链表:插入快,查询慢,存储不连续
分为单链表,双链表和循环链表
在链表中使用虚拟头结点,可以减少增删改查中对头结点的特殊处理
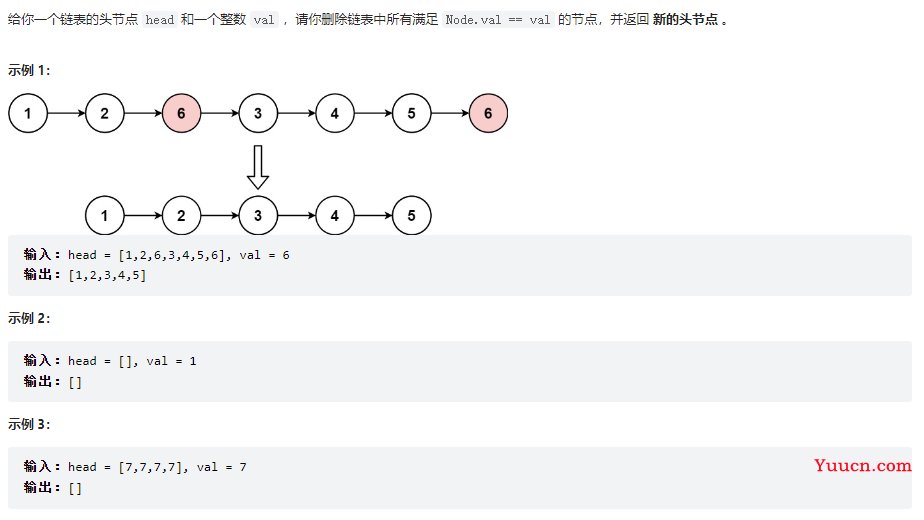
移除链表元素
203
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
// 时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(1)
if(head == null){//空链表的情况
return head;
}
while(head != null && head.val == val){//头结点为val的情况
head = head.next;
}
ListNode temp = head;
while(temp != null && temp.next != null){
while(temp != null && temp.next != null && temp.next.val == val){
if(temp.next.next != null){
temp.next = temp.next.next;
}else{//最后一个节点为val的情况
temp.next = null;
}
}
temp = temp.next;
}
return head;
}
}
707、设计链表

class MyLinkedList {
int size;
ListNode head;
ListNode tail;
// 初始化链表,构建虚拟的头结点和尾节点
public MyLinkedList() {
size = 0;
head = new ListNode(0);
tail = new ListNode(0);
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
public int get(int index) {
ListNode cur = head;
if(index > size - 1 || index < 0){
return -1;
}
while(index >= 0){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur.val;
}
public void addAtHead(int val) {
addAtIndex(0,val);
}
public void addAtTail(int val) {
addAtIndex(size,val);
}
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if(index > size){
return;
}
if(index < 0 ){
index = 0;
}
size++;
ListNode temp = new ListNode(val);
ListNode cur = head;
while(index > 0){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
temp.next = cur.next;
cur.next = temp;
temp.prev = cur;
}
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
ListNode cur = head;
if(index > size - 1 || index < 0){
return;
}
while(index > 0){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
cur.next = cur.next.next;
size--;
}
}
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode prev;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
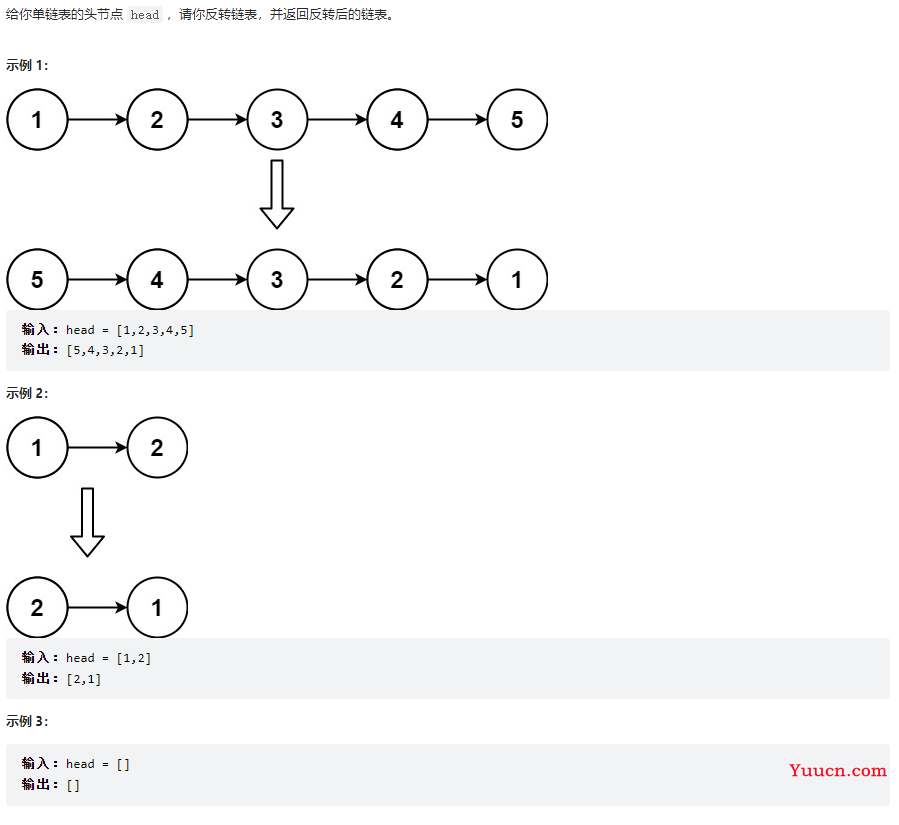
反转链表
206
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// 方法一:在头结点不断插入
// if(head == null){
// return head;//空节点不需要反转
// }
// ListNode temp = head.next;//临时节点前移一位
// head.next = null;//代反转链表的头结点拆出来
// ListNode newHead = head;//待反转链表的头结点赋给新的链表
// while(temp != null){
// head = temp;//找出待反转链表的新头结点
// temp = temp.next;//临时节点前移一位
// head.next = null;//待反转链表的新头拆出来
// head.next = newHead;//待反转链表的心头指向新的链表
// newHead = head;//得到新的链表的新头
// }
// return newHead;
// 方法二:压栈,利用栈的先入后出
// if(head == null){
// return head;
// }
// Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<>();
// ListNode temp = head;
// while(head != null){
// temp = head.next;
// head.next = null;
// stack.push(head);
// head = temp;
// }
// ListNode newHead = new ListNode();
// temp = newHead;
// while(!stack.isEmpty()){
// temp.next = stack.pop();
// temp = temp.next;
// }
// return newHead.next;
// 方法三:递归
return reverse(null, head);
// 方法四:从后往前递归
// if(head == null){
// return null;
// }
// if(head.next == null){
// return head;
// }
// ListNode newHead = reverseList(head.next);
// head.next.next = head;
// head.next = null;
// return newHead;
}
public ListNode reverse(ListNode pre, ListNode cur){
if(cur == null){
return pre;
}
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
return reverse(cur,temp);
}
}
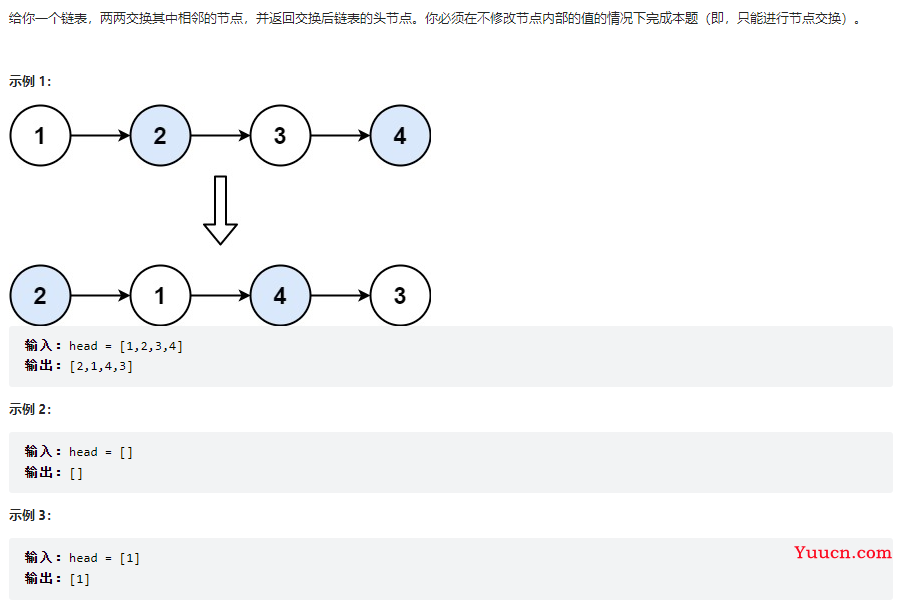
两两交换链表中的节点
24
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
// 方法一:从前往后进行迭代
// if(head == null){
// return null;
// }
// if(head.next == null){
// return head;
// }
// ListNode temp = head.next;//依次记录偶数节点的位置
// head.next = head.next.next;//交换相邻的节点
// temp.next = head;
// temp.next.next = swapPairs(temp.next.next);//迭代交换下一个相邻的节点
// return temp;
// 方法二:双指针
if(head == null){
return null;
}
if(head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode temp = head.next;
ListNode pre = head.next;//记录新的头结点
while(temp != null){
head.next = head.next.next;//交换相邻的节点
temp.next = head;
if(head.next == null || head.next.next == null){
break;
}else{
head = head.next;//指向下一个相邻节点的奇数节点
temp.next.next = temp.next.next.next;//上一个相邻节点的偶数节点指向下一个节点的偶数节点
temp = head.next;//下一个相邻节点的偶数节点
}
}
return pre;
}
}
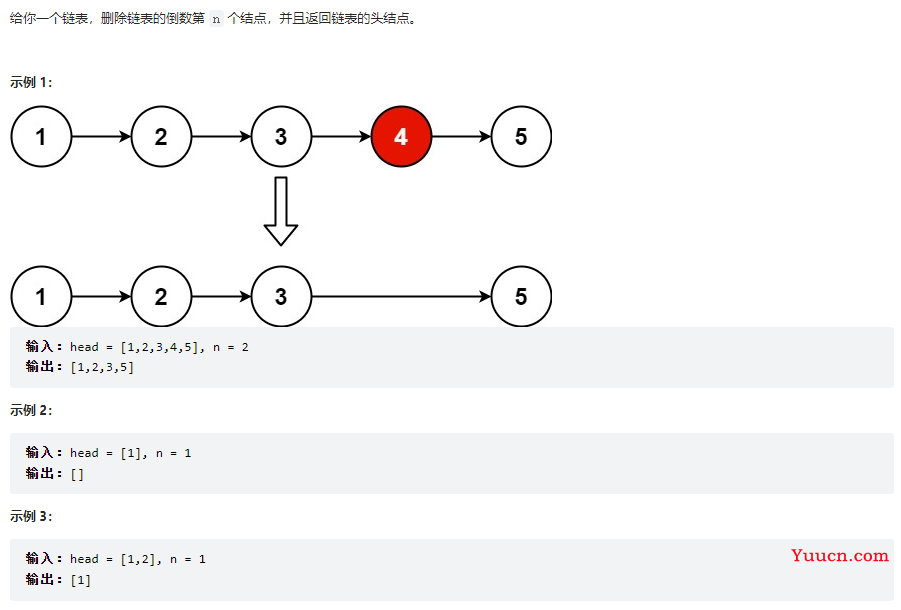
删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
19
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
// 方法一:快慢指针,返回头结点说明head的头结点不能动,所以把链表的地址赋给另外一个对象
// 添加虚拟头结点,方便操作。比如需要删除的是头结点的时候不需要单独考虑这种特殊情况
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode();
dummyHead.next = head;
ListNode cur = dummyHead;
ListNode temp = dummyHead;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
temp = temp.next;
}
while(temp.next != null){
cur = cur.next;
temp = temp.next;
}
cur.next = cur.next.next;
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
链表相交
02.07
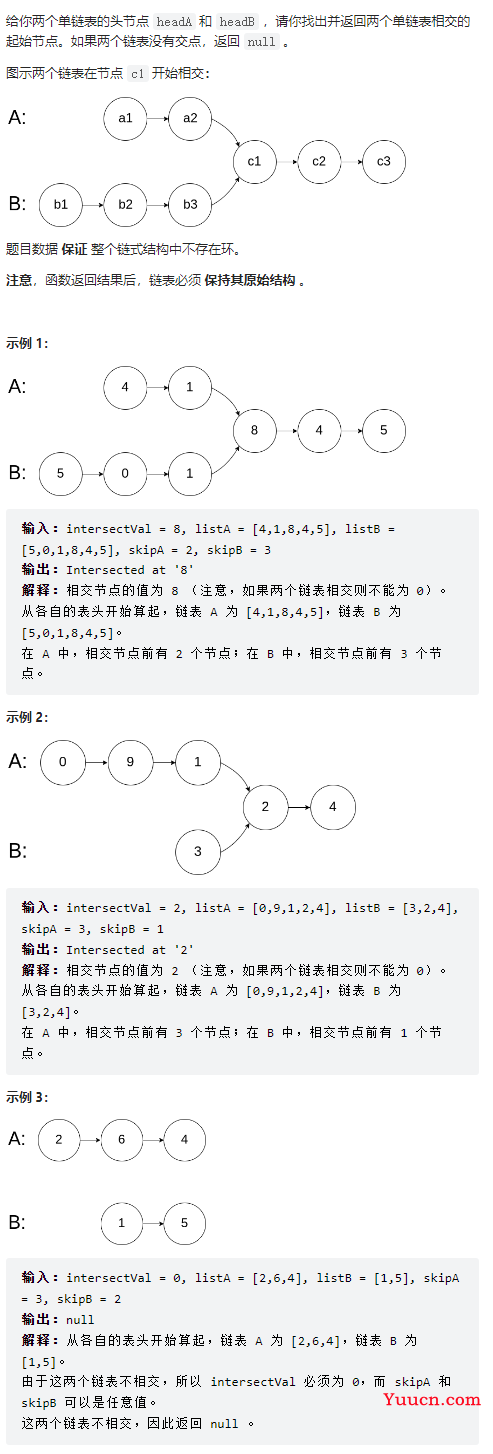
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if(headA == null || headB == null){
return null;
}
ListNode dummyHeadA = headA;
int countA = 0;
int countB = 0;
ListNode dummyHeadB = headB;
while(dummyHeadA.next != null){
dummyHeadA = dummyHeadA.next;
countA++;
}
while(dummyHeadB.next != null){
dummyHeadB = dummyHeadB.next;
countB++;
}
if(dummyHeadA != dummyHeadB){
return null;//尾节点不相交则说明不相交
}
dummyHeadA = headA;
dummyHeadB = headB;
int index = (countA - countB) > 0 ? (countA - countB) : -(countA - countB);//两个链表的长度差
for(int i = 0; i < index; i++){//让较长的链表先移动index位
if((countA - countB) > 0){
dummyHeadA = dummyHeadA.next;
}else{
dummyHeadB = dummyHeadB.next;
}
}
while(dummyHeadA != dummyHeadB){//两个链表逐次向前移动,找出相交的第一个节点
dummyHeadA = dummyHeadA.next;
dummyHeadB = dummyHeadB.next;
}
return dummyHeadA;
}
}
环形链表 II
142
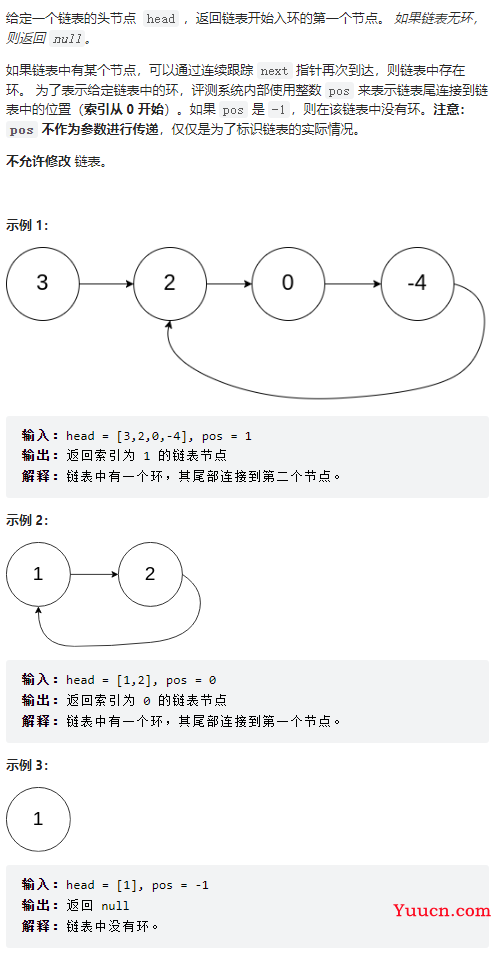
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
// O(1)空间的要求,所以不能用递归
if(head == null){
return null;
}
ListNode slowList = head;
ListNode fastList = head;
boolean flag = false;//判断是否有环
while(fastList != null && fastList.next != null){
fastList = fastList.next.next;
slowList = slowList.next;
if(fastList == slowList){
flag = true;//有环
break;
}
}
if(!flag){//没有环
return null;
}else{//有环,找出环的入口,也就是索引的位置
slowList = head;
while(fastList != slowList){
fastList = fastList.next;
slowList = slowList.next;
}
return slowList;
}
}
}
哈希表:也叫散列表,用来快速判断一个元素是否出现在集合中,实际上是用空间换时间
有效的字母异位词
242
class Solution {
public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) {
// 方法一:使用hashmap
// if(s.length() != t.length()){
// return false;
// }
// HashMap<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
// for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
// map.put(s.charAt(i), (map.getOrDefault(s.charAt(i), 0) + 1));
// }
// for(int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++){
// if(map.containsKey(t.charAt(i))){
// if(map.get(t.charAt(i)) == 1){
// map.remove(t.charAt(i));
// }else{
// map.put(t.charAt(i), (map.get(t.charAt(i)) - 1));
// }
// }else{
// return false;
// }
// }
// return true;
// 方法二:用数组来构造哈希表,字典解法
if(s.length() != t.length()){
return false;
}
int[] arr = new int[26];
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
int index = s.charAt(i) - 'a';
arr[index] = arr[index] + 1;
}
for(int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++){
int index = t.charAt(i) - 'a';
if(arr[index] != 0){
arr[index] = arr[index] - 1;
}else{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
两个数组的交集
349
class Solution {
public int[] intersection(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
// 使用hashset,无序,且不能存储重复数据,符合题目要求
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
HashSet<Integer> record = new HashSet<>();
for(int i = 0; i < nums1.length; i++){
set.add(nums1[i]);
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums2.length; i++){
if(set.remove(nums2[i])){
record.add(nums2[i]);
}
}
return record.stream().mapToInt(x -> x).toArray();
}
}
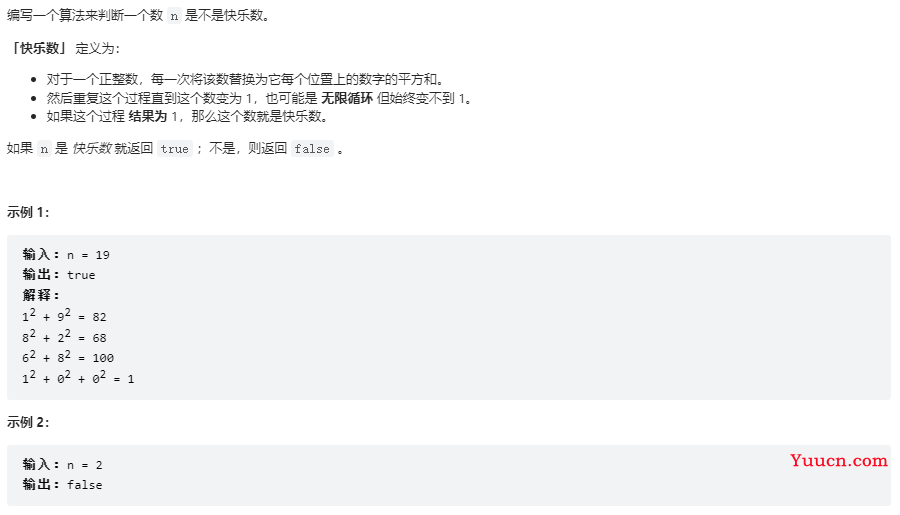
快乐数
202
class Solution {
public boolean isHappy(int n) {
// 使用hashset,当有重复的数字出现时,说明开始重复,这个数不是快乐数
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet();
int sum = 0;
while(true){
while(n != 0){
sum = sum + (n%10)*(n%10);
n = n / 10;
}
if(sum == 1){
return true;
}
if(!set.add(sum)){
return false;
}
n = sum;
sum = 0;
}
}
}
两数之和
1

class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
// 方法一:暴力解法
// int[] arr = new int[2];
// for(int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++){
// for(int j = i + 1 ; j < nums.length; j++){
// if(target == (nums[i] + nums[j])){
// return new int[]{i,j};
// }
// }
// }
// return new int[0];
// 方法二:HashMap
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
int find = target - nums[i];
if(map.containsKey(find)){
return new int[]{i, map.get(find)};
}else{
map.put(nums[i],i);
}
}
return null;
}
}
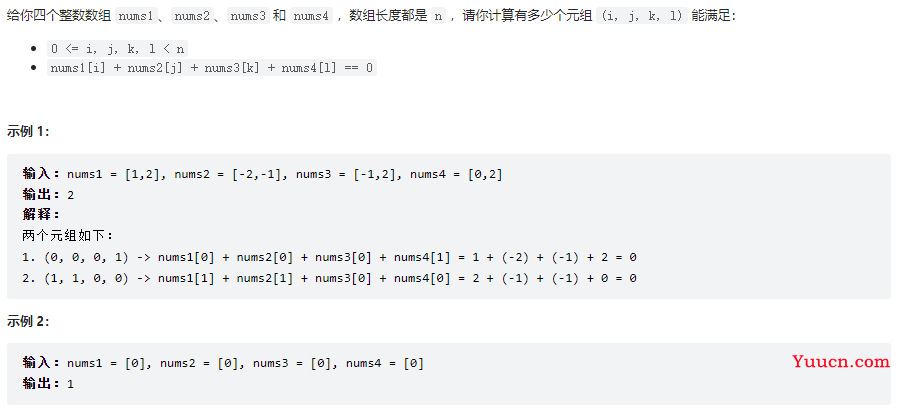
四数相加 II
454
class Solution {
public int fourSumCount(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int[] nums3, int[] nums4) {
// 四个数,用哈希表,参考代码随想录
HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int count = 0;
for(int i : nums1){
for(int j : nums2){
int temp = i + j;
if(map.containsKey(temp)){
map.put(temp, map.get(temp) + 1);
}else{
map.put(temp, 1);
}
}
}
for(int i : nums3){
for(int j : nums4){
int temp = 0- (i + j);
if(map.containsKey(temp)){
count += map.get(temp);
}
}
}
return count;
}
}
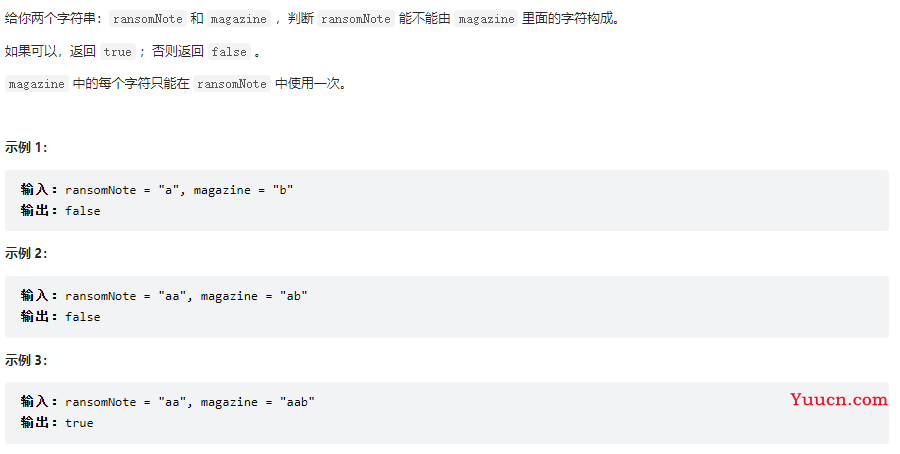
赎金信
383
class Solution {
public boolean canConstruct(String ransomNote, String magazine) {
// 方法一;hashmap
// HashMap<Character,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
// char temp;
// for(int i = 0; i < ransomNote.length(); i++){
// temp = ransomNote.charAt(i);
// if(map.containsKey(temp)){
// map.put(temp, map.get(temp) + 1);
// }else{
// map.put(temp, 1);
// }
// }
// for(int i = 0; i < magazine.length(); i++){
// temp = magazine.charAt(i);
// if(map.containsKey(temp)){
// if(map.get(temp) == 1){
// map.remove(temp);
// }else{
// map.put(temp, map.get(temp) - 1);
// }
// }
// }
// if(map.isEmpty()){
// return true;
// }else{
// return false;
// }
// 方法二:数组在哈希法的应用,比起方法一更加节省空间,因为字符串只有小写的英文字母组成
int[] arr = new int[26];
int temp;
for(int i = 0; i < ransomNote.length(); i++){
temp = ransomNote.charAt(i) - 'a';
arr[temp] = arr[temp] + 1;
}
for(int i = 0; i < magazine.length(); i++){
temp = magazine.charAt(i) - 'a';
if(arr[temp] != 0){
arr[temp] = arr[temp] - 1;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
if(arr[i] != 0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
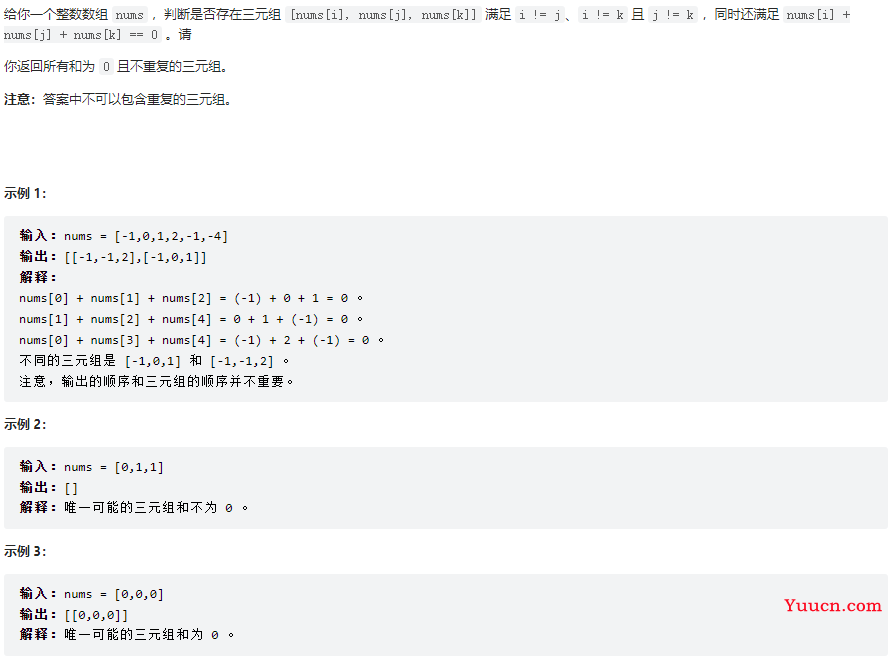
三数之和
15
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
// 如果考虑使用跟四数之和类似的求解方式,由于三元组是在同一个数组中寻找的,且要求不重复的三元组,因此求解会比较复杂
// 题目要求返回的是三元组的具体数值,而不是索引值,因此可以考虑使用双指针
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
for(int i=0;i<nums.length-1;i++){
for(int j=0;j<nums.length-1-i;j++){
if(nums[j]>nums[j+1]){
int temp = nums[j+1];
nums[j+1] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}
}
}
int leftNode;
int rightNode;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if (nums[i] > 0) {
return list;
}
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
leftNode = i + 1;
rightNode = nums.length - 1;
while(leftNode < rightNode){
if((nums[i] + nums[leftNode] + nums[rightNode]) < 0){
leftNode++;
}else if((nums[i] + nums[leftNode] + nums[rightNode]) > 0){
rightNode--;
}else{
list.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[leftNode], nums[rightNode]));
while (rightNode > leftNode && nums[rightNode] == nums[rightNode - 1]) rightNode--;
while (rightNode > leftNode && nums[leftNode] == nums[leftNode + 1]) leftNode++;
rightNode--;
leftNode++;
}
}
}
return list;
}
}
四数之和
18
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
for(int i=0;i<nums.length-1;i++){
for(int j=0;j<nums.length-1-i;j++){
if(nums[j]>nums[j+1]){
int temp = nums[j+1];
nums[j+1] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if (nums[i] > 0 && nums[i] > target) {
return list;
}
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]){
continue;
}
for(int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++){
if(j > i + 1 && nums[j] == nums[j - 1]){
continue;
}
int left = j + 1;
int right = nums.length - 1;
while(left < right){
long sum = (long)(nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[left] + nums[right]);
if(sum > target){
right--;
}else if(sum < target){
left++;
}else{
list.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i] , nums[j] , nums[left] , nums[right]));
while(left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]){
left++;
}
while(left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]){
right--;
}
left++;
right--;
}
}
}
}
return list;
}
}