一、Props 是什么
先来看一个 demo :
function Chidren(){
return <div> 我是子组件 </div>
}
/* props 接受处理 */
function Father(props) {
const { children , mes , renderName , say ,Component } = props
const renderFunction = children[0]
const renderComponent = children[1]
/* 对于子组件,不同的props是怎么被处理 */
return (
<div>
{ renderFunction() }
{ mes }
{ renderName() }
{ renderComponent }
<Component />
<button onClick={ () => say() } > 触发更改 </button>
</div> )
}
/* props 定义绑定 */
class App extends React.Component{
state={
mes: "hello,React"
}
node = null
say= () => this.setState({ mes:'let us learn React!' })
render(){
return <div>
<Father
mes={this.state.mes} // ① props 作为一个渲染数据源
say={ this.say } // ② props 作为一个回调函数 callback
Component={ Chidren } // ③ props 作为一个组件
renderName={ ()=><div> my name is YinJie </div> } // ④ props 作为渲染函数
>
{ ()=> <div>hello,world</div> } { /* ⑤render props */ }
<Chidren /> { /* ⑥render component */ }
</Father>
</div>
}
}
我们看一下输出结果:

当点击触发更改时就能够调用回调更改数据源:

所以 props 可以是:
① props 作为一个子组件渲染数据源。
② props 作为一个通知父组件的回调函数。
③ props 作为一个单纯的组件传递。
④ props 作为渲染函数。
⑤ render props , 和④的区别是放在了 children 属性上。
⑥ render component 插槽组件。
二、props children模式
我们先来看看 prop + children 的几个基本情况:
1. props 插槽组件
<Container> <Children> </Container>
上述可以在 Container 组件中,通过 props.children 属性访问到 Children 组件,为 React element 对象。
作用:
- 可以根据需要控制 Children 是否渲染。
- 像上一节所说的, Container 可以用 React.cloneElement 强化 props (混入新的 props ),或者修改 Children 的子元素。
举一个用React.cloneElement 强化 props 的例子,多用于编写组件时对子组件混入新的 props,下面我们要做一个导航组件,我们希望它的结构如下:
<Menu> <MenuItem > active </MenuItem> <MenuItem> disabled </MenuItem> <MenuItem > xyz </MenuItem> </Menu>
我们想给每个 MenuItem 子组件都添加 index 属性,这个事情不应该让用户手动添加,最好是可以在 Menu 组件中自动为每个 MenuItem 子组件添加上,并且 Menu 组件还应该判断子组件的类型,如果子组件的类型不是 MenuItem 组件就报错。
Menu.tsx:
const Menu: React.FC<MenuProps> = (props) => {
// ... 一些操作
const renderChildren = () => { // 让子级的children都是 menuItem,有不是的就报错
return React.Children.map(children, (child, index) => {
const childElement = child as React.FunctionComponentElement<MenuItemProps>
const { displayName } = childElement.type
if(displayName === 'MenuItem' || displayName === "SubMenu") {
return React.cloneElement(childElement, { index: index.toString() })
} else {
console.error('warning: Menu has a child whitch is not a MenuItem')
}
})
}
return (
<ul className={classes} style={style} data-testid="test-menu">
<MenuContext.Provider value={passedContext}>
{renderChildren()}
</MenuContext.Provider>
</ul>
)
}
在 Menu 组件中我们通过 React.children.map 来循环子组件,通过 child.type 可以获取到每个子组件的 displayName 静态属性,这个在子组件中有定义:
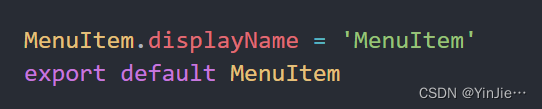
通过子组件的 displayName 来判断是否是我们需要的 MenuItem,如果是的话就调用 React.cloneElement 来为子组件添加 index 属性。
2. render props模式
<Container>
{ (ContainerProps)=> <Children {...ContainerProps} /> }
</Container>
这种情况,在 Container 中, props.children 属性访问到是函数,并不是 React element 对象,我们应该调用这个函数:
function Container(props) {
const ContainerProps = {
name: 'alien',
mes:'let us learn react'
}
return props.children(ContainerProps)
}
这种方式作用是:
1 根据需要控制 Children 渲染与否。
2 可以将需要传给 Children 的 props 直接通过函数参数的方式传递给执行函数 children 。
3. render props模式
如果 Container 的 Children 既有函数也有组件,这种情况应该怎么处理呢?
<Container>
<Children />
{ (ContainerProps)=> <Children {...ContainerProps} name={'haha'} /> }
</Container>
const Children = (props)=> (<div>
<div>hello, my name is { props.name } </div>
<div> { props.mes } </div>
</div>)
function Container(props) {
const ContainerProps = {
name: 'alien',
mes:'let us learn react'
}
return props.children.map(item=>{
if(React.isValidElement(item)){ // 判断是 react elment 混入 props
return React.cloneElement(item,{ ...ContainerProps },item.props.children)
}else if(typeof item === 'function'){
return item(ContainerProps)
}else return null
})
}
const Index = ()=>{
return <Container>
<Children />
{ (ContainerProps)=> <Children {...ContainerProps} name={'haha'} /> }
</Container>
}
这种情况需要先遍历 children ,判断 children 元素类型:
- 针对 element 节点,通过 cloneElement 混入 props ;
- 针对函数,直接传递参数,执行函数。
三、进阶实践
实现一个简单的<Form> <FormItem>嵌套组件
接下来到实践环节了。需要编写一个实践 demo ,用于表单状态管理的<Form>和<FormItem>组件
-
<Form>用于管理表单状态; -
<FormItem>用于管理<Input>输入框组件。,
编写的组件能够实现的功能是:
①Form组件可以被 ref 获取实例。然后可以调用实例方法submitForm获取表单内容,用于提交表单,resetForm方法用于重置表单。
②Form组件自动过滤掉除了FormItem之外的其他React元素
③FormItem中 name 属性作为表单提交时候的 key ,还有展示的 label 。
④FormItem可以自动收集<Input/>表单的值。
App.js:
import React, { useState, useRef } from "react";
import Form from './Form'
import FormItem from './FormItem'
import Input from './Input'
function App () {
const form = useRef(null)
const submit =()=>{
/* 表单提交 */
form.current.submitForm((formValue)=>{ // 调用 form 中的submitForm方法
console.log(formValue)
})
}
const reset = ()=>{
/* 表单重置 */
form.current.resetForm() //调用 form 中的 resetForm 方法
}
return <div className='box' >
<Form ref={ form } >
<FormItem name="name" label="我是" >
<Input />
</FormItem>
<FormItem name="mes" label="我想对大家说" >
<Input />
</FormItem>
<FormItem name="lees" label="ttt" >
<Input />
</FormItem>
</Form>
<div className="btns" >
<button className="searchbtn" onClick={ submit } >提交</button>
<button className="concellbtn" onClick={ reset } >重置</button>
</div>
</div>
}
export default App
Form.js:
class Form extends React.Component{
state={
formData:{}
}
/* 用于提交表单数据 */
submitForm=(cb)=>{
cb({ ...this.state.formData })
}
/* 获取重置表单数据 */
resetForm=()=>{
const { formData } = this.state
Object.keys(formData).forEach(item=>{
formData[item] = ''
})
this.setState({
formData
})
}
/* 设置表单数据层 */
setValue=(name,value)=>{
this.setState({
formData:{
...this.state.formData,
[name]:value
}
})
}
render(){
const { children } = this.props
const renderChildren = []
React.Children.forEach(children,(child)=>{
if(child.type.displayName === 'formItem'){
const { name } = child.props
/* 克隆`FormItem`节点,混入改变表单单元项的方法 */
const Children = React.cloneElement(child,{
key:name , /* 加入key 提升渲染效果 */
handleChange:this.setValue , /* 用于改变 value */
value:this.state.formData[name] || '' /* value 值 */
},child.props.children)
renderChildren.push(Children)
}
})
return renderChildren
}
}
/* 增加组件类型type */
Form.displayName = 'form'
设计思想:
- 首先考虑到
<Form>在不使用forwardRef前提下,最好是类组件,因为只有类组件才能获取实例。 - 创建一个 state 下的 formData属性,用于收集表单状态。
- 要封装重置表单,提交表单,改变表单单元项的方法。
- 要过滤掉除了
FormItem元素之外的其他元素,那么怎么样知道它是不是FormItem,这里教大家一种方法,可以给函数组件或者类组件绑定静态属性来证明它的身份,然后在遍历 props.children 的时候就可以在 React element 的 type 属性(类或函数组件本身)上,验证这个身份,在这个 demo 项目,给函数绑定的 displayName 属性,证明组件身份。 - 要克隆
FormItem节点,将改变表单单元项的方法 handleChange 和表单的值 value 混入 props 中。
FormItem.js:
function FormItem(props){
const { children , name , handleChange , value , label } = props
const onChange = (value) => {
/* 通知上一次value 已经改变 */
handleChange(name,value)
}
return <div className='form' >
<span className="label" >{ label }:</span>
{
React.isValidElement(children) && children.type.displayName === 'input'
? React.cloneElement(children,{ onChange , value })
: null
}
</div>
}
FormItem.displayName = 'formItem'
设计思想:
-
FormItem一定要绑定 displayName 属性,用于让<Form>识别<FormItem /> - 声明
onChange方法,通过 props 提供给<Input>,作为改变 value 的回调函数。 -
FormItem过滤掉除了input以外的其他元素。
Input.js:
/* Input 组件, 负责回传value值 */
function Input({ onChange , value }){
return <input className="input" onChange={ (e)=>( onChange && onChange(e.target.value) ) } value={value} />
}
/* 给Component 增加标签 */
Input.displayName = 'input'
设计思想:
- 绑定 displayName 标识
input。 -
inputDOM 元素,绑定 onChange 方法,用于传递 value 。
下面通过函数组件再重写一下:
App.js,FormItem.js 和 Input.js 还是一样的,Form.js使用了 hooks 钩子来管理状态,并且通过forwardRef, useImperativeHandle,让 App 组件访问到 Form 中的方法:
import React, { useState, forwardRef, useImperativeHandle } from "react"
const Form = (props, ref) =>{
const { children } = props
const [ formData, setFormData ] = useState({})
useImperativeHandle(ref, () => ({
submitForm: submitForm,
resetForm: resetForm
}))
/* 用于提交表单数据 */
const submitForm=(cb)=>{
cb(formData)
}
/* 获取重置表单数据 */
const resetForm=()=>{
const newData = formData
Object.keys(newData).forEach(item=>{
newData[item] = ''
})
setFormData(newData)
}
/* 设置表单数据层 */
const setValue=(name,value)=>{
setFormData({
...formData,
[name]:value
})
}
const renderChildren = () => {
return React.Children.map(children,(child)=>{
if(child.type.displayName === 'formItem'){
const { name } = child.props
/* 克隆`FormItem`节点,混入改变表单单元项的方法 */
const Children = React.cloneElement(child,{
key:name , /* 加入key 提升渲染效果 */
handleChange: setValue , /* 用于改变 value */
value: formData[name] || '' /* value 值 */
},child.props.children)
return Children
}
})
}
return (
renderChildren()
)
}
/* 增加组件类型type */
Form.displayName = 'form'
export default forwardRef(Form)
启动项目,查看效果:
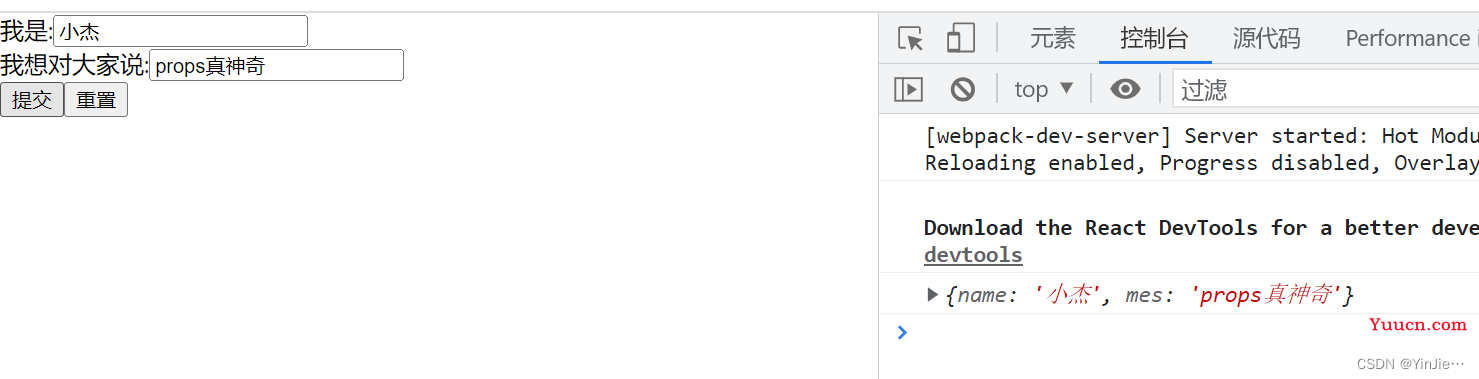
点击提交,我们在输入框里输入的内容就能显示在控制台上。
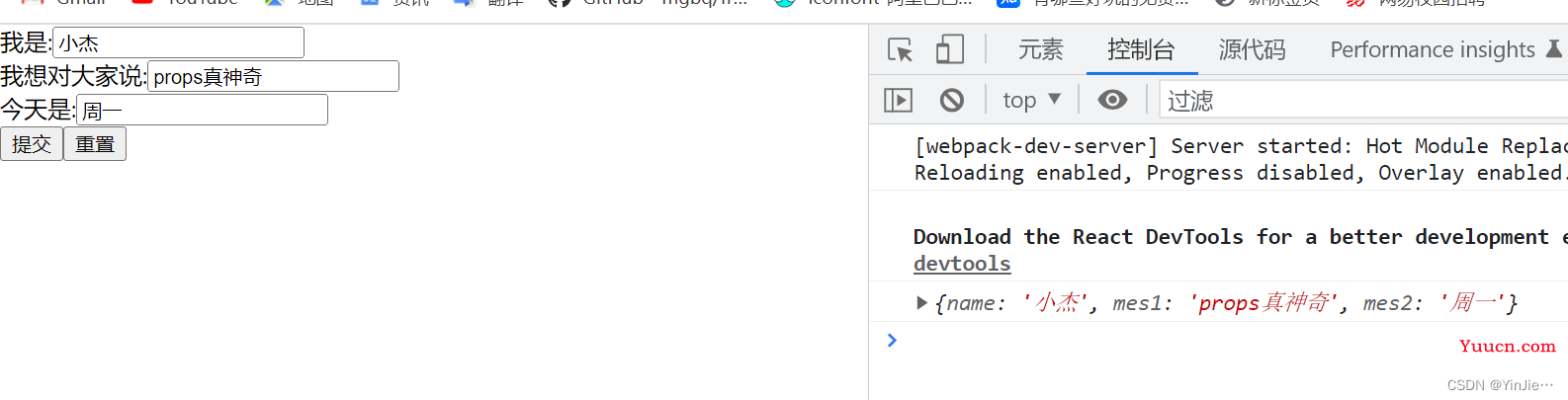
为了体现出咱们这个嵌套组件的高可复用性,我们可以在根组件中随意添加子项:
到此这篇关于React props全面详细解析的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关React props内容请搜索本站以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持本站!