1、环境准备
1.1Nacos
单机启动:startup.cmd -m standalone
1.2 Sentinel
启动命令:java -Dserver.port=8858 -Dcsp.sentinel.dashboard.server=localhost:8858 -Dproject.name=sentinel-dashboard -jar sentinel-dashboard-1.8.0.jar
1.3 JMeter
2、流控规则限流
2.0 环境搭建
2.0.1 依赖
<!-- nacos 依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- sentinel 流量防卫依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 暴露/actuator/sentinel端点 单独配置,management开头 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.0.2 application.yml
# 端口
server:
port: 9604
# 服务名
spring:
application:
name: kgcmall-sentinel
# 数据源配置
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/kh96_alibaba_kgcmalldb?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=GMT
username: root
password: 17585273765
# jpa配置
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: update
show-sql: true
cloud:
#nacos 配置
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
#sentinel 配置
sentinel:
transport:
dashboard: 127.0.0.1:8858 # sentinel 控制台地址
port: 9605 # 客户端(核心应用)和控制台的通信端口,默认8719,子当以一个为被使用的唯一端口即可
web-context-unify: false #关闭收敛
# 暴露/actuator/sentinel端点 单独配置,management 开顶格写
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: '*'
2.0.3 测试
http://localhost:9604/actuator/sentinel
2.1 流控模式
2.1.1 直接模式
2.1.1.1 测试请求
/**
* @param : [sentinelDesc]
* @return : java.lang.String
* @author : huayu
* @date : 26/11/2022
* @description : 测试 Sentinel 流控 - 直接失败
*/
@GetMapping("testSentinelFlowFail")
public String testSentinelFlowFail(@RequestParam String sentinelDesc) {
log.info("------ testSentinelFlowFail 接口调用 ------ ");
return sentinelDesc;
}
2.1.1.2 添加直接流控规则
2.1.1.2.1 需要先发起异常请求
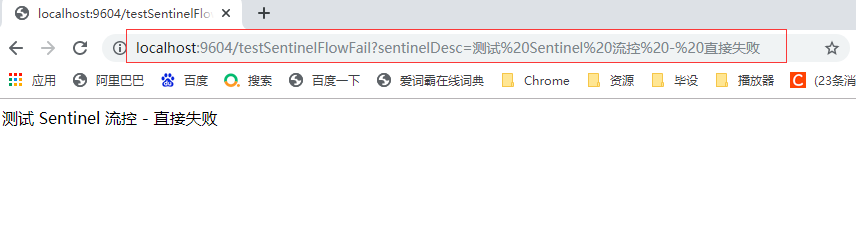
2.1.1.2.2 簇点链路 添加流控规则
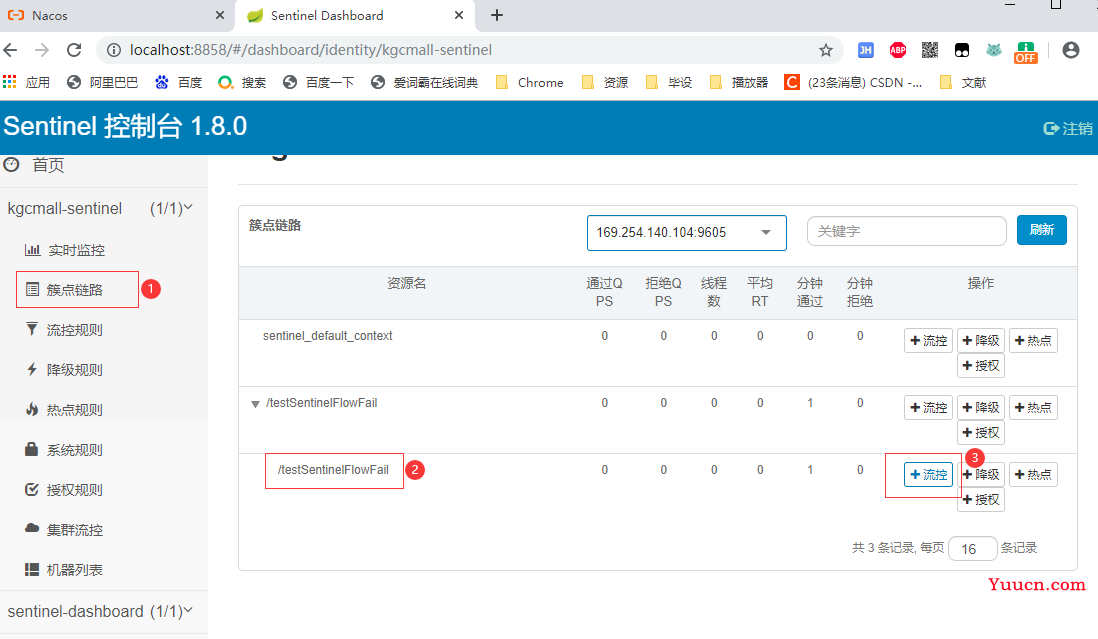
2.1.1.2.3 设置流控规则
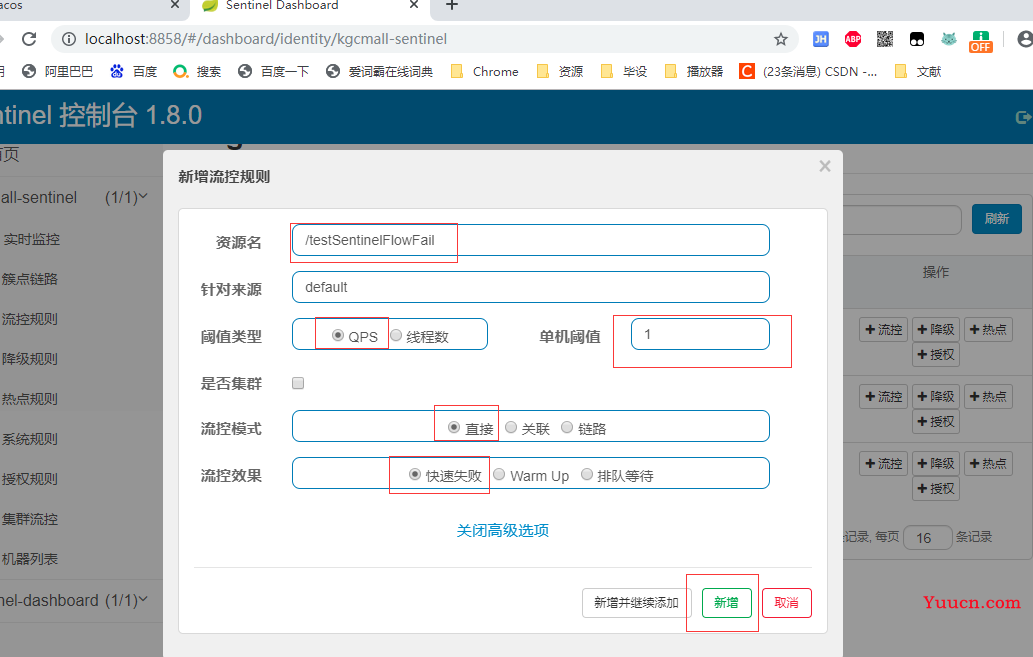
2.1.1.3查看流控规则
2.1.1.4 测试
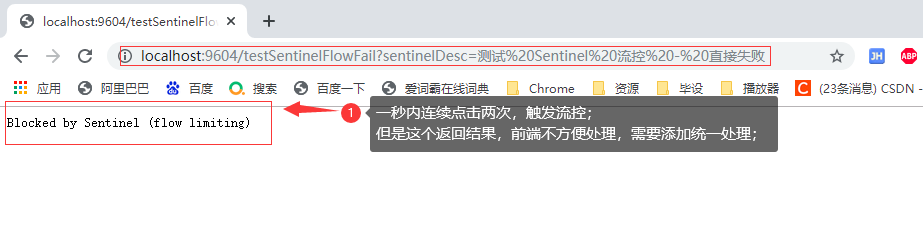
2.1.1.5 自定义sentinel统一已成返回处理
/**
* Created On : 26/11/2022.
* <p>
* Author : huayu
* <p>
* Description: 自定义sentinel统一已成返回处理
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MySentinelBlockExceptionHandler implements BlockExceptionHandler {
@Override
public void handle(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, BlockException e) throws Exception {
// 记录异常日志
log.warn("------ MySentinelBlockExceptionHandler 规则Rule:{} ------", e.getRule());
// 增加自定义统一异常返回对象
RequestResult<String> requestResult = null;
// 针对不同的流控异常,统一返回
if (e instanceof FlowException) {
requestResult = ResultBuildUtil.fail("9621", "接口流量限流");
} else if (e instanceof DegradeException) {
requestResult = ResultBuildUtil.fail("9622", "接口服务降级");
} else if (e instanceof ParamFlowException) {
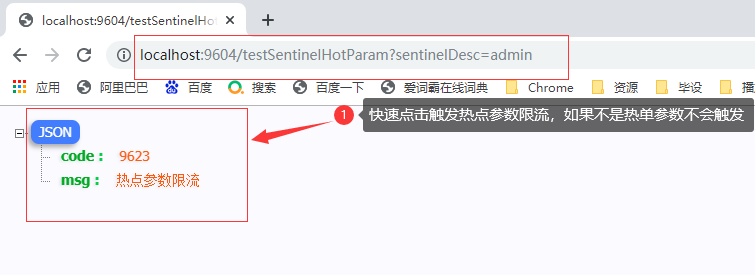
requestResult = ResultBuildUtil.fail("9623", "热点参数限流");
} else if (e instanceof SystemBlockException) {
requestResult = ResultBuildUtil.fail("9624", "触发系统保护");
} else if (e instanceof AuthorityException) {
requestResult = ResultBuildUtil.fail("9625", "授权规则限制");
}
// 统一返回json结果
httpServletResponse.setStatus(HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN.value());
httpServletResponse.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
httpServletResponse.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE);
// 借助SpringMVC自带的Jackson工具,返回结果
new ObjectMapper().writeValue(httpServletResponse.getWriter(), requestResult);
}
}
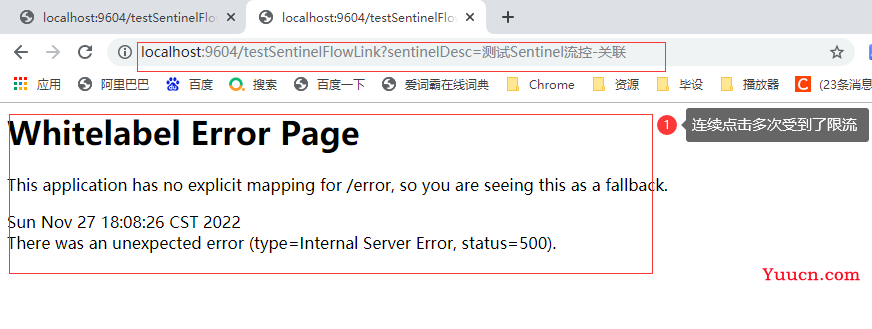
2.1.1.6 再次测试
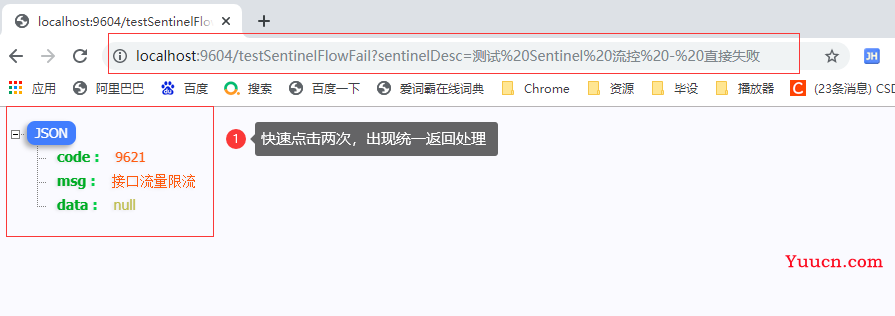
2.1.2 关联模式
2.1.2.1 测试请求
/**
* @param : [sentinelDesc]
* @return : java.lang.String
* @author : huayu
* @date : 26/11/2022
* @description : 测试 Sentinel 流控 - 关联
*/
@GetMapping("testSentinelFlowLink")
public String testSentinelFlowLink(@RequestParam String sentinelDesc) {
log.info("------ testSentinelFlowLink 接口调用 ------ ");
return sentinelDesc;
}
2.1.1.2 添加关联流控规则
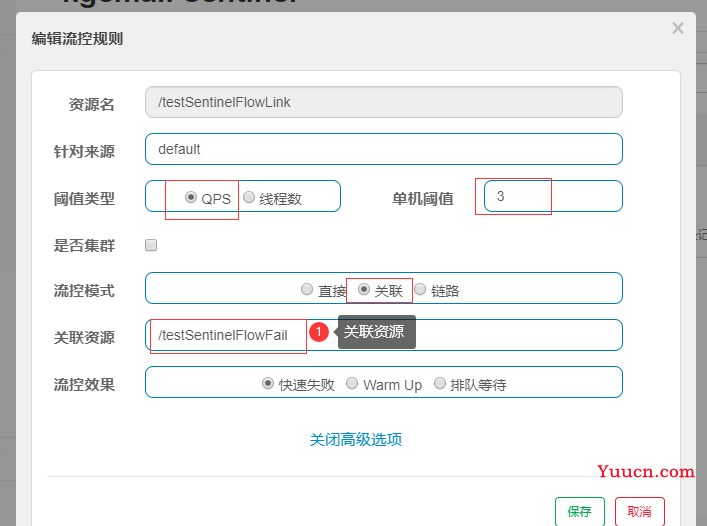
2.1.1.3 JMeter压测配置
2.1.1.3.1 线程组
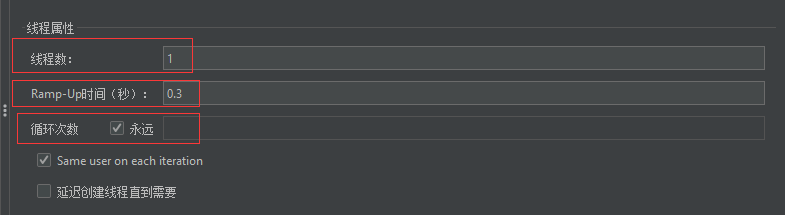
2.1.1.3.2 Http请求
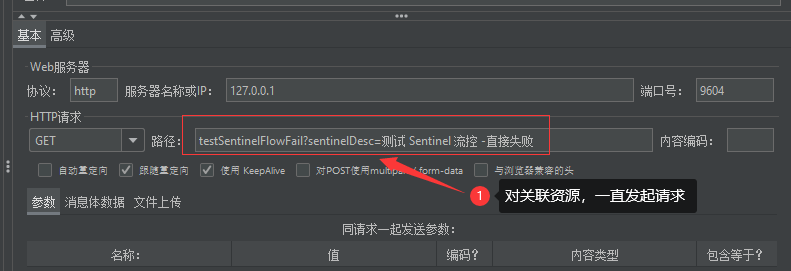
2.1.1.3.3 测试 testSentinelFlowLink 接口
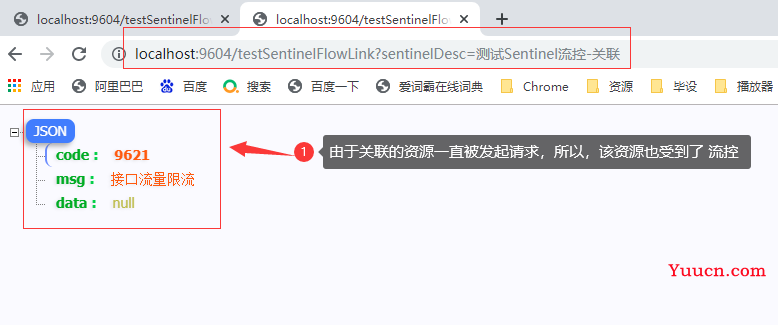
2.1.3 链路模式
链路流控模式指的是,当从某个接口过来的资源达到限流条件时,开启限流。它的功能有点类似于针对来源配置项,区别在于:针对来源是针对上级微服务,而链路流控是针对上级接口,也就是说它的粒度更细。
2.1.3.1 添加调用方法
2.1.3.1.1 接口
/**
* Created On : 26/11/2022.
* <p>
* Author : huayu
* <p>
* Description: 测试链路 模式
*/
public interface SentinelService {
void message();
}
2.1.3.1.2 实现类
/**
* Created On : 26/11/2022.
* <p>
* Author : huayu
* <p>
* Description: 测试链路 模式 实现类
*/
@Service
public class SentinelServiceImpl implements SentinelService {
@Override
@SentinelResource("message") // 在@SentinelResource中指定资源名
public void message() {
System.out.println("message");
}
}
2.1.3.2 两个接口,调用相同的资源
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class KgcMallSentinelController {
@Autowired
private SentinelService sentinelService;
//测试 Sentinel 流控 - 直接失败
@GetMapping("testSentinelFlowFail")
public String testSentinelFlowFail(@RequestParam String sentinelDesc) {
log.info("------ testSentinelFlowFail 接口调用 ------ ");
//测试 链路模式调用相同的资源
sentinelService.message();
return sentinelDesc;
}
//测试 Sentinel 流控 - 关联
@GetMapping("testSentinelFlowLink")
public String testSentinelFlowLink(@RequestParam String sentinelDesc) {
log.info("------ testSentinelFlowLink 接口调用 ------ ");
//测试 链路模式调用相同的资源
sentinelService.message();
return sentinelDesc;
}
}
2.1.3.3 添加链路流控规则
2.1.3.4 测试
如果message触发流控,指定的入口就会被限流;
2.1.3.4.0 高版本此功能直接使用不生效:
1.7.0 版本开始(对应SCA的2.1.1.RELEASE),官方在CommonFilter 引入了WEB_CONTEXT_UNIFY 参数,用于控制是否收敛context。将其配置为 false 即可根据不同的URL 进行链路限流。
spring:
cloud:
#sentinel 配置
sentinel:
web-context-unify: false #关闭收敛
2.1.3.4.1 testSentinelFlowFail 请求
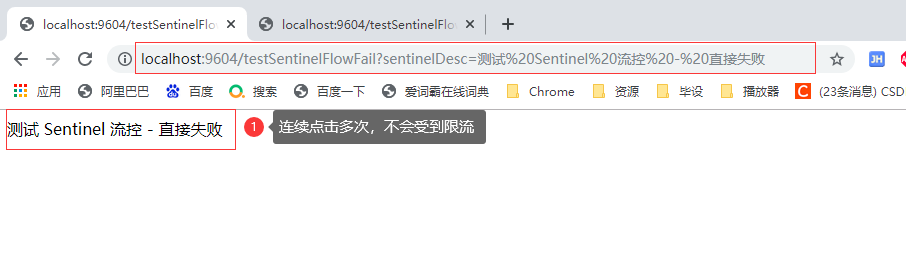
2.1.3.4.2 testSentinelFlowLink请求 (message 资源对此入口进行了限流)
使用链路规则,会导致统一返回处理,无法生效;
2.2 流控规则
2.2.1 快速失败
快速失败:直接抛出异常,默认的流量控制方式
当QPS超过任意规则的阈值后,新的请求就会被立即拒绝。这种方式适用于对系统处理能力确切已知的情况下;
2.2.2 Warm Up(激增模式)
Warm Up(激增流量)即预热/冷启动方式;
冷加载因子: codeFactor 默认是3,即请求 QPS 从 1 / 3 开始,经预热时长逐渐升至设定的 QPS 阈值。
当系统长期处于低水位的情况下,当流量突然增加时,直接把系统拉升到高水位可能瞬间把系统压垮。通过"冷启动",让通过的流量缓慢增加,在一定时间内逐渐增加到阈值上限,给冷系统一个预热的时间,避免冷系统被压垮。
2.2.2.1 使用 testSentinelFlowFail 请求测试
请求方法省略;
2.2.2.2 流控配置
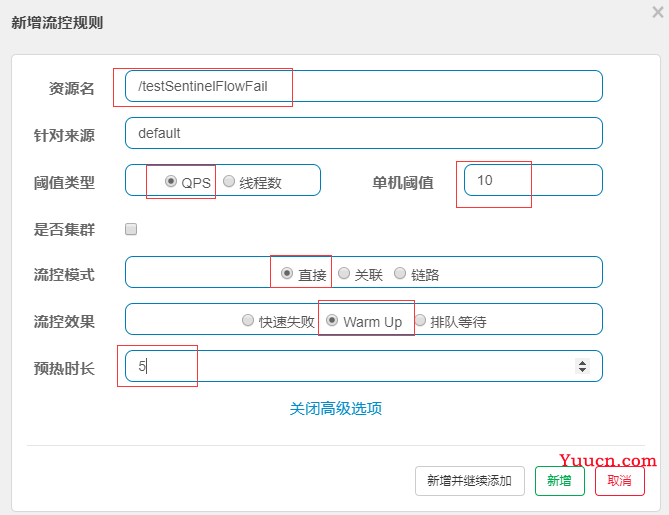
2.2.2.3 压测配置
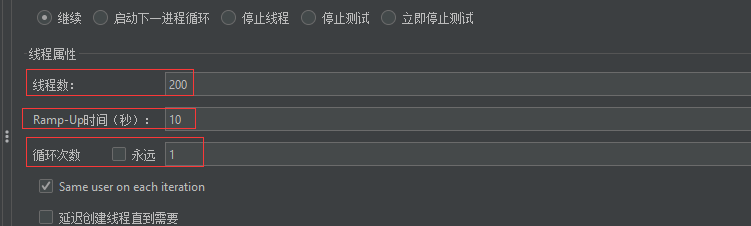
2.2.3.4 实时监控
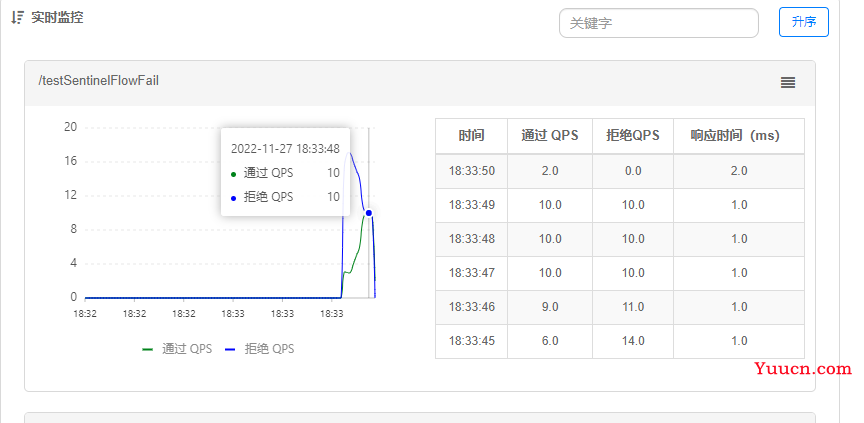
2.2.3 匀速模式
会严格控制请求通过的间隔时间,也即是让请求以均匀的速度通过,其余的排队等待,对应的是漏桶算法。
用于处理间隔性突发的流量,例如消息队列,在某一秒有大量的请求到来,而接下来的几秒则处于空闲状态,这个时候我们不希望一下子把所有的请求都通过,这样可能会把系统压垮;同时我们也期待系统以稳定的速度,逐步处理这些请求,以起到“削峰填谷”的效果,而不是第一秒拒绝所有请求。
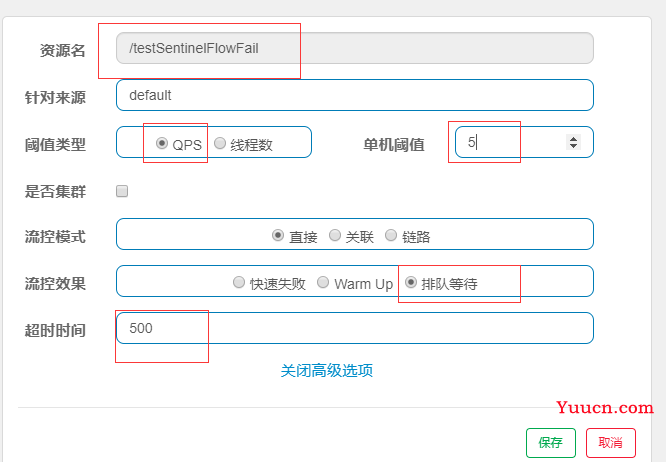
选择排队等待的阈值类型必须是QPS,且暂不支持>1000的模式
2.2.3.1 使用 testSentinelFlowFail 请求测试
请求方法省略;
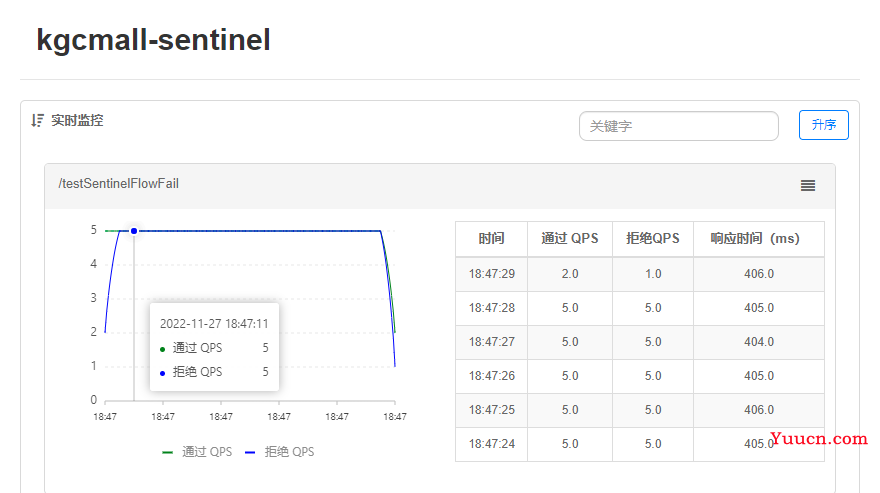
单机阈值:每秒通过的请求个数是5,则每隔200ms通过一次请求;每次请求的最大等待时间为500ms=0.5s,超过0.5S就丢弃请求。
2.2.3.2 流控配置
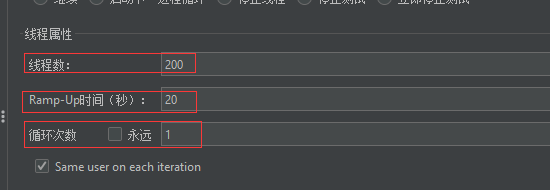
2.2.3.3 压测配置
2.2.3.4 实时监控
3、降级规则限流
3.1慢调用比例-SLOW_REQUEST_RATIO
选择以慢调用比例作为阈值,需要设置允许的慢调用 RT(即最大的响应时间),请求的响应时间大于该值则统计为慢调用。当单位统计时长(statIntervalMs)内请求数目大于设置的最小请求数目,并且慢调用的比例大于阈值,则接下来的熔断时长内请求会自动被熔断。经过熔断时长后熔断器会进入探测恢复状态(HALFOPEN 状态),若接下来的一个请求响应时间小于设置的慢调用 RT 则结束熔断,若大于设置的慢调用 RT 则会再次被熔断。
3.1.1 模拟慢调用请求
/**
* @param : [sentinelDesc]
* @return : java.lang.String
* @author : huayu
* @date : 26/11/2022
* @description : 测试 Sentinel-降级-慢调用
*/
@GetMapping("testSentinelDown")
public String testSentinelDown(@RequestParam String sentinelDesc) throws InterruptedException {
log.info("------ testSentinelDown 接口调用 ------ ");
//模拟慢调用
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100);
return sentinelDesc;
}
3.1.2 降级策略
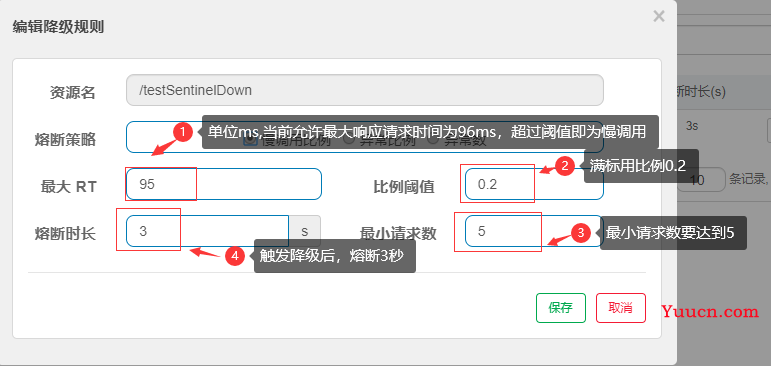
3.1.3 压测配置
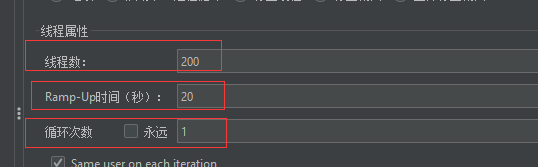
3.1.4 实时监控
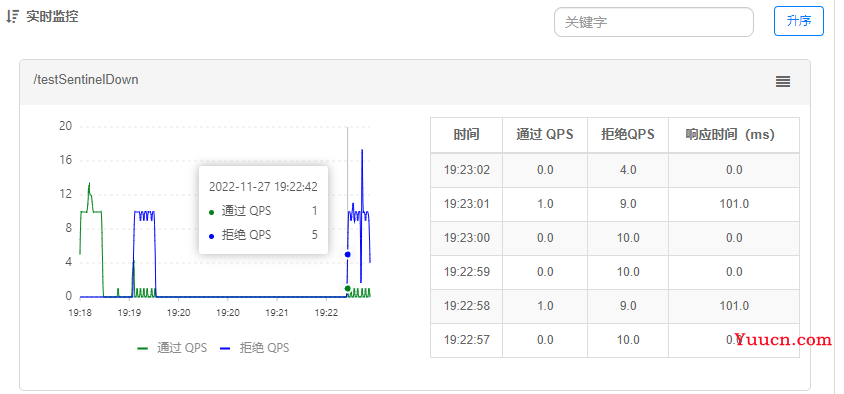
3.1.5 从浏览器请求测试
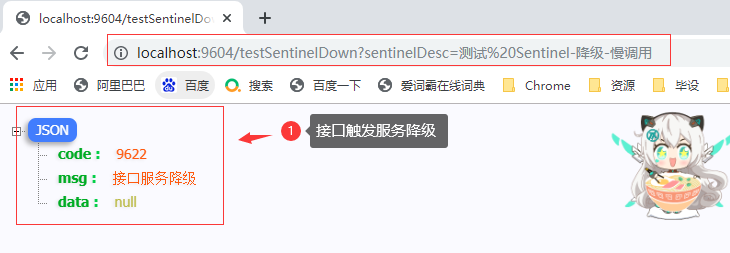
3.2 异常比例-ERROR_RATIO
当单位统计时长(statIntervalMs)内请求数目大于设置的最小请求数目,并且异常的比例大于阈值,则接下来的熔断时长内请求会自动被熔断。
经过熔断时长后熔断器会进入探测恢复状态(HALFOPEN 状态),若接下来的一个请求成功完成(没有错误)则结束熔断,否则会再次被熔断。异常比率的阈值范围是 [0.0, 1.0],代表 0% 100%。
3.2.1 模拟异常比例请求
/**
* @param : [sentinelDesc]
* @return : java.lang.String
* @author : huayu
* @date : 26/11/2022
* @description : 测试 Sentinel-降级-异常比例 异常数
*/
@GetMapping("testSentinelDownExpScale")
public String testSentinelDownExpScale(@RequestParam String sentinelDesc) throws InterruptedException {
log.info("------ testSentinelDownExpScale 接口调用 ------ ");
//模拟异常
int num = new Random().nextInt(10);
if (num % 2 == 1) {
num = 10 / 0;
}
return sentinelDesc;
}
3.2.2 降级策略
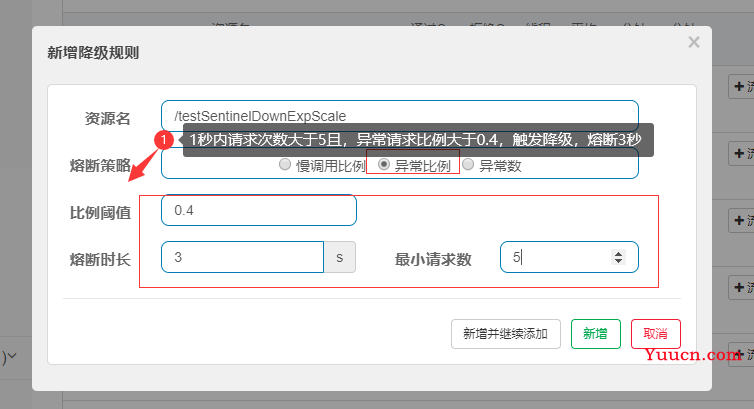
3.2.3 压测配置
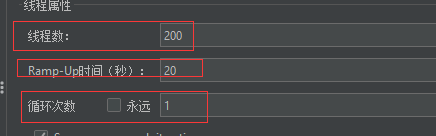
3.2.4 实时监控
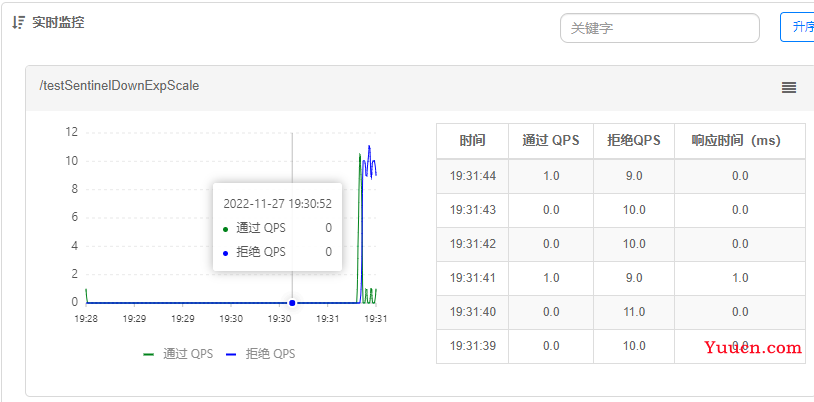
3.2.5 从浏览器请求测试
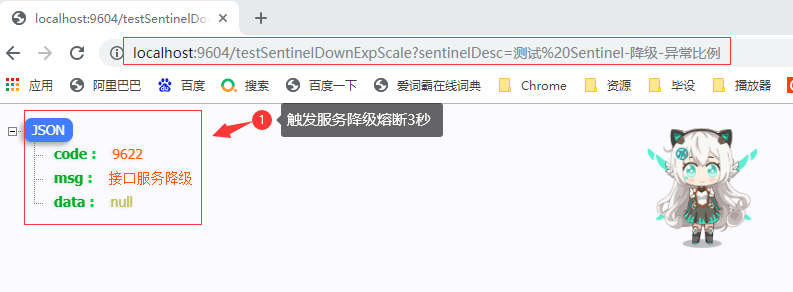
3.3 异常数-ERROR_COUNT
当单位统计时长内的异常数目超过阈值之后会自动进行熔断。经过熔断时长后熔断器会进入探测恢复状态(HALFOPEN 状态),若接下来的一个请求成功完成(没有错误)则结束熔断,否则会再次被熔断。
注意:异常降级仅针对业务异常,对 Sentinel 限流降级本身的异常(BlockException)不生效。
3.3.1 模拟异常参数请求
/**
* @param : [sentinelDesc]
* @return : java.lang.String
* @author : huayu
* @date : 26/11/2022
* @description : 测试 Sentinel-降级-异常比例 异常数
*/
@GetMapping("testSentinelDownExpScale")
public String testSentinelDownExpScale(@RequestParam String sentinelDesc) throws InterruptedException {
log.info("------ testSentinelDownExpScale 接口调用 ------ ");
//模拟异常
int num = new Random().nextInt(10);
if (num % 2 == 1) {
num = 10 / 0;
}
return sentinelDesc;
}
3.3.2 降级策略
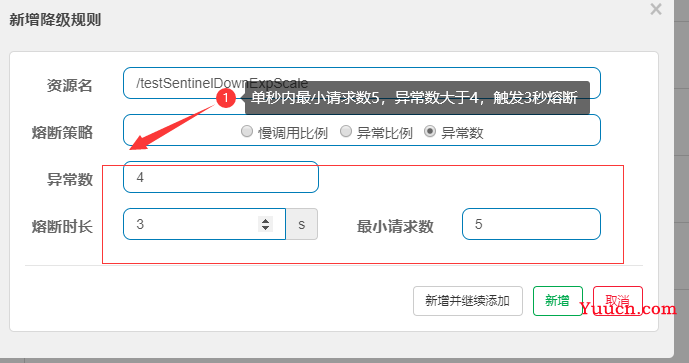
3.3.3 压测配置
3.3.4 实时监控
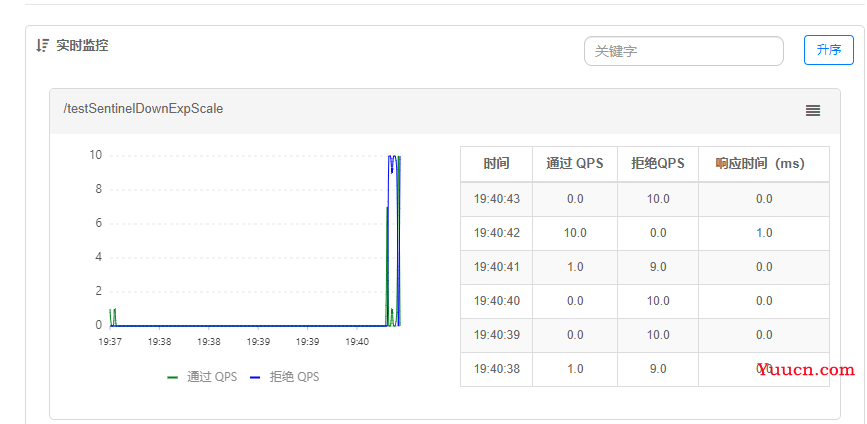
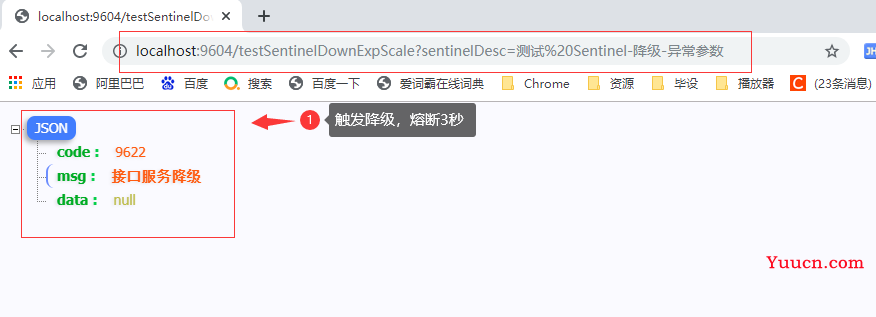
3.3.5 从浏览器请求测试
4、热点规则限流
何为热点?热点即经常访问的数据。很多时候我们希望统计某个热点数据中访问频次最高的数据,并对其访问进行限制。
热点参数限流会统计传入参数中的热点参数,并根据配置的限流阈值与模式,对包含热点参数的资源调用进行限流。热点参数限流可以看做是一种特殊的流量控制,仅对包含热点参数的资源调用生效
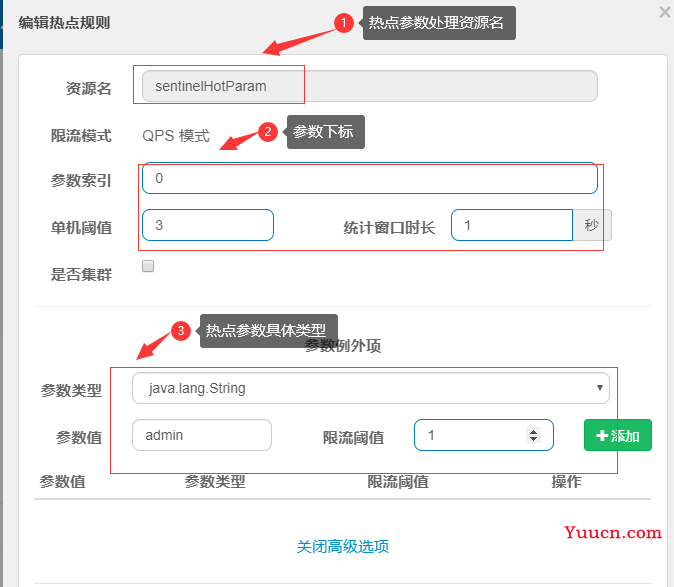
4.1 单机阈值
单机阈值: 针对所有参数的值进行设置的一个公共的阈值
- 假设当前 参数 大部分的值都是热点流量, 单机阈值就是针对热点流量进行设置, 额外针对普通流量进行参数值流控;
- 假设当前 参数 大部分的值都是普通流量, 单机阈值就是针对普通流量进行设置, 额外针对热点流量进行参数值流控
配置热点参数规则:
资源名必须是@SentinelResource(value="资源名")中 配置的资源名,热点规则依赖于注解;
单独指定参数例外的参数具体值,必须是指定的7种数据类型才会生效;
4.1.1 模拟 单机阈值请求
/**
* @param : [sentinelDesc]
* @return : java.lang.String
* @author : huayu
* @date : 26/11/2022
* @description : 测试 Sentinel-热点
*/
@GetMapping("testSentinelHotParam")
@SentinelResource(value = "sentinelHotParam", blockHandlerClass = MySentinelHotBlockExceptionHandler.class, blockHandler = "hotBlockExceptionHandle")
//热点参数,必须使用此注解,指定资源名
//注意使用此注解无法处理BlockExecption,会导致统一异常处理失效
public String testSentinelHotParam(@RequestParam String sentinelDesc) {
log.info("------ testSentinelHotParam 接口调用 ------ ");
return sentinelDesc;
}
4.1.2注意使用此注解无法处理BlockExecption,会导致统一异常处理失效
4.1.2.1 方法一:类内处理方法
@GetMapping("testSentinelHotParam")
@SentinelResource(value = "sentinelHotParam",blockHandler = "hotBlockExceptionHandle")
//热点参数,必须使用此注解,指定资源名
//注意使用此注解无法处理BlockExecption,会导致统一异常处理失效
public String testSentinelHotParam(@RequestParam String sentinelDesc) {
log.info("------ testSentinelHotParam 接口调用 ------ ");
return sentinelDesc;
}
/**
* @author : huayu
* @date : 26/11/2022
* @param : [sentinelDesc, e]
* @return : java.lang.String
* @description : 类内处理方法 增加一个自定义处理方法,参数必须跟入口一致
*/
public String hotBlockExceptionHandle(@RequestParam String sentinelDesc, BlockException e){
//记录异常日志
log.warn("------ hotBlockExceptionHandle 规则Rule:{} ------", e.getRule());
return JSON.toJSONString(ResultBuildUtil.fail("9623", "热点参数限流")) ;
}
4.1.2.2 方法二:单独处理类
@GetMapping("testSentinelHotParam")
@SentinelResource(value = "sentinelHotParam", blockHandlerClass = MySentinelHotBlockExceptionHandler.class, blockHandler = "hotBlockExceptionHandle")
//热点参数,必须使用此注解,指定资源名
//注意使用此注解无法处理BlockExecption,会导致统一异常处理失效
public String testSentinelHotParam(@RequestParam String sentinelDesc) {
log.info("------ testSentinelHotParam 接口调用 ------ ");
return sentinelDesc;
}
//==========处理类
/**
* Created On : 26/11/2022.
* <p>
* Author : huayu
* <p>
* Description: 方式2 自定义热点参数限流处理异常并指定治理方法
*/
@Slf4j
public class MySentinelHotBlockExceptionHandler {
/**
* @param : [sentinelDesc, e]
* @return : java.lang.String
* @author : huayu
* @date : 26/11/2022
* @description : hotBlockExceptionHandle 方法 必须是 静态的 增加一个自定义处理方法,参数必须跟入口一致
*/
public static String hotBlockExceptionHandle(@RequestParam String sentinelDesc, BlockException e) {
//记录异常日志
log.warn("------ hotBlockExceptionHandle 规则Rule:{} ------", e.getRule());
return JSON.toJSONString(ResultBuildUtil.fail("9623", "热点参数限流"));
}
}
4.1.3 热点参数策略和规则(sentinelHotParam)
4.1.4 浏览器快速请求测试
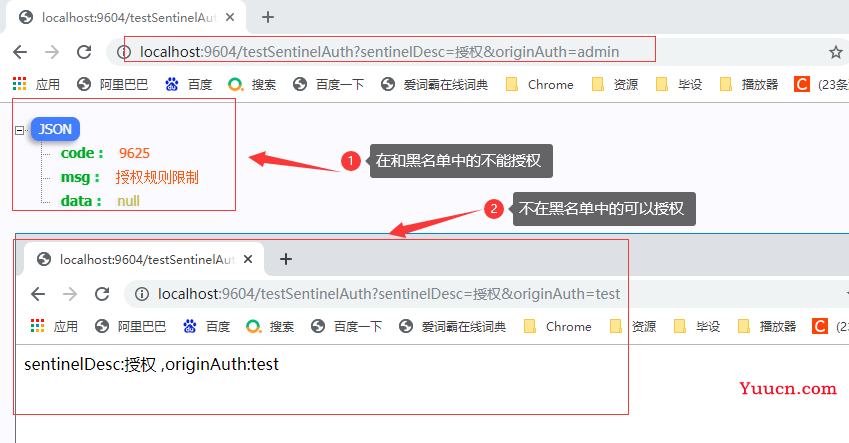
5、授权规则限流
根据调用来源来判断该次请求是否允许放行,这时候可以使用 Sentinel 的来源访问控制的功能。
来源访问控制根据资源的请求来源(origin)限制资源是否通过:
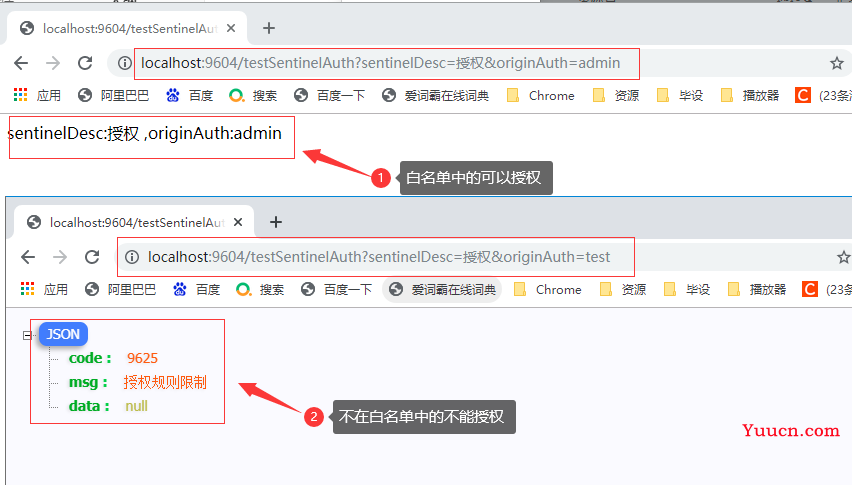
- 若配置白名单,则只有请求来源位于白名单内时才可通过;
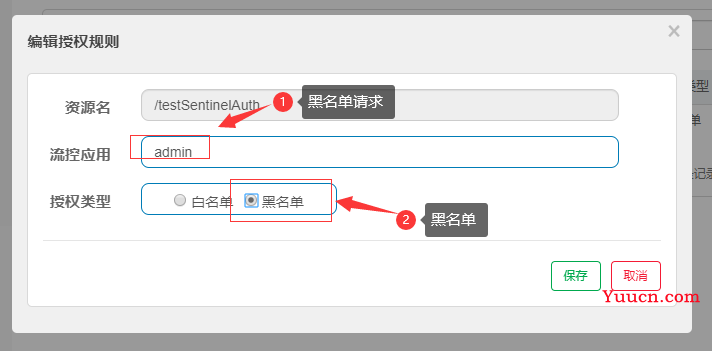
- 若配置黑名单,则请求来源位于黑名单时不通过,其余的请求通过。
配置项:
- 资源名resource,即限流规则的作用对象
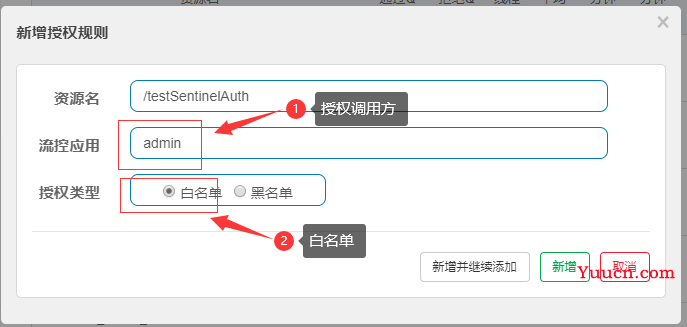
- 流控应用limitApp,对应的黑名单/白名单,不同 origin 用 , 分隔,如 appA,appB
- Sentinel提供了 RequestOriginParser 接口来处理来源
- 只要Sentinel保护的接口资源被访问,Sentinel就会调用 RequestOriginParser 的实现类去解析访问来源。
- 限制模式strategy,AUTHORITY_WHITE 为白名单模式,AUTHORITY_BLACK 为黑名单模式,默认为白名单模式
5.1 自定义来源处理规则
/**
* Created On : 26/11/2022.
* <p>
* Author : huayu
* <p>
* Description: 自定义授权规则解析 来源 处理类
*/
@Component
public class MySentinelAuthRequestOriginParser implements RequestOriginParser {
@Override
public String parseOrigin(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest) {
// TODO 实际应用场景中,可以根据请求来源ip,进行ip限制
//模拟,通过请求参数中,是否携带了自定义的来源参数OriginAuth
//根据授权规则中的流控应用规则指定的参数列表,限制是否可以访问
//授权规则,指定白名单,就代表请求携带的参数OriginAuth,参数值必须是在流控应用指定的参数列表中,才可以访问,否者不允许
//黑名单相反
return httpServletRequest.getParameter("originAuth");
}
}
5.2 模拟授权请求
/**
* @param : [sentinelDesc]
* @return : java.lang.String
* @author : huayu
* @date : 26/11/2022
* @description : 测试 Sentinel-授权
*/
@GetMapping("testSentinelAuth")
public String testSentinelAuth(@RequestParam String sentinelDesc,
@RequestParam String originAuth) {
log.info("------ testSentinelHotParam 接口调用 ------ ");
return "sentinelDesc:" + sentinelDesc + "\n,originAuth:" + originAuth;
}
5.3 白名单
5.3.1 配置白名单
5.3.2 测试
5.4黑名单
5.4.1 配置黑名单
5.4.2 测试
6、系统规则限流
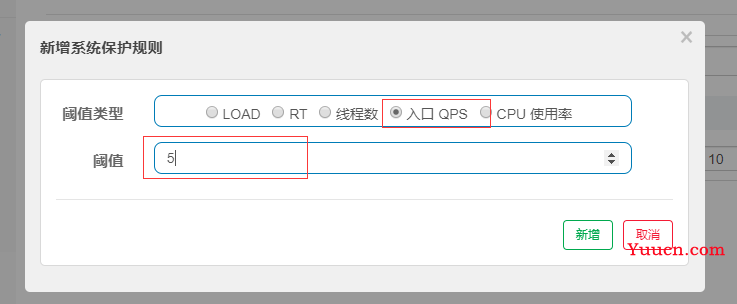
系统保护规则是从应用级别的入口流量进行控制,从单台机器的总体 Load、RT、入口 QPS 、CPU使用
率和线程数五个维度监控应用数据,让系统尽可能跑在最大吞吐量的同时保证系统整体的稳定性。系统
保护规则是应用整体维度的,而不是资源维度的,并且仅对入口流量 (进入应用的流量) 生效。
- Load 自适应(仅对 Linux/Unixlike 机器生效):系统的 load1 作为启发指标,进行自适应系统保护。当系统load1 超过设定的启发值,且系统当前的并发线程数超过估算的系统容量时才会触发系统保护。系统容量由系统的 maxQps * minRt 估算得出。设定参考值一般是 CPU cores * 2.5。
- CPU usage(1.5.0+ 版本):当系统 CPU 使用率超过阈值即触发系统保护(取值范围 0.0 - 1.0),比较灵敏。
- 平均 RT:当单台机器上所有入口流量的平均 RT 达到阈值即触发系统保护,单位是毫秒。
- 并发线程数:当单台机器上所有入口流量的并发线程数达到阈值即触发系统保护。
- 入口 QPS:当单台机器上所有入口流量的 QPS 达到阈值即触发系统保护
6.1 模拟系统限流请求
/**
* @param : [sentinelDesc]
* @return : java.lang.String
* @author : huayu
* @date : 26/11/2022
* @description : 测试 Sentinel-系统
* //设置一个, 全部请求都受限制
*/
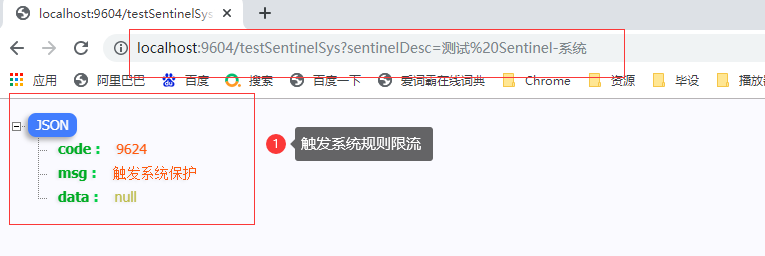
@GetMapping("testSentinelSys")
public String testSentinelSys(@RequestParam String sentinelDesc) {
log.info("------ testSentinelHotParam 接口调用 ------ ");
return "sentinelDesc:" + sentinelDesc;
}
6.2 系统规则配置
6.3 压测配置
6.4 浏览器测试
7、Sentinel 规则持久化
Dashboard控制台来为每个Sentinel客户端设置各种各样的规则,但是这里有一个问题,就是这些规则默认是存放在内存中,每次微服务重新启动,设置的各种规则都会消失。
7.1 方式1:本地文件(测试,线上不推荐)
本地文件数据源会定时轮询文件的变更,读取规则。这样我们既可以在应用本地直接修改文件来更新规则,也可以通过 Sentinel 控制台推送规则。
原理:首先 Sentinel 控制台通过 API 将规则推送至客户端并更新到内存中,接着注册的写数据源会将新的规则保存到本地的文件中。
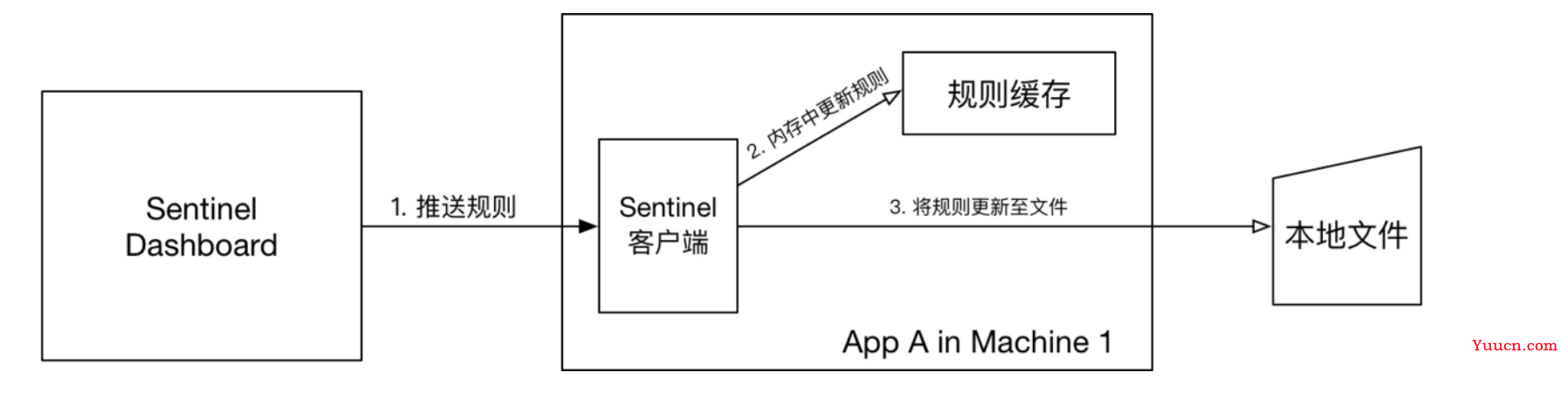
7.1.1 配置类
创建配置类: SentinelFilePersistence
点击查看代码
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.command.handler.ModifyParamFlowRulesCommandHandler;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.*;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.init.InitFunc;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.authority.AuthorityRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.authority.AuthorityRuleManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRuleManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRuleManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.param.ParamFlowRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.param.ParamFlowRuleManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemRuleManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.transport.util.WritableDataSourceRegistry;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.TypeReference;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Created On : 26/11/2022.
* <p>
* Author : huayu
* <p>
* Description: MySentinelRulePersistenceDunc
*/
public class MySentinelRulePersistencefunc implements InitFunc{
// String ruleDir = System.getProperty("user.home") + "/sentinel/rules/";
//填写 规则存放的绝对路径
String ruleDir = "D:/KEGONGCHANG/DaiMa/IDEA/KH96/SpringCloud/springcloud-alibaba-96/kgcmall96-sentinel/sentinel/rules/";
// String ruleDir = "/kgcmall96-sentinel/sentinel/rules/";
String flowRulePath = ruleDir + "/flow-rule.json";
String degradeRulePath = ruleDir + "/degrade-rule.json";
String systemRulePath = ruleDir + "/system-rule.json";
String authorityRulePath = ruleDir + "/authority-rule.json";
String paramFlowRulePath = ruleDir + "/param-flow-rule.json";
@Override
public void init() throws Exception {
// 创建规则存放目录
this.mkdirIfNotExits(ruleDir);
// 创建规则存放文件
this.createFileIfNotExits(flowRulePath);
this.createFileIfNotExits(degradeRulePath);
this.createFileIfNotExits(systemRulePath);
this.createFileIfNotExits(authorityRulePath);
this.createFileIfNotExits(paramFlowRulePath);
// 注册一个可读数据源,用来定时读取本地的json文件,更新到规则缓存中
// 流控规则
ReadableDataSource<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRuleRDS =
new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(flowRulePath, flowRuleListParser);
// 将可读数据源注册至FlowRuleManager,这样当规则文件发生变化时,就会更新规则到内存
FlowRuleManager.register2Property(flowRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource<List<FlowRule>> flowRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
flowRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
// 将可写数据源注册至transport模块的WritableDataSourceRegistry中
// 这样收到控制台推送的规则时,Sentinel会先更新到内存,然后将规则写入到文件中
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerFlowDataSource(flowRuleWDS);
// 降级规则
ReadableDataSource<String, List<DegradeRule>> degradeRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
degradeRulePath,
degradeRuleListParser
);
DegradeRuleManager.register2Property(degradeRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource<List<DegradeRule>> degradeRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
degradeRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerDegradeDataSource(degradeRuleWDS);
// 系统规则
ReadableDataSource<String, List<SystemRule>> systemRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
systemRulePath,
systemRuleListParser
);
SystemRuleManager.register2Property(systemRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource<List<SystemRule>> systemRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
systemRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerSystemDataSource(systemRuleWDS);
// 授权规则
ReadableDataSource<String, List<AuthorityRule>> authorityRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
authorityRulePath,
authorityRuleListParser
);
AuthorityRuleManager.register2Property(authorityRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource<List<AuthorityRule>> authorityRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
authorityRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerAuthorityDataSource(authorityRuleWDS);
// 热点参数规则
ReadableDataSource<String, List<ParamFlowRule>> paramFlowRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
paramFlowRulePath,
paramFlowRuleListParser
);
ParamFlowRuleManager.register2Property(paramFlowRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource<List<ParamFlowRule>> paramFlowRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
paramFlowRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
ModifyParamFlowRulesCommandHandler.setWritableDataSource(paramFlowRuleWDS);
}
private Converter<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference<List<FlowRule>>() {
}
);
private Converter<String, List<DegradeRule>> degradeRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference<List<DegradeRule>>() {
}
);
private Converter<String, List<SystemRule>> systemRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference<List<SystemRule>>() {
}
);
private Converter<String, List<AuthorityRule>> authorityRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference<List<AuthorityRule>>() {
}
);
private Converter<String, List<ParamFlowRule>> paramFlowRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference<List<ParamFlowRule>>() {
}
);
private void mkdirIfNotExits(String filePath) throws IOException {
File file = new File(filePath);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.mkdirs();
}
}
private void createFileIfNotExits(String filePath) throws IOException {
File file = new File(filePath);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
}
private <T> String encodeJson(T t) {
return JSON.toJSONString(t);
}
}
7.1.2 InitFunc 文件
在resources文件下创建META-INF/services文件夹;
创建文档com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.init.InitFunc,文档名就是配置类实现接口的全类名;
在文件中添加第一步配置类的全类名即可;
测试:启动服务,当访问系统规则限流接口,自动创建目录和文件,添加规则后,重启服务,刚进来,之前的配置看不到,必须先访问对应的入口才可以,要注意
com.kgc.scda.config.MySentinelRulePersistencefunc
8、Openfeign 远程调用
8.1 依赖
<!-- openfeign 远程调用 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
8.2 配置
# 整合Sentinel 和OpenFeign ,默认关闭
feign:
sentinel:
enabled: true #开启
8.3 注解
著启动类: @EnableFeignClients
接口:@FeignClient(value = "服务名")
8.4 测试 (与单独使用Openfeign一样不在赘述)
9、GateWay 服务网关
9.1 依赖
<!-- Gatway 网关会和springMvc冲突,不能添加web依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- gateway 依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
9.2 配置
# 端口
server:
port: 9606
# 服务名
spring:
application:
name: kgcmall-gatway
cloud:
#nacos 配置
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
# 网关配置
gateway:
routes: # 路由,是list集合,可以配置多个路由
#product模块
- id: kh96_route_first # 当前route路由的唯一标识,不能重复
#uri: http://localhost:9602 # 路由转发的目标资源地址,不支持多负载调用,不利于扩展,不推荐
uri: lb://kgcmall96-prod # lb 从nacos注册中心的服务列表中,根据指定的服务名,调用服务,推荐用法
predicates: # 指定路由断言配置,支持多个断言,只要断言成功(满足路由转发条件),才会执行转发到目标资源地址访问
- Path=/prod-gateway/** # 指定path路径断言,必须满足请求地址是/prod-gateway开始,才会执行路由转发
filters: # 指定路由过滤配置,支持多个过滤器,在断言成功,执行路由转发时,对请求和响应数据进行过滤处理
- StripPrefix=1 # 在请求断言成功后,执行路由转发时,自动去除第一层的访问路径/prod-gateway
#user模块
- id: kh96_route_second
uri: lb://kgcmall96-user
predicates:
- Path=/user-gateway/**
filters:
- StripPrefix=1
9.3 测试
9.3.1 nacos

9.3.2 请求测试
9.3.2.1 通过gateway网关调用prod模块

9.3.2.1 通过gateway网关调用user模块
