Kmap1
化简卡诺图即可。
module top_module( input a, input b, input c, output out ); assign out=b|c|a; endmodule
Kmap2
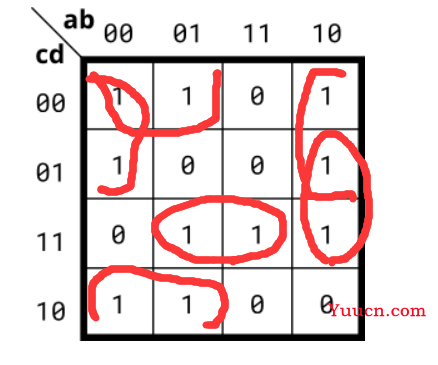
我是这样化简的。
module top_module( input a, input b, input c, input d, output out ); assign out=(~a&~d)|(~b&~c)|(a&~b&d)|(b&c&d); endmodule
Kmap3
这里d代表的是无关项,要不要圈起来都可以。
module top_module( input a, input b, input c, input d, output out ); assign out=(~b&c)|(a&c)|(a&~d); endmodule
Kmap4
这道题一眼看过去根本没办法化简,但是根据提示,改变一个输入值总会使输出反转,所以可以推断出a、b、c、d应该进行的是异或运算。
module top_module( input a, input b, input c, input d, output out ); assign out=a^b^c^d; endmodule
Exams/ece241 2013 q2
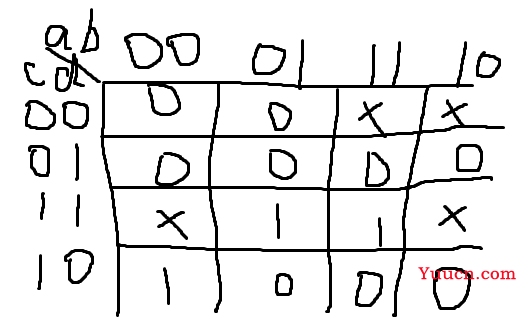
sop形式直接写就可以了,pos形式则需要sop形式使用摩根定理取反两次进行变换。
module top_module ( input a, input b, input c, input d, output out_sop, output out_pos ); assign out_sop=(c&d)|(~a&~b&c); assign out_pos=c&(~a|d)&(~b|d); endmodule
Exams/m2014 q3
也是直接化简就可以了。
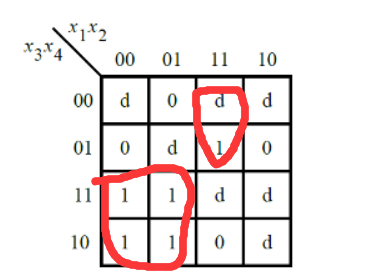
module top_module ( input [4:1] x, output f ); assign f=(~x[1]&x[3])|(x[1]&x[2]&~x[3]); endmodule
Exams/2012 q1g
化简的时候注意四个角。
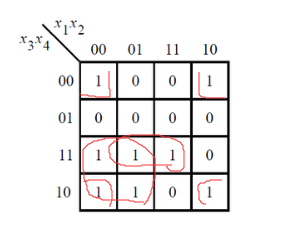
module top_module ( input [4:1] x, output f ); assign f=(~x[2]&~x[4])|(~x[1]&x[3])|(x[2]&x[3]&x[4]); endmodule
Exams/ece241 2014 q3
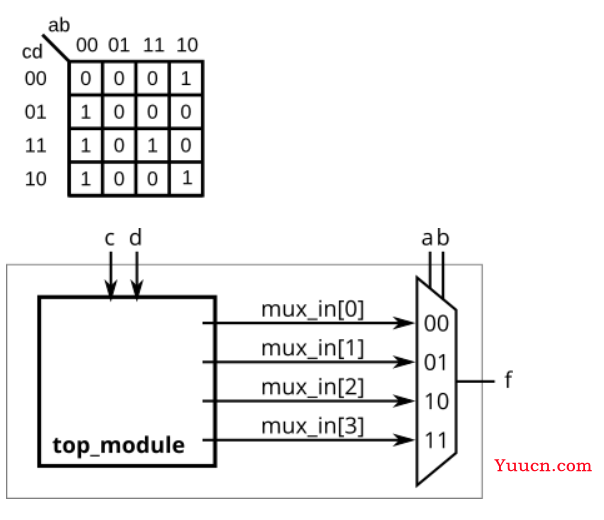
这里要使用一个4-to-1的数据选择器实现四输入的逻辑。
逻辑为:f=(~a&~b&~c&d) |(~a&~b&c&d) |(~a&~b&c&~d) | (a&b&c&d) | (a&~b&~c&~d) | (a&~b&c&~d);
当a、b为00时,选中mux_in[0],也就是说控制mux_in[0]就可以了。
module top_module ( input c, input d, output [3:0] mux_in ); assign mux_in[0]=(~c&~d)?1'b0:1'b1; assign mux_in[1]=1'b0; assign mux_in[2]=(~d)?1'b1:1'b0; assign mux_in[3]=(c&d)?1'b1:1'b0; endmodule
我这里貌似还是用了逻辑门,不符合要求,答案的表达式更加简洁,可以参考一下。
module top_module ( input c, input d, output [3:0] mux_in ); // After splitting the truth table into four columns, // the rest of this question involves implementing logic functions // using only multiplexers (no other gates). // I will use the conditional operator for each 2-to-1 mux: (s ? a : b) assign mux_in[0] = c ? 1 : d; // 1 mux: c|d assign mux_in[1] = 0; // No muxes: 0 assign mux_in[2] = d ? 0 : 1; // 1 mux: ~d assign mux_in[3] = c ? d : 0; // 1 mux: c&d endmodule