Spring管理Bean-IOC-04
3.基于注解配置bean
3.1基本使用
3.1.1说明
基本说明:基于注解的方式配置bean,主要是项目开发中的组件,比如Controller,Service和Dao
组件的注解形式有:
-
@Component表示当前注解标识的是一个组件 -
@Controller表示当前注解标识的是一个控制器,通常用于Servlet -
@Service表示当前注解标识的是一个处理业务逻辑的类,通常用于Service类 -
@Repository表示当前注解标识的是一个持久化层的类,通常用于Dao类
3.1.2快速入门
应用案例:使用注解的方式来配置Controller /Service/ Repository/ Component
代码实现:
1.使用注解方式,需要引入spring-aop.jar包,该jar包位于spring/lib下
2.创建 UserAction.java、UserService.java、UserDao.java、MyComponent.java
UserDao:
package com.li.component;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
* 使用 @Repository 表示该类是一个Repository,一个持久化层的类/对象
*/
@Repository
public class UserDao {
}
UserService:
package com.li.component;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
* @Service 标识该类是一个Service类/对象
*/
@Service
public class UserService {
}
UserAction:
package com.li.component;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
* @Controller 标识该类是一个控制器Controller,通常该类是一个Servlet
*/
@Controller
public class UserAction {
}
MyComponent:
package com.li.component;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
* @Component 用于标识该类是一个组件,是一个通用的注解
*/
@Component
public class MyComponent {
}
上面我们在类中添加了注解,但是还没有在配置文件中指定容器要扫描哪个包下的注解类
3.配置beans04.xml:
<!--配置容器要扫描的包:
1.component-scan 表示对指定的包下的类进行扫描,并创建对象到容器
2.base-package 指定要扫描的包
3.下面整个配置的含义是:当spring容器创建/初始化时,会扫描 com.li.component 包下
的所有含有四种注解(Controller/Service/Repository/Component)的类,
并将其实例化,生成对象,放入到ioc容器
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.li.component"/>
注意引入context命名空间
4.测试
//通过注解来配置Bean
@Test
public void setBeanByAnnotation() {
ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans04.xml");
System.out.println("ok");
}
在 System.out.println("ok");旁打上断点,点击debug。
查看ioc对象-->beanFactory-->singletoObjects-->table的属性。因为table属性有很多null值,为了显示方便,这里配置了IDEA不显示null值
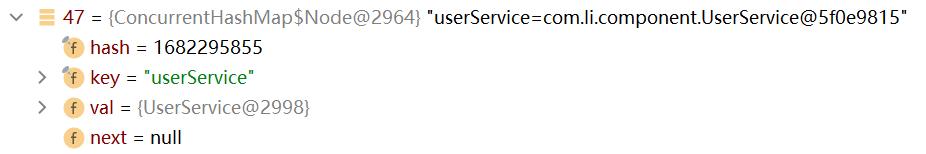
如下,spring容器中成功创建了四个对象,并且在默认情况下,按照注解方式进行扫描创建的对象,它对应的id就是它的类名(首字母小写)
其他的对象是系统自带的

查看类型id(key)
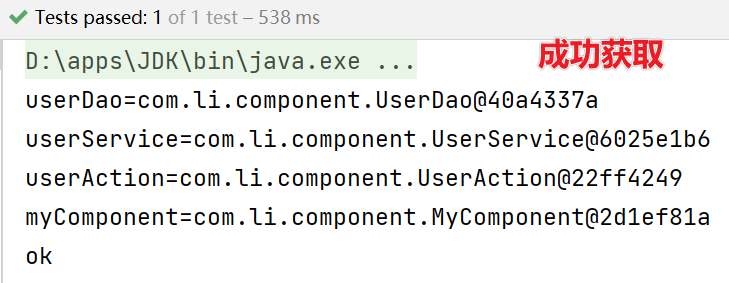
因为配置的这四个对象是单例对象,因此可以直接通过类的类型来获取:
因为spring在创建时赋予了默认id,也可以通过id来获取
//通过注解来配置Bean
@Test
public void setBeanByAnnotation() {
ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans04.xml");
UserDao userDao = ioc.getBean(UserDao.class);
UserService userService = ioc.getBean(UserService.class);
UserAction userAction = ioc.getBean(UserAction.class);
MyComponent myComponent = ioc.getBean(MyComponent.class);
System.out.println("userDao=" + userDao);
System.out.println("userService=" + userService);
System.out.println("userAction=" + userAction);
System.out.println("myComponent=" + myComponent);
System.out.println("ok");
}
3.1.3注意事项和细节
-
基于注解配置bean,需要导入spring-aop.jar包
-
必须在Spring配置文件中指定“自动扫描的包”,IOC容器才能够检测到当前项目中哪些类被标识了注解
(1)在配置时注意导入context名称空间
(2)指定扫描的包时,可以使用通配符,如:
com.li.component.*表示扫描com.li.component包下的类, 包括com.li.component包下的子包(递归扫描) -
Spring的IOC容器不能检测一个使用了@Controller注解的类到底是不是一个真正的控制器。注解的名称只是用于程序员自己识别当前标识的是什么组件。其他的注解@Service、@Reposity 也是一样。
也就是说,Spring的容器只要检测到注解就会生成对象,但是这个注解的含义spring不会识别,只是给程序员方便区分的
如果你只在spring容器上用,@Controller、@Service、@Reposity基本是等价的;如果你用在springmvc上面,它们是有区别的:彻底弄懂@Controller 、@Service、@Component
-
配置只扫描满足要求的类:
如下面的resource-pattern="User*.class",表示扫描指定包下以User开头的类
<context:component-scan base-package="com.li.component" resource-pattern="User*.class" />一般来说,想要扫描某个类只需要写上注解,不想扫描的类就不会写注解,因此上面这种写法不常使用
-
配置排除扫描的类:
如果我们希望排除某个包/子包下的某种类型的注解,可以通过exclude-filter来指定
(1)context:exclude-filter 指定要排除哪些类
(2)type 指定排除方式(annotation 表示通过注解来排除)
(3)expression 指定要排除的注解的全路径
下面的配置表示,在扫描com.li.component包下注解的类时,排除以@Service注解的类
<context:component-scan base-package="com.li.component" > <!-- 排除哪些类, 以 annotaion注解为例(通过注解来排除) --> <context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Service"/> </context> -
自定义规则指定扫描哪些注解类:
<!--如果我们希望通过自己的规则,来扫描包/子包下的某些注解类,可以通过include-filter 1. use-default-filters="false": 表示不使用默认的过滤/扫描机制 2. context:include-filter: 表示只是扫描指定的注解的类 3. type="annotation" 表示按照注解方式来扫描 4. expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller" 指定要扫描的注解的全类路径 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.li.component" use-default-filters="false"> <context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Service"/> <context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/> </context:component-scan> -
在默认情况下,注解标识的类创建对象后,在容器中它默认对应的id就是它的类名(首字母小写)
-
也可以使用注解的value属性指定 id 值,并且 value 可以省略:


3.2手动开发-简单的Spring基于注解配置的程序
3.2.1需求说明
自己写一个简单的Spring容器,通过读取类的注解(@Component、@Controller、@Service、@Repository),将对象注入到IOC容器。即不使用Spring原生框架,我们自己使用IO+Annotation+反射+集合实现,加深对Spring注解方式开发的理解。
3.2.2思路分析
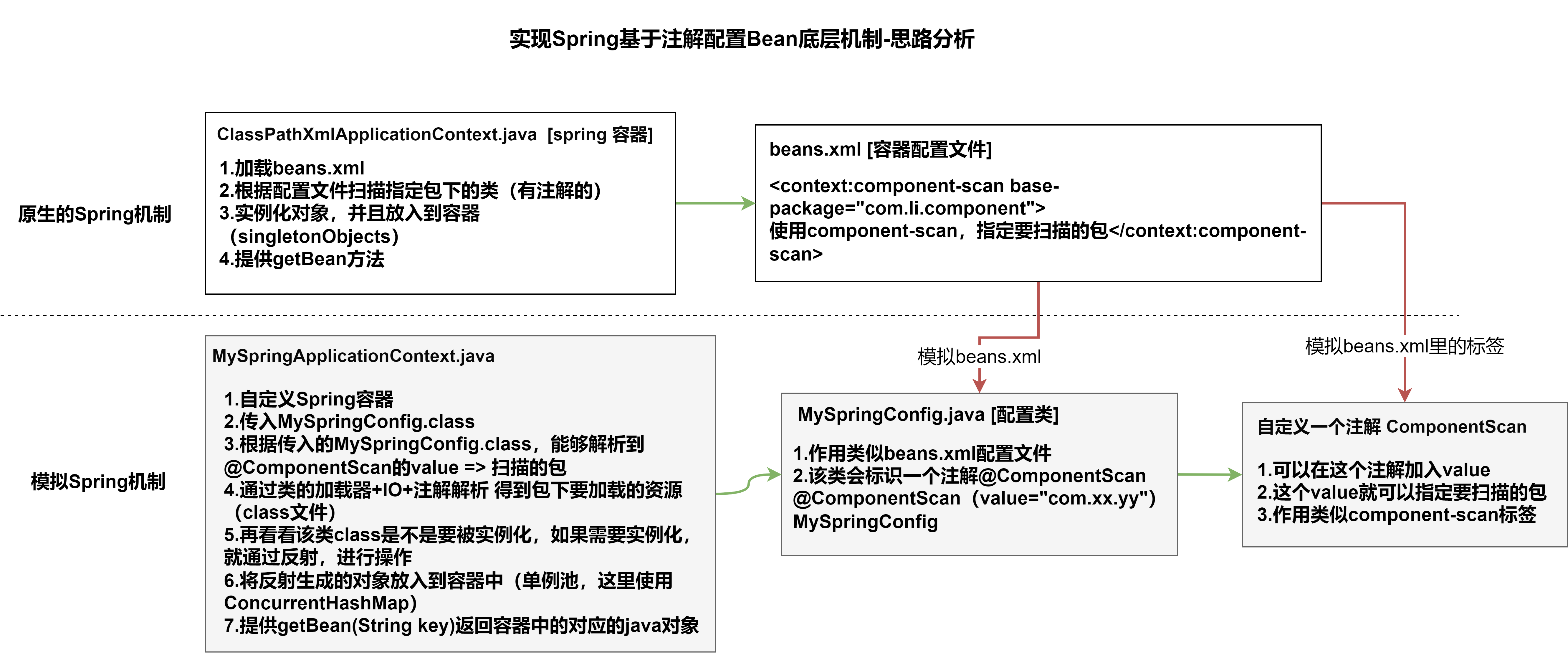
3.2.3代码实现
步骤一.搭建基本结构并获取扫描包
1.ComponentScan注解
package com.li.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
* 模仿spring原生注解,自定义一个注解
* 1. @Target(ElementType.TYPE) 指定ComponentScan注解可以修饰TYPE元素
* 2. @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 指定ComponentScan注解 的保留范围
* 3. String value() default ""; 表示 ComponentScan 可以传入一个value值
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface ComponentScan {
String value() default "";
}
2.MySpringConfig配置类
package com.li.annotation;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
* 这是一个配置类,作用类似我们原生spring的容器配置文件beans.xml
*/
@ComponentScan(value = "com.li.component")
public class MySpringConfig {
}
未完。。。