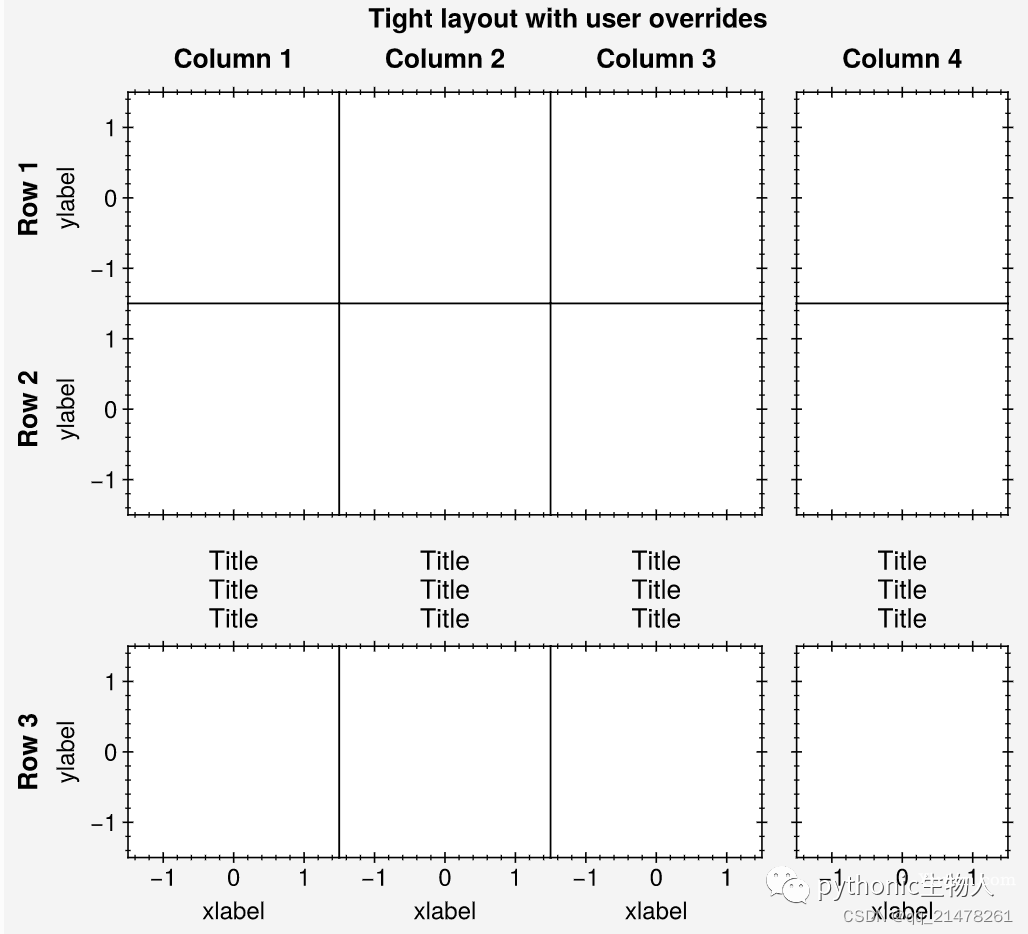
4.多子图个性化设置
-
子图灵活设置坐标轴标签:sharex, sharey, spanx, spany, alignx和aligny参数控制,效果见下图(相同颜色比较来看)
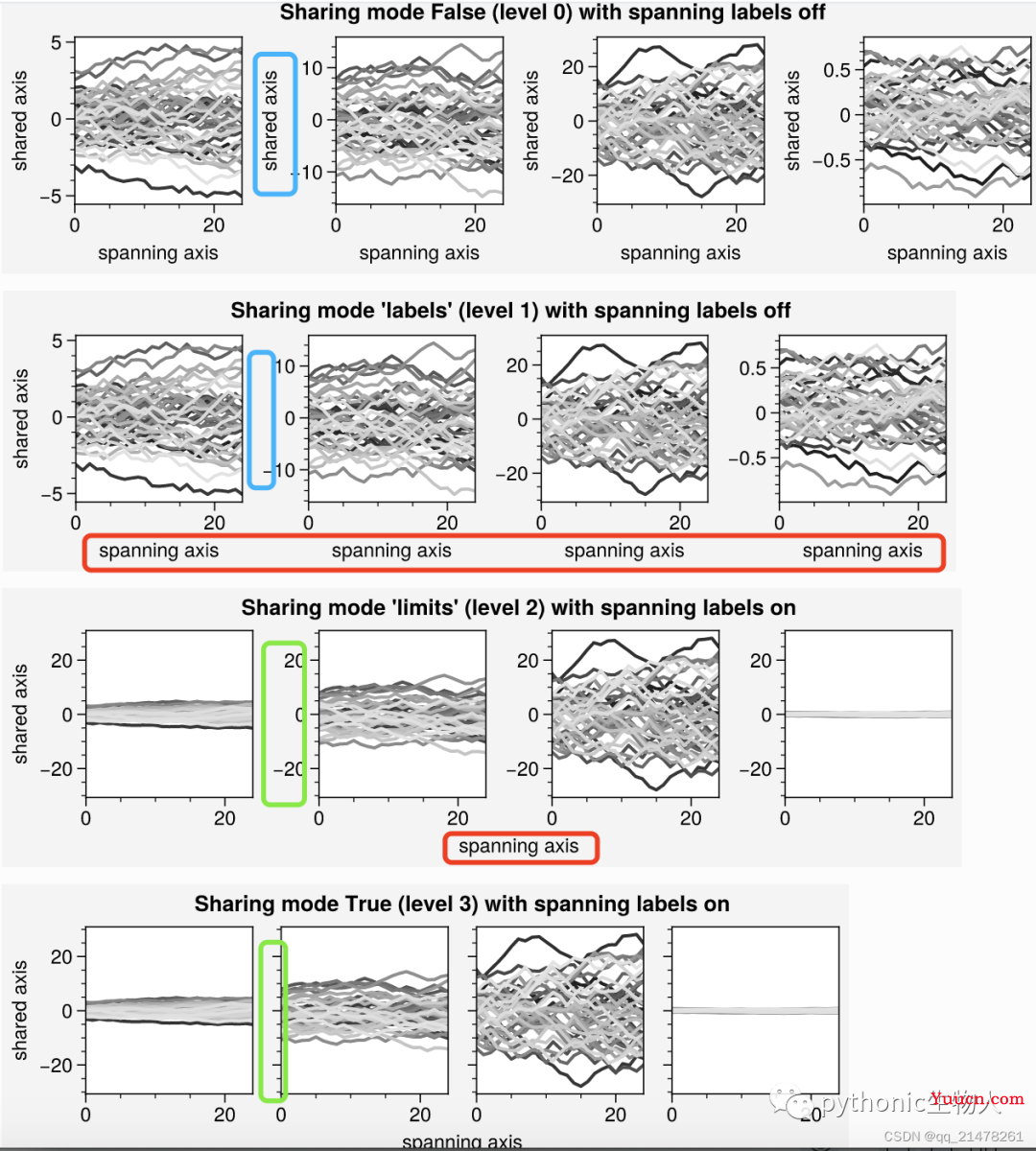
-
子图灵活添加编号
import proplot as pplt
import numpy as np
N = 20
state = np.random.RandomState(51423)
data = N + (state.rand(N, N) - 0.55).cumsum(axis=0).cumsum(axis=1)
cycle = pplt.Cycle('greys', left=0.2, N=5)
fig, axs = pplt.subplots(ncols=2, nrows=2, figwidth=5, share=False)
axs[0].plot(data[:, :5], linewidth=2, linestyle='--', cycle=cycle)
axs[1].scatter(data[:, :5], marker='x', cycle=cycle)
axs[2].pcolormesh(data, cmap='greys')
m = axs[3].contourf(data, cmap='greys')
axs.format(
abc='a.', titleloc='l', title='Title',
xlabel='xlabel', ylabel='ylabel', suptitle='Quick plotting demo'
) #abc='a.'为各子图添加编号
fig.colorbar(m, loc='b', label='label')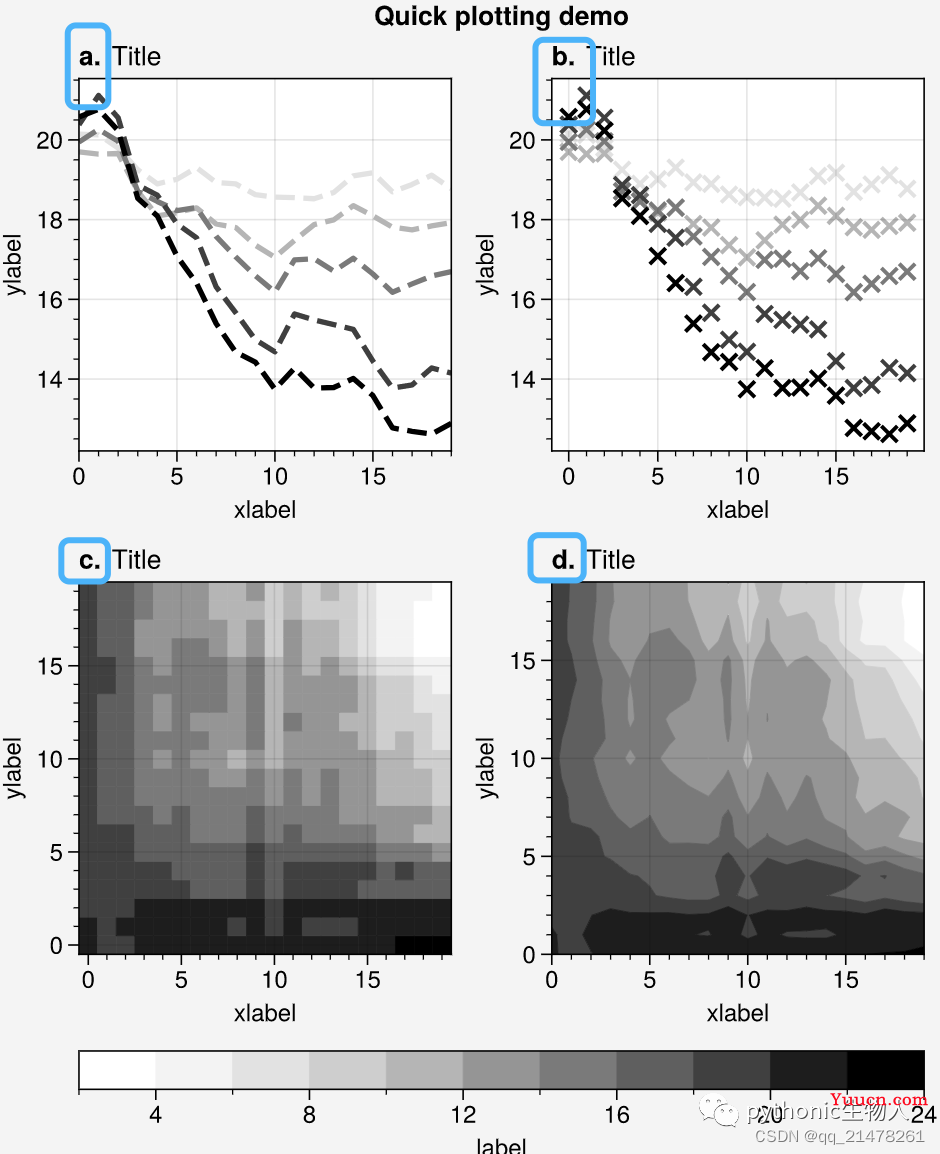
-
子图灵活设置Panels
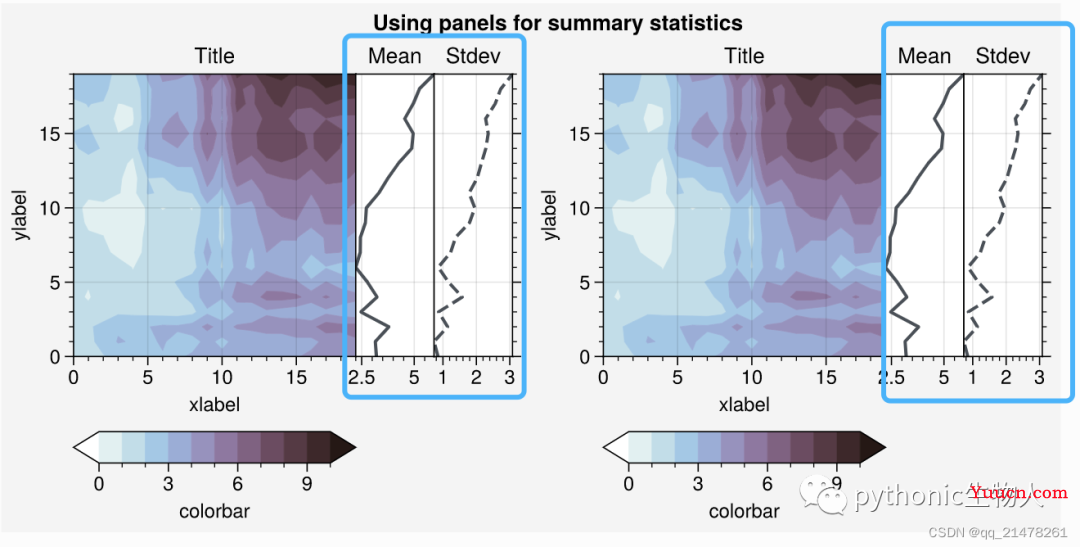
-
子图各自外观灵活自定义
import proplot as pplt
import numpy as np
state = np.random.RandomState(51423)
# Selected subplots in a simple grid
fig, axs = pplt.subplots(ncols=4, nrows=4, refwidth=1.2, span=True)
axs.format(xlabel='xlabel', ylabel='ylabel', suptitle='Simple SubplotGrid')
axs.format(grid=False, xlim=(0, 50), ylim=(-4, 4))
# 使用axs[:, 0].format自定义某个子图外观
axs[:, 0].format(facecolor='blush', edgecolor='gray7', linewidth=1) # eauivalent
axs[:, 0].format(fc='blush', ec='gray7', lw=1)
axs[0, :].format(fc='sky blue', ec='gray7', lw=1)
axs[0].format(ec='black', fc='gray5', lw=1.4)
axs[1:, 1:].format(fc='gray1')
for ax in axs[1:, 1:]:
ax.plot((state.rand(50, 5) - 0.5).cumsum(axis=0), cycle='Grays', lw=2)
# 使用axs[1, 1:].format自定义某个子图外观
fig = pplt.figure(refwidth=1, refnum=5, span=False)
axs = fig.subplots([[1, 1, 2], [3, 4, 2], [3, 4, 5]], hratios=[2.2, 1, 1])
axs.format(xlabel='xlabel', ylabel='ylabel', suptitle='Complex SubplotGrid')
axs[0].format(ec='black', fc='gray1', lw=1.4)
axs[1, 1:].format(fc='blush')
axs[1, :1].format(fc='sky blue')
axs[-1, -1].format(fc='gray4', grid=False)
axs[0].plot((state.rand(50, 10) - 0.5).cumsum(axis=0), cycle='Grays_r', lw=2)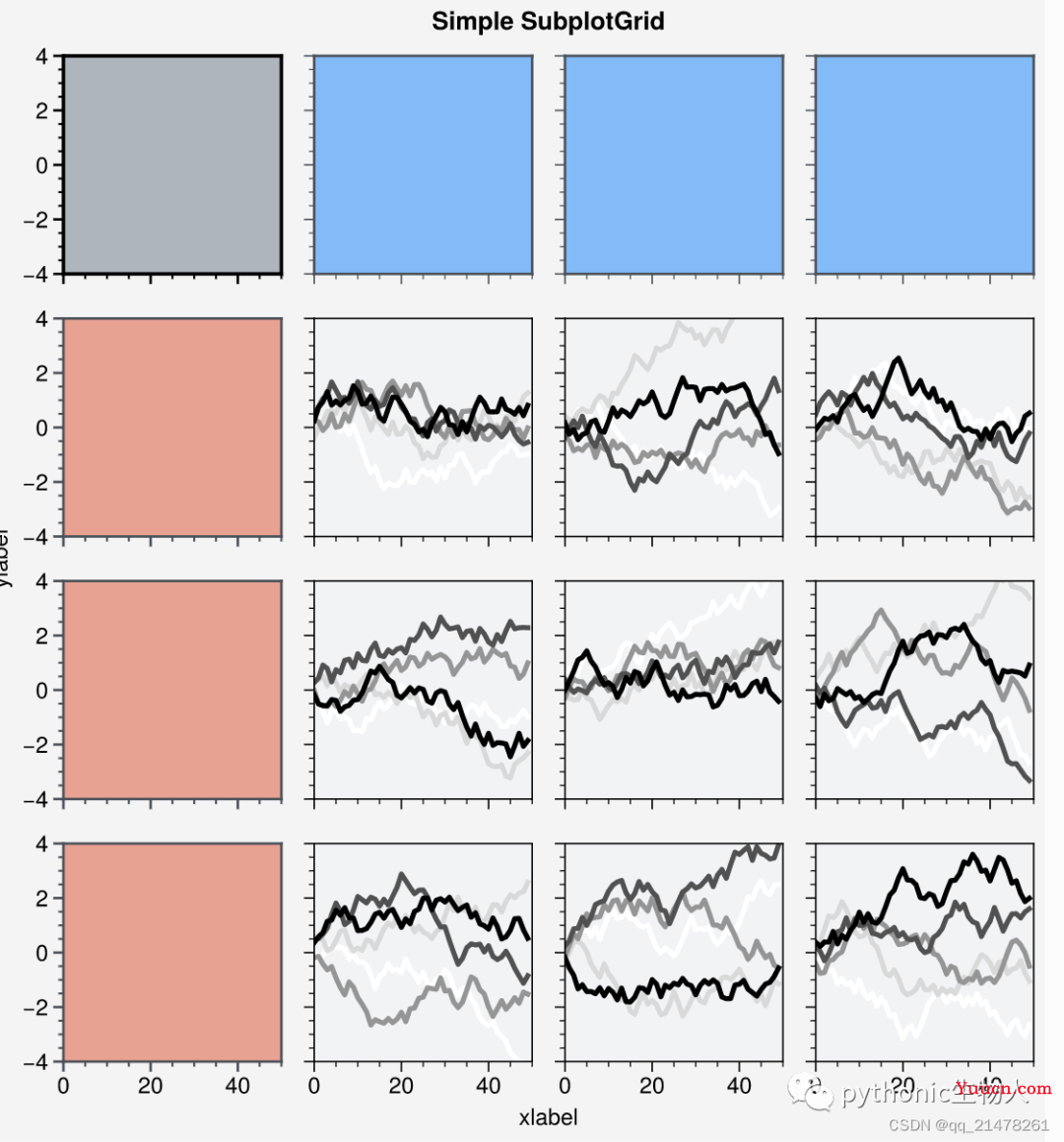
5.图例、colorbar灵活设置
-
图例、colorbar位置指定
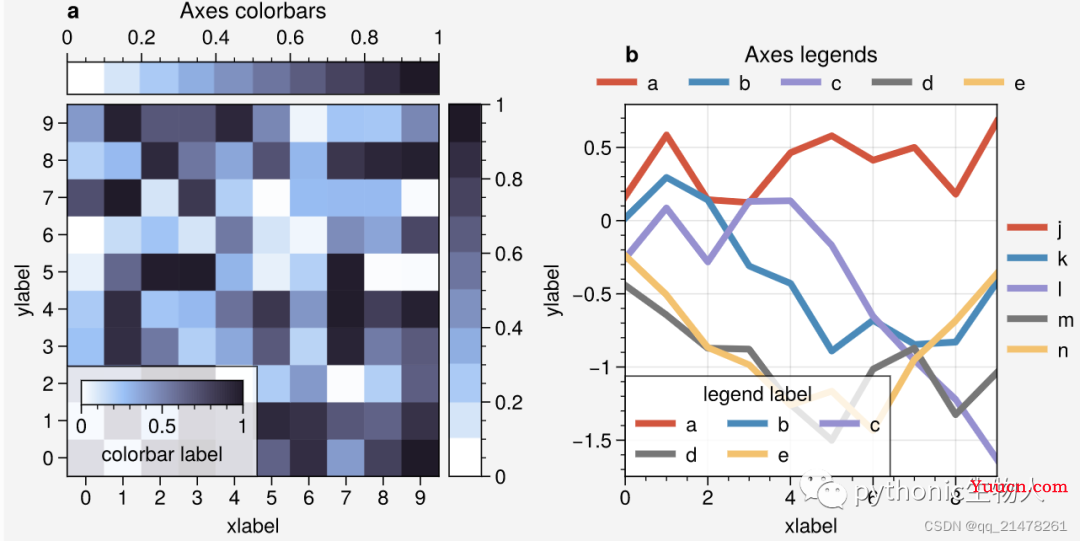
-
图例、colorbar:On-the-fly,
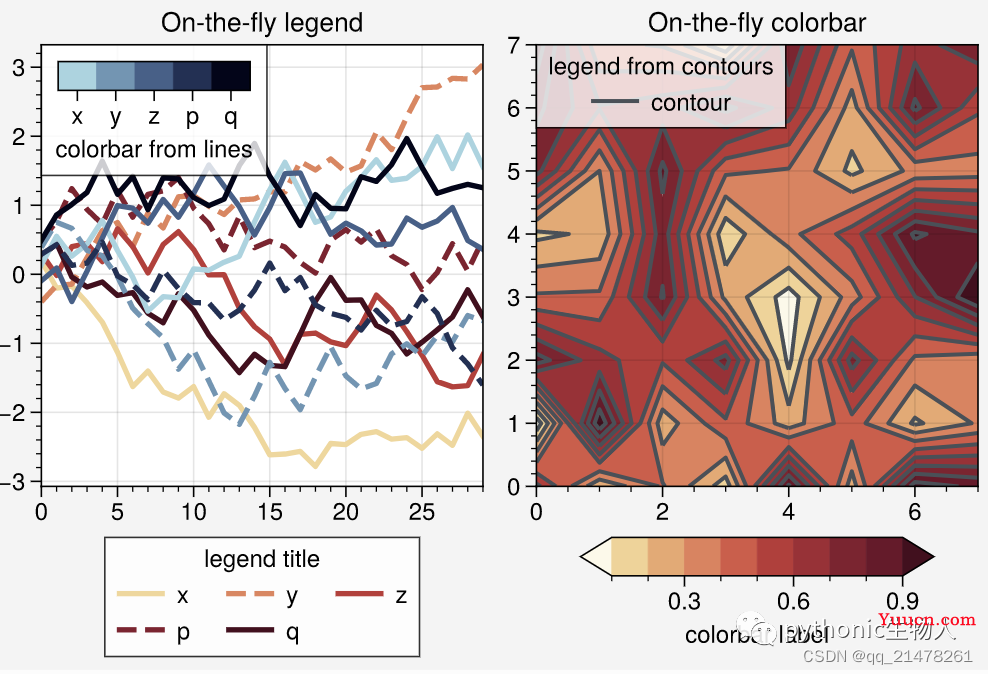
-
图例、colorbar:Figure-wide
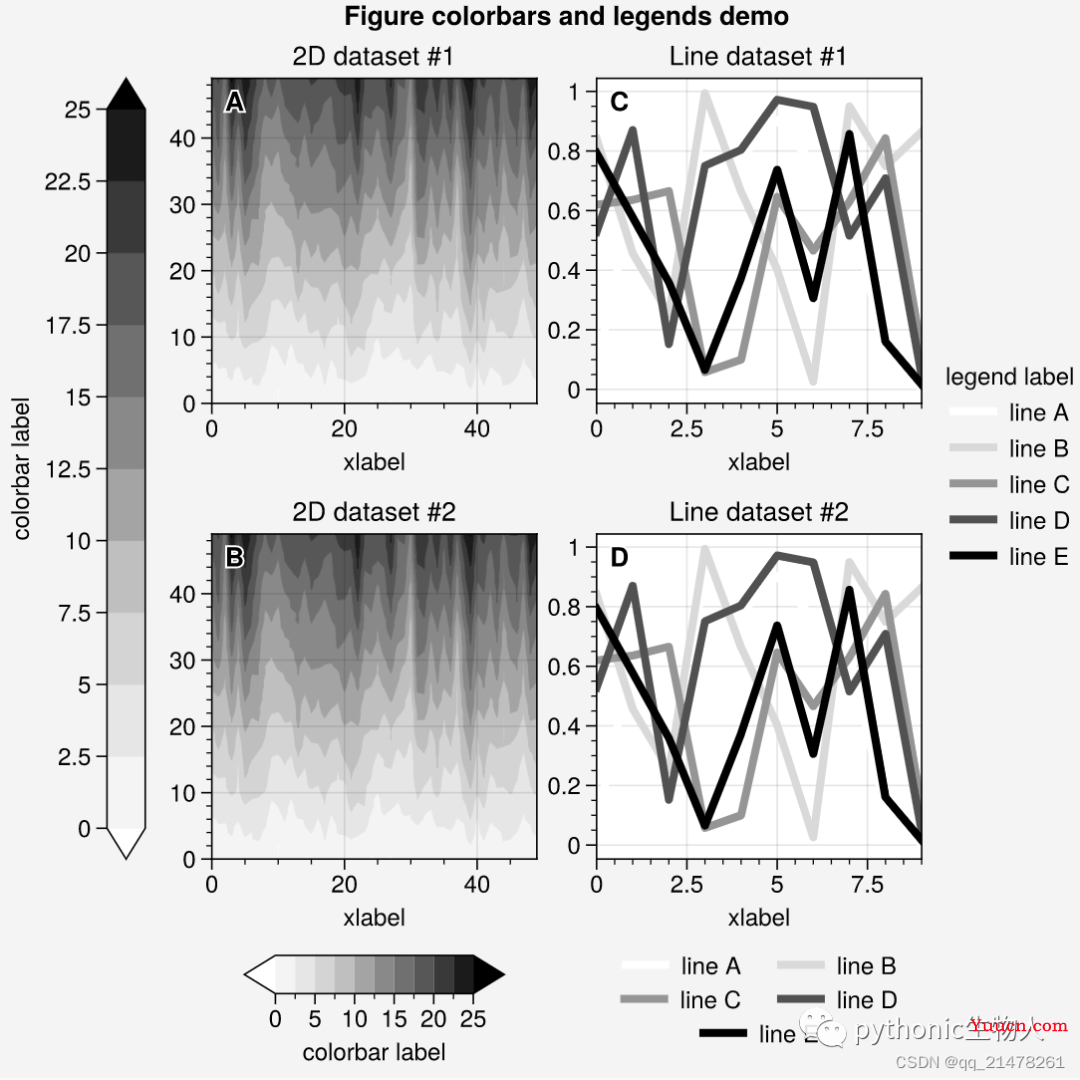
-
图例外观个性化:可轻松设置图例顺序、位置、颜色等等,
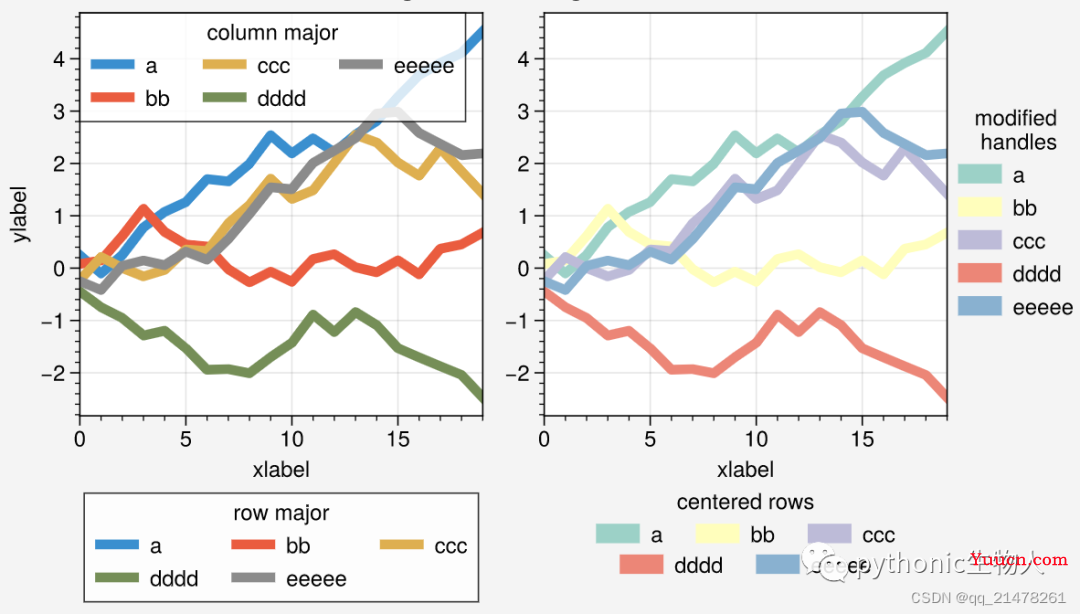
-
colorbar外观个性化:可轻松设置colorbar的刻度、标签、宽窄等,
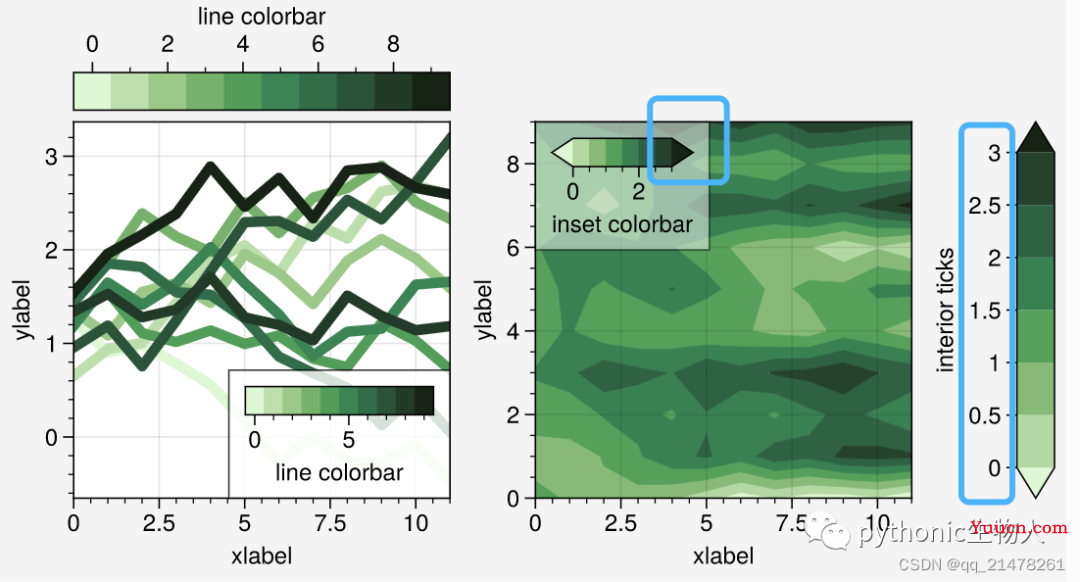
6.更加优化的绘图指令
7、整合地图库Cartopy和basemap
Cartopy和basemap是Python里非常强大的地图库,proplot将cartopy和basemap进行了整合,解决了basemap使用需要创建新的axes、cartopy使用时代码冗长等缺陷。
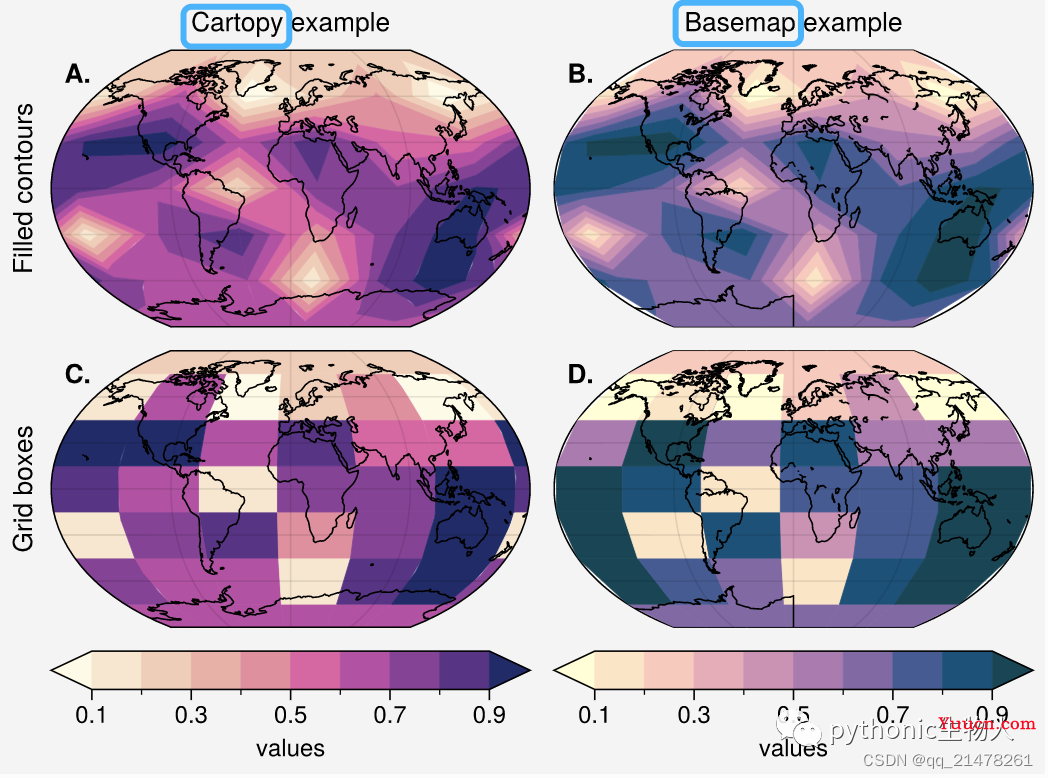
个性化设置,
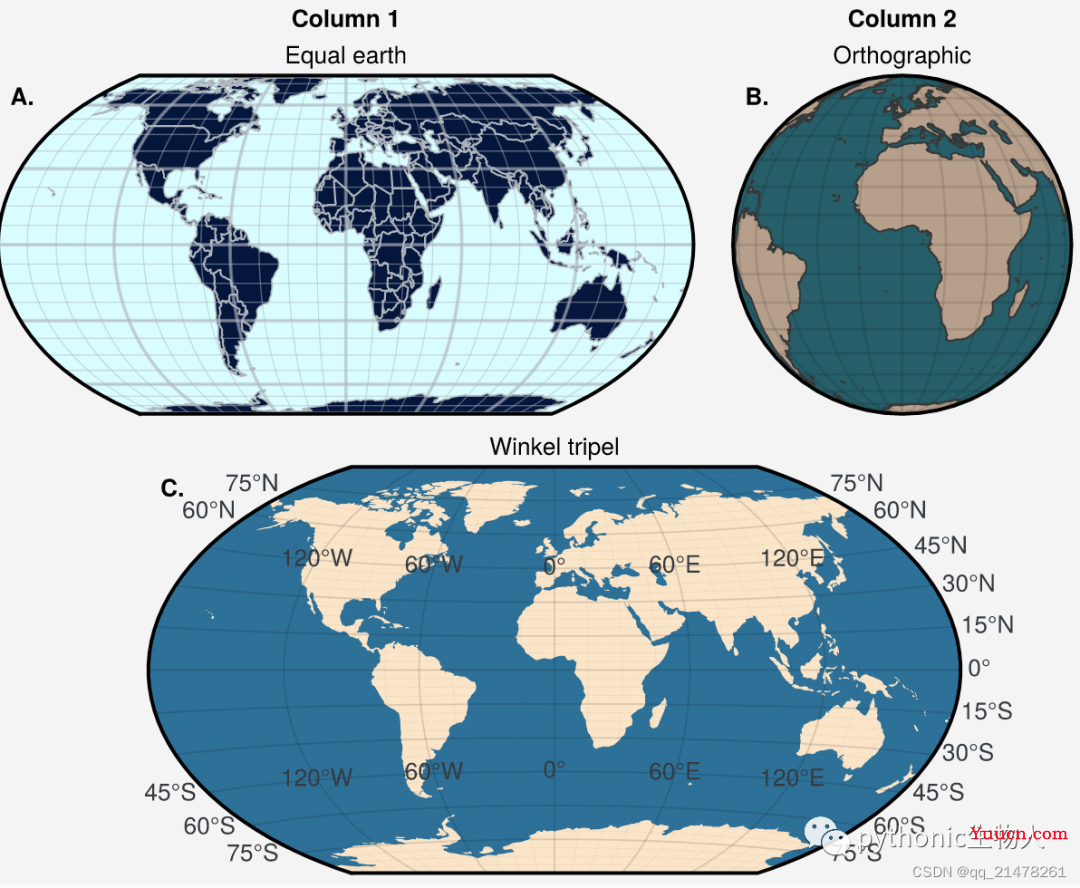
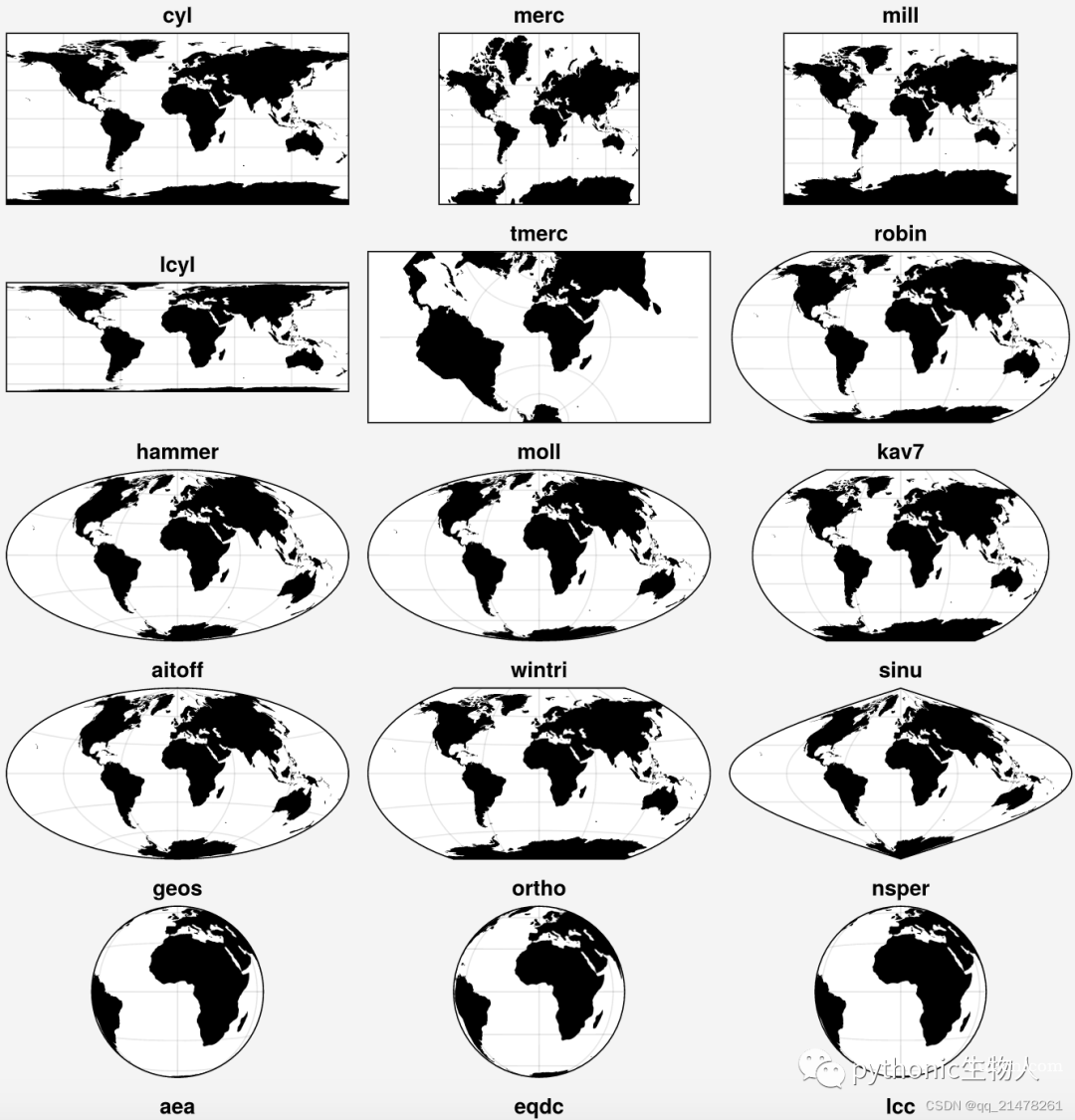
支持cartopy中的各种投影,'cyl', 'merc', 'mill', 'lcyl', 'tmerc', 'robin', 'hammer', 'moll', 'kav7', 'aitoff', 'wintri', 'sinu', 'geos', 'ortho', 'nsper', 'aea', 'eqdc', 'lcc', 'gnom', 'npstere', 'nplaea', 'npaeqd', 'npgnom', 'igh', 'eck1', 'eck2', 'eck3', 'eck4', 'eck5', 'eck6'
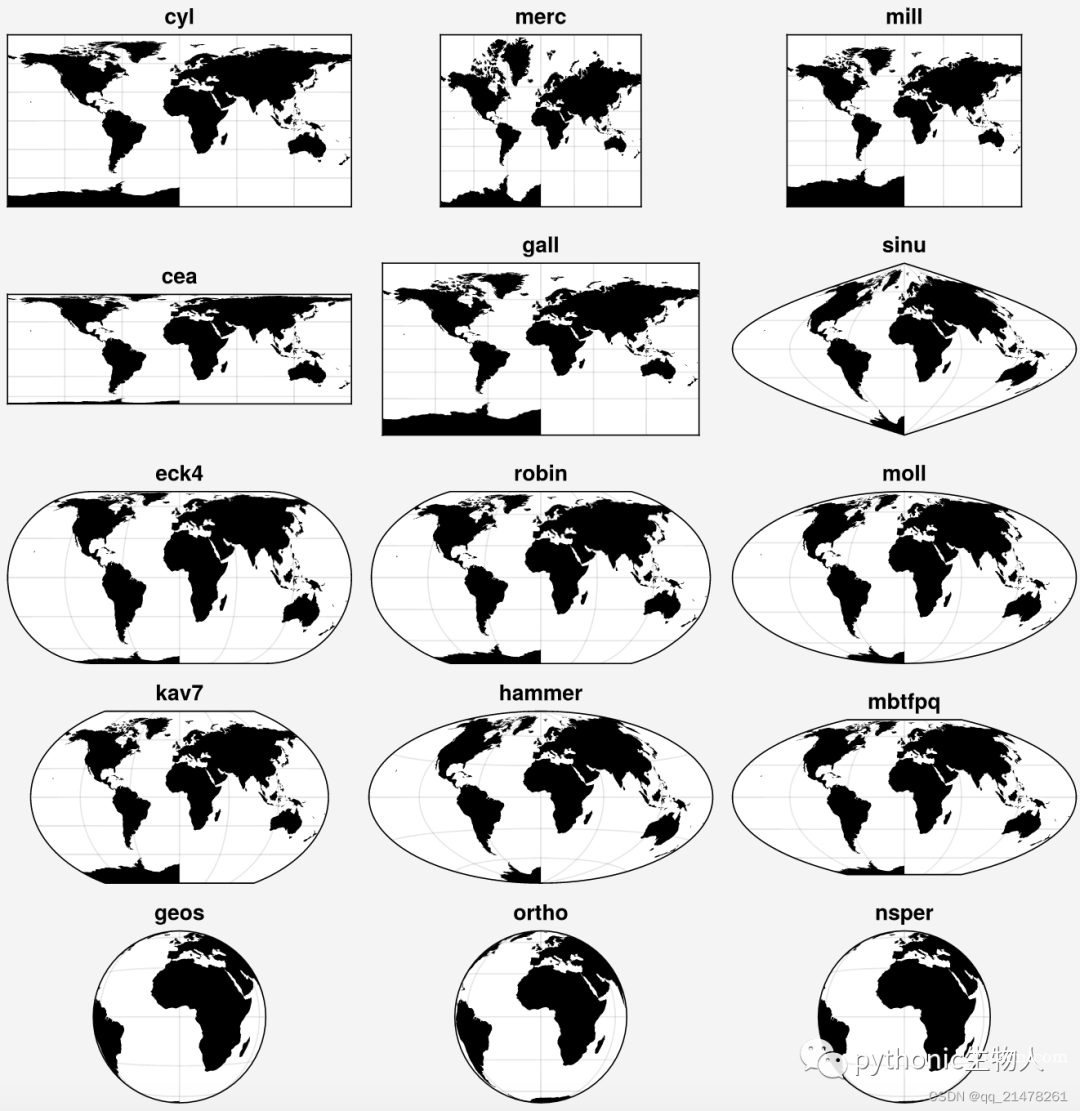
当然,也支持basemap中的各种投影,'cyl', 'merc', 'mill', 'cea', 'gall', 'sinu', 'eck4', 'robin', 'moll', 'kav7', 'hammer', 'mbtfpq', 'geos', 'ortho', 'nsper', 'vandg', 'aea', 'eqdc', 'gnom', 'cass', 'lcc', 'npstere', 'npaeqd', 'nplaea'。
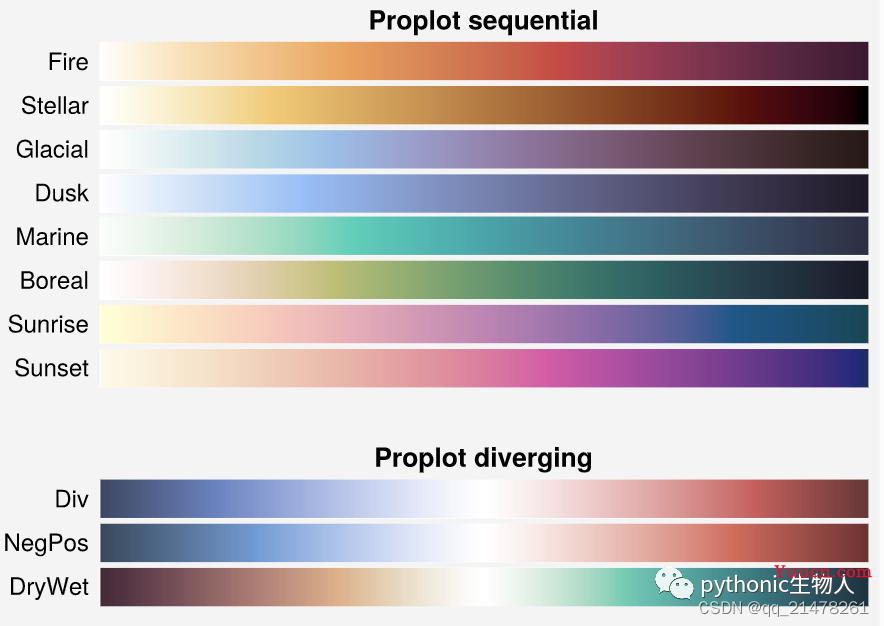
8、更美观的colormaps, colors和fonts
proplot除了整合seaborn, cmocean, SciVisColor及Scientific Colour Maps projects中的colormaps之外,还增加了新的colormaps,同时增加PerceptualColormap方法来制作colormaps(貌似比Matplotlib的ListedColormap、LinearSegmentedColormap好用),ContinuousColormap和DiscreteColormap方法修改colormaps等等。
proplot中可非常便利的添加字体。
-
proplot新增colormaps
-
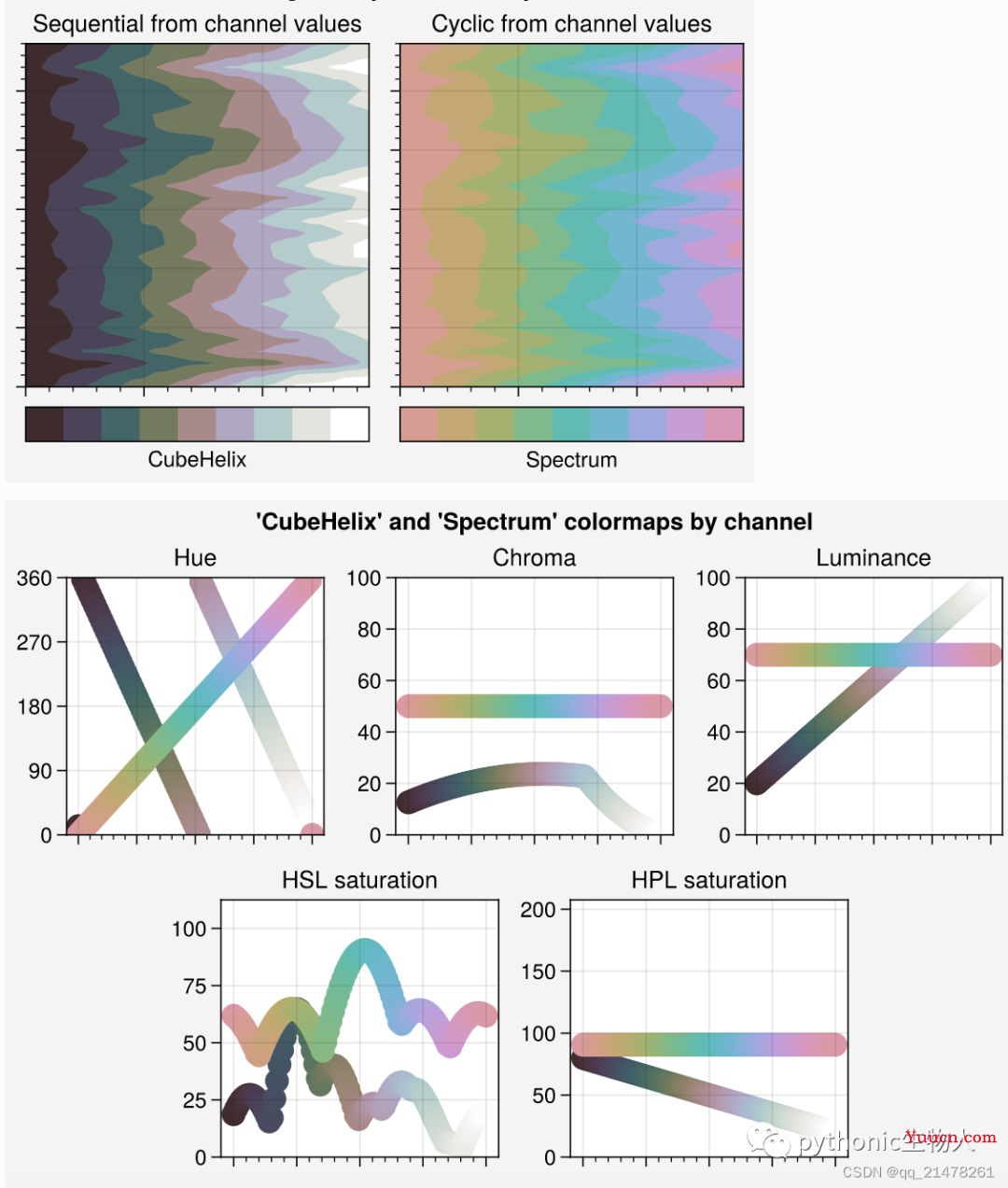
PerceptualColormap制作colormaps
-
将多个colormaps融合
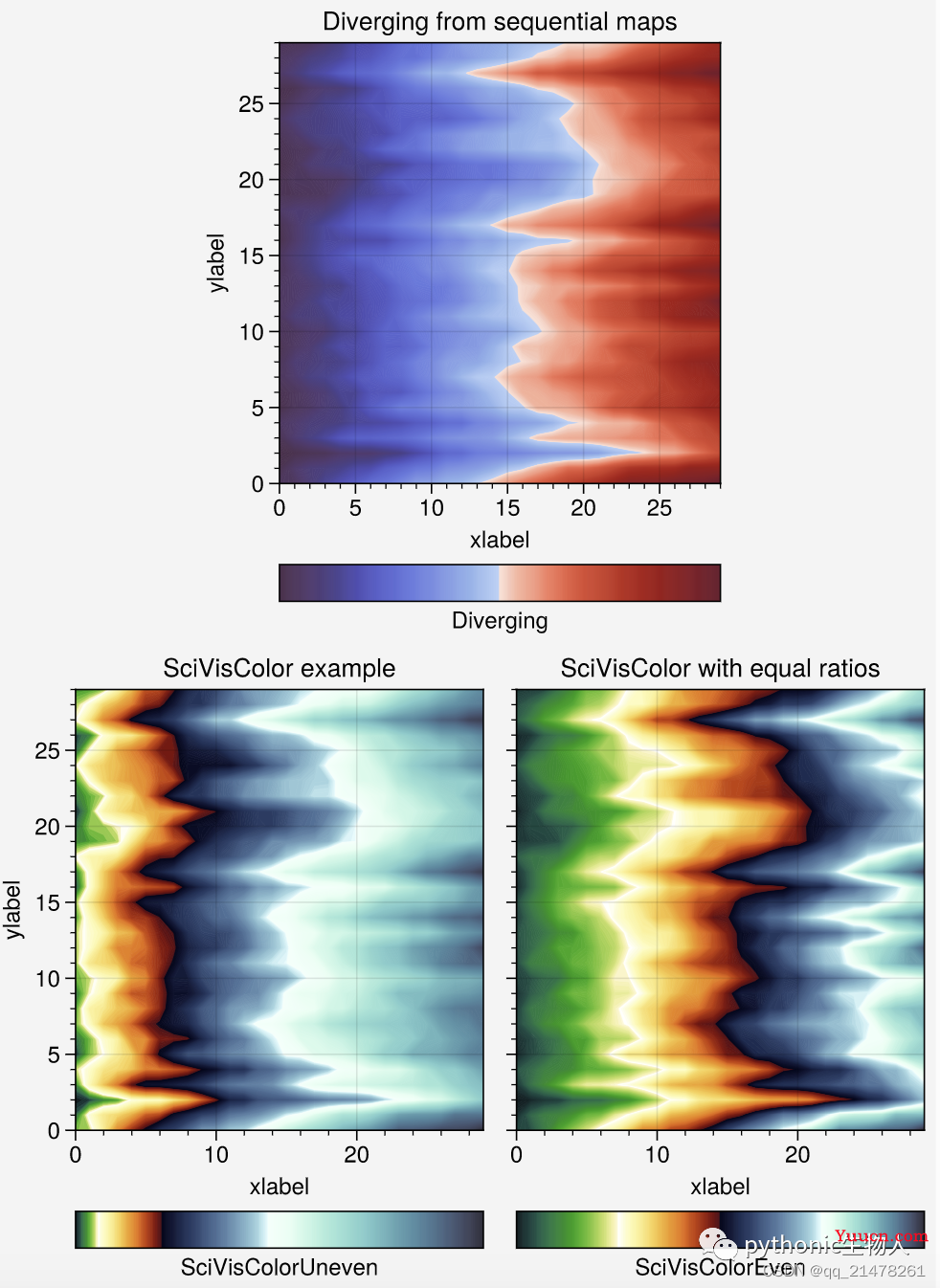
-
ContinuousColormap和DiscreteColormap方法修改colormaps
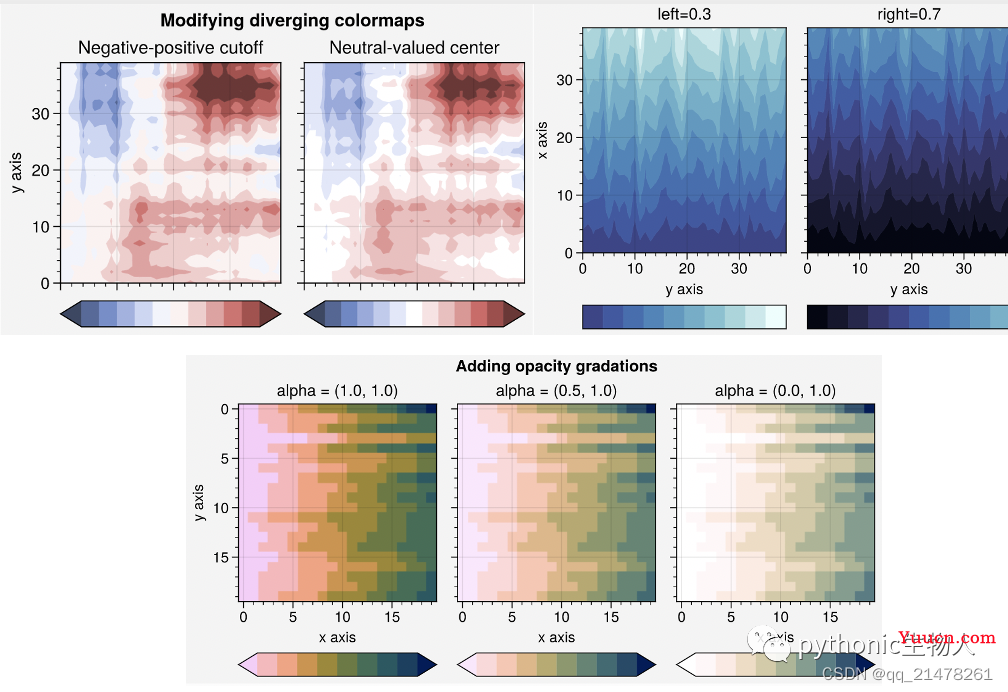
-
proplot添加字体
自定义的.ttc、.ttf等格式字体保存~/.proplot/fonts文件中。
9、全局参数设置更灵活
新的rc方法更新全局参数
import proplot as pplt
import numpy as np
# 多种方法Update全局参数
pplt.rc.metacolor = 'gray6'
pplt.rc.update({'fontname': 'Source Sans Pro', 'fontsize': 11})
pplt.rc['figure.facecolor'] = 'gray3'
pplt.rc.axesfacecolor = 'gray4'
# 使用Update后的全局参数:with pplt.rc.context法
with pplt.rc.context({'suptitle.size': 13}, toplabelcolor='gray6', metawidth=1.5):
fig = pplt.figure(figwidth=6, sharey='limits', span=False)
axs = fig.subplots(ncols=2)
N, M = 100, 7
state = np.random.RandomState(51423)
values = np.arange(1, M + 1)
cycle = pplt.get_colors('grays', M - 1) + ['red']
for i, ax in enumerate(axs):
data = np.cumsum(state.rand(N, M) - 0.5, axis=0)
lines = ax.plot(data, linewidth=3, cycle=cycle)
# 使用Update后的全局参数:format()法
axs.format(
grid=False, xlabel='xlabel', ylabel='ylabel',
toplabels=('Column 1', 'Column 2'),
suptitle='Rc settings demo',
suptitlecolor='gray7',
abc='[A]', abcloc='l',
title='Title', titleloc='r', titlecolor='gray7'
)
# 恢复设置
pplt.rc.reset()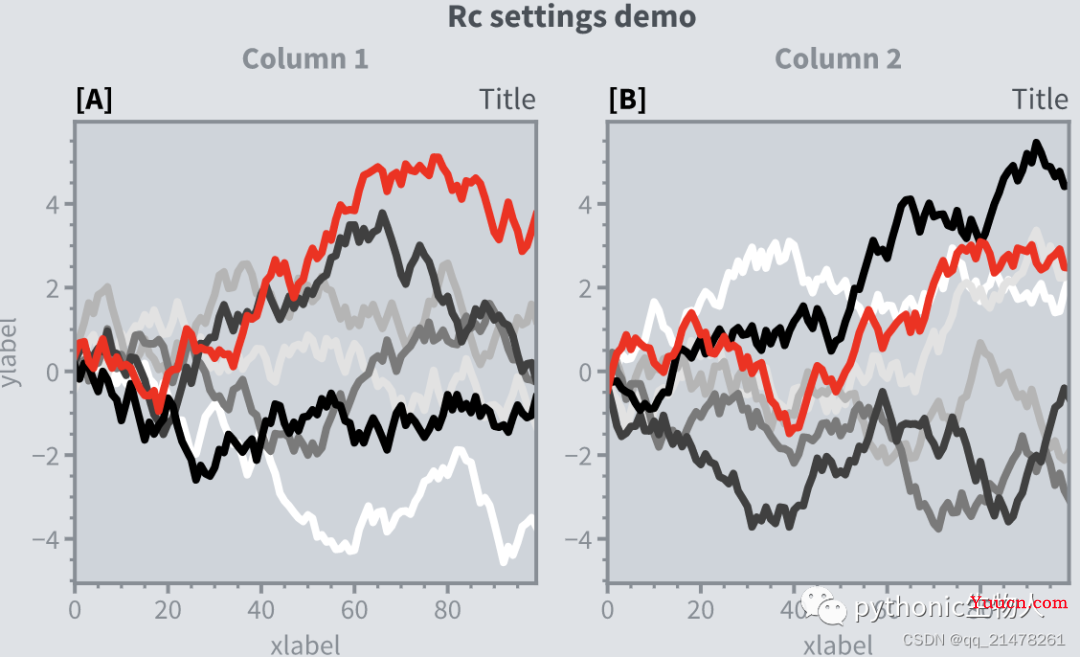
全局设置'ggplot', 'seaborn'的style
import proplot as pplt
import numpy as np
state = np.random.RandomState(51423)
data = state.rand(10, 5)
# Set up figure
fig, axs = pplt.subplots(ncols=2, nrows=2, span=False, share=False)
axs.format(suptitle='Stylesheets demo')
styles = ('ggplot', 'seaborn', '538', 'bmh')
# 直接使用format()方法
for ax, style in zip(axs, styles):
ax.format(style=style, xlabel='xlabel', ylabel='ylabel', title=style)
ax.plot(data, linewidth=3)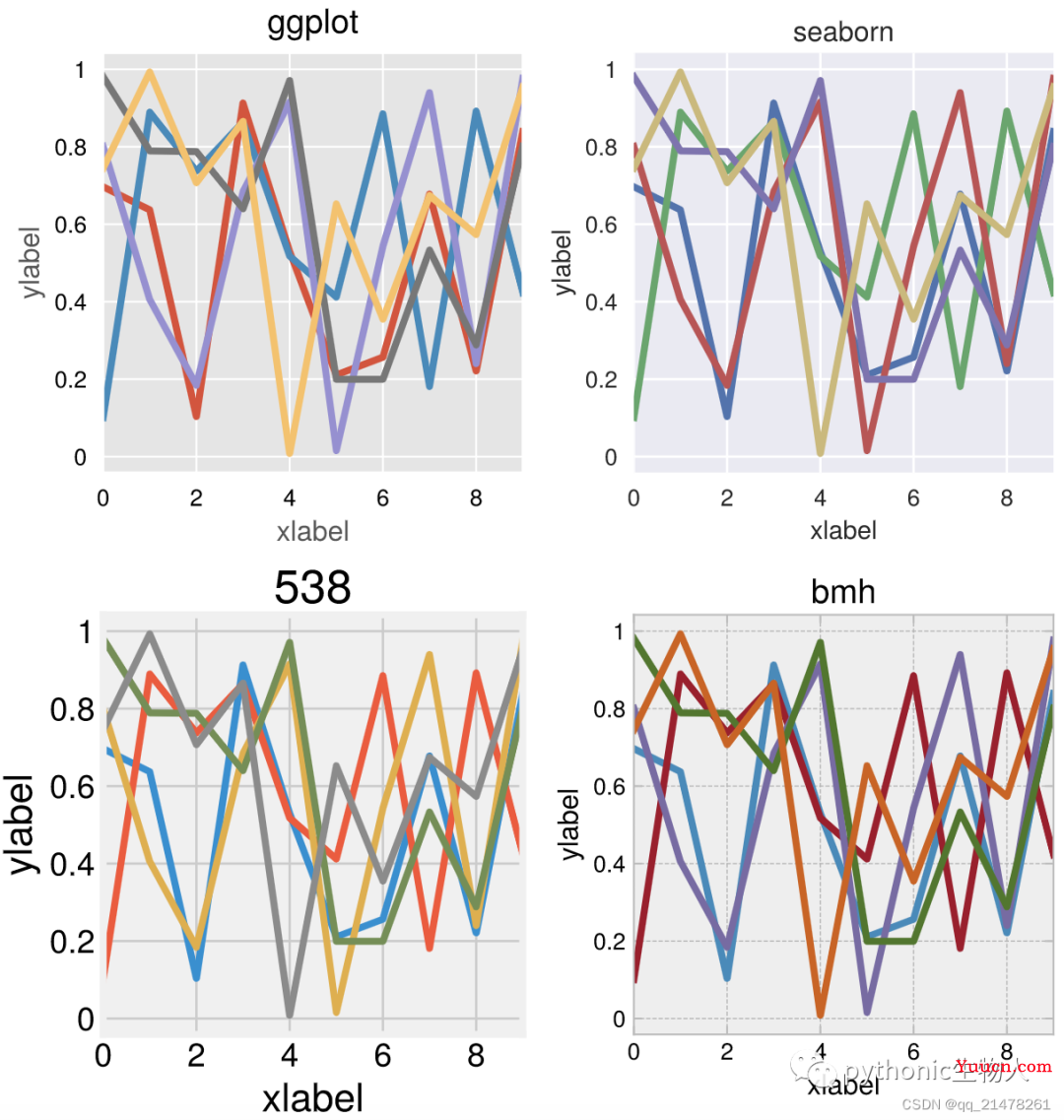
END
本篇到这里就结束了。想学习更多Python、人工智能、交叉学科相关知识,点击关注博主,带你从基础到进阶。若有需要提供科研指导、代码支持,资源获取或者付费咨询的伙伴们,可以添加博主个人联系方式!
码字不易,希望大家可以点赞+收藏+关注+评论!
来源:https://github.com/lukelbd/proplot
参考:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/8M5GRGj13hcfnnruqz7kmA
声明:部分内容来源于网络,仅供读者学术交流之目的。文章版权归原作者所有。如有不妥,请联系删除。