验证以及国际化
1.概述
(1)概述
- 对于输入的数据(比如表单数据),进行必要的验证,并给出相应的提示信息
- 对于验证表单数据,SpringMVC 提供了很多使用的注解,这些注解由 JSR 303验证框架提供。
(2)JSR 303 验证框架
- JSR 303 是 Java 为 Bean 数据合法性校验提供的标准框架,它已经包含在 JavaEE 中
- JSR 303 通过在 Bean 属性上标注类似于 @NotNull、@Max 等标注的注解指定校验规则,并通过标准的验证接口对 Bean 进行验证
- JSR 303 提供的基本验证注解有:
| 注解 | 功能说明 |
|---|---|
| @Null | 被注释的元素必须为null |
| @NotNull | 被注释的元素不能为null |
| @AssertTrue | 被注释的元素必须为true |
| @AssertFalse | 被注释的元素必须为false |
| @Min(value) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值 |
| @Max(value) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值 |
| @DecimalMin(value) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值 |
| @DecimalMax(value) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值 |
| @Size(max,min) | 被注释的元素的大小必须在指定的范围内 |
| @Digits(integer,fraction) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须在可接受的范围内 |
| @Past | 被注释的元素必须是一个过去的日期 |
| @Future | 被注释的元素必须是一个将来的日期 |
| @Pattern(value) | 被注释的元素必须符合指定的正则表达式 |
(3)Hibernate Validator 扩展注解
-
Hibernate Validator 和 Hibernate 没有关系,只是 JSR 303 实现的一个扩展
-
Hibernate Validator 是 JSR 303的一个参考实现,除支持所有标准的校验注解外,它还支持以下的扩展注解:
| 注解 | 功能说明 |
|---|---|
| 被注释的元素必须是电子邮件地址 | |
| @Length | 被注释的字符串的大小必须在指定的范围内 |
| @NotEmpty | 被注释的字符串必须非空 |
| @Range | 被注释的元素必须在合适的范围内 |
2.应用实例
需求说明
指定表单的数据格式,后端在接收到数据后,能够对数据进行校验,并给不符合格式的数据返回提示信息,显示在前端页面

2.1代码实现
(1)引入验证和国际化相关的jar包

(2)Monster.java,属性添加注解以验证格式
package com.li.web.datavalid.entity;
import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.Email;
import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.NotEmpty;
import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.Range;
import org.springframework.format.annotation.DateTimeFormat;
import org.springframework.format.annotation.NumberFormat;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Monster {
@NotEmpty
private Integer id;
@Email
private String email;
//表示接收到的age的值必须在1-100之间
@Range(min = 1, max = 100)
private Integer age;
//Asserts that the annotated string, collection,
// map or array is not {@code null} or empty.
@NotEmpty
private String name;
@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd")
private Date birthday;
@NumberFormat(pattern = "###,###.##")
private Float salary;
public Monster() {
}
public Monster(Integer id, String email, Integer age, String name, Date birthday, Float salary) {
this.id = id;
this.email = email;
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
this.birthday = birthday;
this.salary = salary;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public Float getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(Float salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Monster{" +
"id=" + id +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", birthday=" + birthday +
", salary=" + salary +
'}';
}
}
(3)MonsterHandler.java
package com.li.web.datavalid;
import com.li.web.datavalid.entity.Monster;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.validation.Errors;
import org.springframework.validation.ObjectError;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import javax.validation.Valid;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author 李
* @version 1.0
*/
@Controller
@Scope(value = "prototype")
public class MonsterHandler {
/**
* 1.SpringMVC可以将提交的数据,按照参数名和形参对象的属性名匹配,
* 然后直接封装到对象中[模型数据]
* 2.@Valid Monster monster 表示对monster接收的数据进行校验
* 3.校验的发生的时机:在SpringMVC底层反射调用目标方法时,会接收到http请求接收到的数据,
* 然后根据注解来进行验证。在验证过程中,如果出现了错误,就把错误信息填充到errors和 map中
* @param monster
* @param errors 表示如果校验出现了错误,会将校验的错误信息保存到errors中
* @param map map不但会保存monster对象,如果校验出现错误,也会将校验的错误信息放到map中
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/save", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String save(@Valid Monster monster, Errors errors, Map<String, Object> map) {
System.out.println("----monster----" + monster);
//为了查看验证的情况,输出map和errors
System.out.println("=======map=======");
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("key=" + entry.getKey() +
" value=" + entry.getValue());
System.out.println("--------");
}
System.out.println("=======errors=======");
for (ObjectError error : errors.getAllErrors()) {
System.out.println("error="+error);
}
return "datavalid/success";
}
}
(4)monster_addUI.jsp:
<%@taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>添加妖怪</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>添加妖怪</h3>
<form:form action="save" method="post" modelAttribute="monster">
妖怪id:<form:input path="id"/><br/><br/>
妖怪名字:<form:input path="name"/><br/><br/>
妖怪年龄:<form:input path="age"/><br/><br/>
妖怪生日:<form:input path="birthday"/> 要求以"yyyy-MM-dd"的格式<br/><br/>
妖怪工资:<form:input path="salary"/> 要求以"###,###.##"的格式<br/><br/>
电子邮件:<form:input path="email"/><br/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="添加妖怪"/>
</form:form>
</body>
</html>
(5)测试
提交的数据:年龄这里故意填写不符合格式的数据(1-100)
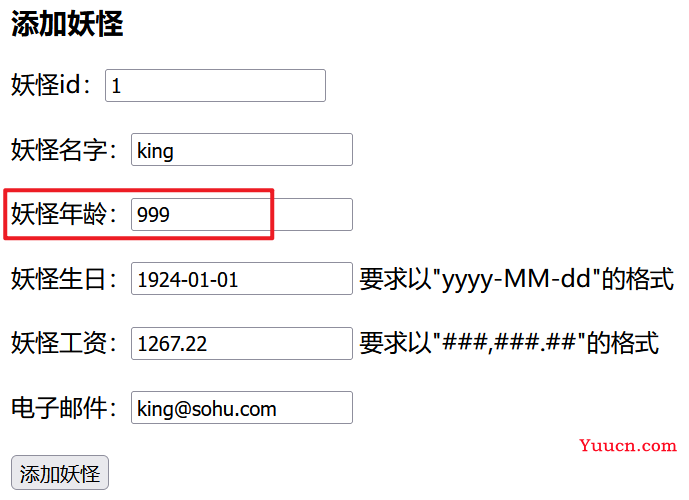
后台输出了默认的错误信息:
----monster----Monster{id=1, email='king@sohu.com', age=999, name='king', birthday=Tue Jan 01 00:00:00 CST 1924, salary=1267.22}
=======map=======
key=monster value=Monster{id=1, email='king@sohu.com', age=999, name='king', birthday=Tue Jan 01 00:00:00 CST 1924, salary=1267.22}
--------
key=org.springframework.validation.BindingResult.monster value=org.springframework.validation.BeanPropertyBindingResult: 1 errors
Field error in object 'monster' on field 'age': rejected value [999]; codes [Range.monster.age,Range.age,Range.java.lang.Integer,Range]; arguments [org.springframework.context.support.DefaultMessageSourceResolvable: codes [monster.age,age]; arguments []; default message [age],100,1]; default message [需要在1和100之间]
--------
=======errors=======
error=Field error in object 'monster' on field 'age': rejected value [999]; codes [Range.monster.age,Range.age,Range.java.lang.Integer,Range]; arguments [org.springframework.context.support.DefaultMessageSourceResolvable: codes [monster.age,age]; arguments []; default message [age],100,1]; default message [需要在1和100之间]
(6)自定义错误信息:配置 springDispatcherServlet-servlet.xml
<!--配置国际化错误信息的资源处理 bean-->
<bean class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource"
id="messageSource">
<!--
配置国际化文件名字
如果下面这样配置,表示 messageSource对象会到src/i18nXXX.properties 去读取错误信息
-->
<property name="basename" value="i18n"/>
</bean>
(7)在src 目录下创建国际化文件 i18n.properties
中文要使用 unicode 编码处理
NotEmpty.monster.name=\u7528\u6237\u540d\u4e0d\u80fd\u4e3a\u7a7a
typeMismatch.monster.age=\u5e74\u9f84\u8981\u6c42\u5728\u0031\u002d\u0031\u0035\u0030\u4e4b\u95f4
typeMismatch.monster.birthday=\u751f\u65e5\u683c\u5f0f\u4e0d\u6b63\u786e
typeMismatch.monster.salary=\u85aa\u6c34\u683c\u5f0f\u4e0d\u6b63\u786e
(8)修改 monster_addUI.jsp 的 form ,回显错误信息
<form:form action="save" method="post" modelAttribute="monster">
妖怪id:<form:input path="id"/><form:errors path="id"/><br/><br/>
妖怪名字:<form:input path="name"/><form:errors path="name"/><br/><br/>
妖怪年龄:<form:input path="age"/><form:errors path="age"/><br/><br/>
妖怪生日:<form:input path="birthday"/><form:errors path="birthday"/>
要求以"yyyy-MM-dd"的格式<br/><br/>
妖怪工资:<form:input path="salary"/><form:errors path="salary"/>
要求以"###,###.##"的格式<br/><br/>
电子邮件:<form:input path="email"/><form:errors path="email"/><br/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="添加妖怪"/>
</form:form>
(9)再次进行测试
没有在properties文件中配置的提示,将会按照默认的错误信息回显

2.2细节说明和注意事项
-
在需要验证的 Javabean/POJO 的字段上添加相应的验证注解
-
目标方法上,在 Javabean/POJO 类型的参数前,添加 @Valid 注解以告知 SpringMVC 该 Bean 是需要验证的
-
在 @Valid 注解之后,添加一个 Errors 或 BindingResult 类型的参数,可以获取到验证的错误信息
校验的发生的时机:SpringMVC 底层反射调用目标方法前,会接收到 http 请求接收到的数据,然后根据验证注解来进行验证。在验证过程中,如果出现了错误,就把错误信息填充到 errors,map 等参数中
-
需要使用
<form:errors path="xxx"></form:errors>标签来显示错误信息,该标签需要写在<form:form>标签内生效 -
自定义错误消息的国际化文件 i18n.properties,如果是中文需要使用 unicode 编码处理。
格式为:
验证规则.表单modelAttribute值.属性名=错误提示信息
-
注意@NotNull 和 @NotEmpty 的区别
@NotEmpty:
Asserts that the annotated string, collection, map or array is not {@code null} or empty.@NotNull:
The annotated element must not be {@code null}. Accepts any type.如果是字符串验证空,建议使用 @NotEmpty
-
SpringMVC 验证时,同一个属性,会根据不同的验证错误,返回不同的错误信息